在上篇算法题的文章中,我们介绍了 LeetCode 中的一道数学题 - 快乐数 。今天,我们来聊聊质数(英文是Prime,也称为素数)相关的面试题。以前很多编程书上会有个经典问题,即判断一个数是否是质数,在那之后大家应该对判定质数的逻辑有了一定的认识。今天呢,我们来解决一个进阶问题,如何计算一个区间内素数(质数)的数量。

今天要给大家分析的面试题是 LeetCode 上第 204 号问题,
LeetCode - 204. 统计质数
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/count-primes/
题目描述
统计所有小于非负整数 n 的质数的数量。
示例:
输入: 10输出: 4解释: 小于 10 的质数一共有 4 个, 它们是 2, 3, 5, 7 。
贡献者: LeetCode
题目难度: Easy
通过率:
30.23%
相关话题
哈希表
https://leetcode-cn.com/tag/hash-table/
数学
https://leetcode-cn.com/tag/math
相似题目
丑数
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/ugly-number/ 难度: 简单
丑数 II
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/ugly-number-ii/ 难度: 中等
完全平方数
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/perfect-squares/ 难度: 中等
解题思路:
遍历每个数,判断它是否为素数。
基于传统教科书中的算法 IsPrime(其流程见下图)来做,即在 IsPrime算法外套一个循环来做,由于下面流程的时间复杂度 T(n) = O(n*log n),于是整体算下来整个算法最后的时间复杂度为 O(n * n * log n),这个算法的时间复杂度是不达标的。

2. 使用一个筛子,把每一个是合数的数干掉,记录其状态 isDelete,用isDelete=true表示不是质数,已被删掉,而fasle表示留下了,是质数。这个方法被称为筛法(Sieve Method)。
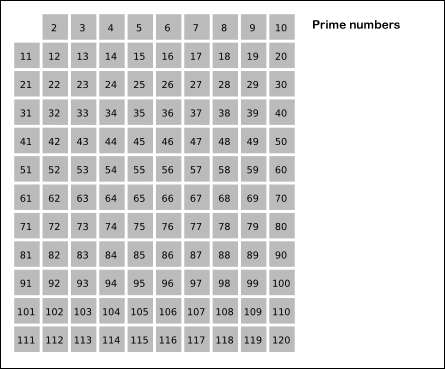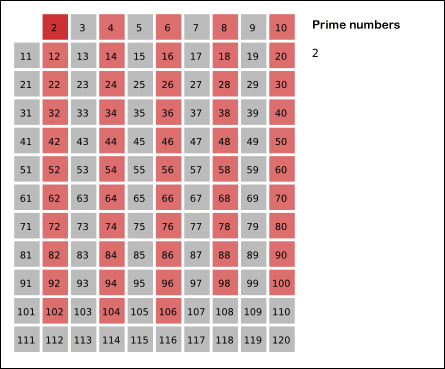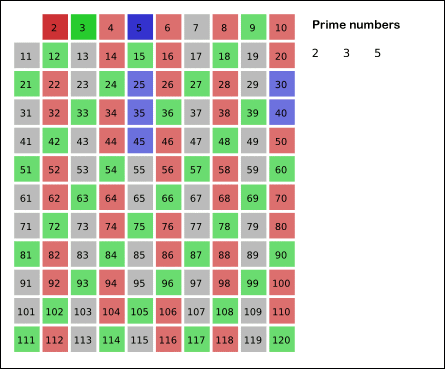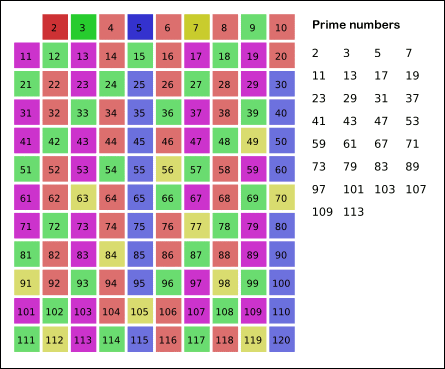
筛法又分为埃拉托斯特尼筛法(埃筛)和欧拉筛(线性筛)两种。埃筛是用一个数组标记是否为素数,然后依次筛去这个素数的倍数,其时间复杂度是O(n*log n)。而欧拉筛是在埃筛的基础上,让每一个合数都只被他的最小质因子筛去,从而减小时间。欧拉筛的复杂度几乎是O(n),由于其代码相对比较难理解,就不详细介绍了。
下面我们使用埃筛来统计质数数量,具体操作是从2开始维护一个bool数组isDelete来记录该数是否被删掉,依次删掉当前索引 i 的倍数,最后数组中未被删掉的值(其isDelete值为false)都是素数。
已AC代码 解法1:
class Solution:def countPrimes(self, n: int) -> int:if n < 2:return 0else:isDelete = [False]*nmax0 = int(math.sqrt(n))count = 0for i in range(2, n):if isDelete[i] == True:continuecount += 1if i > max0:continuefor j in range(i*i, n, i):isDelete[j] = Truereturn count
ps: 由于这段代码使用了数学库函数 sqrt(),于是本地测试需要在开头引入 math库,其代码如下:
import mathclass Solution:def countPrimes(self, n: int) -> int:if n < 2:return 0else:isDelete = [False]*nmax0 = int(math.sqrt(n))count = 0for i in range(2, n):if isDelete[i] == True:continuecount += 1if i > max0:continuefor j in range(i*i, n, i):isDelete[j] = Truereturn countsol = Solution()print(sol.countPrimes(5566))

执行用时 : 492ms, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 47.44%的用户.
已AC代码 解法2:
class Solution:def countPrimes(self, n: int) -> int:if n < 2:return 0else:isPrime = [1]*n # isPrime = not deletedisPrime[0] = 0isPrime[1] = 0for i in range(2, int(n**0.5) + 1):if isPrime[i]:isPrime[i*i:n:i] = [0]*((n-1-i*i)//i + 1) # slice: a[start:stop:step] # items from the beginning through stop-1return sum(isPrime)

执行用时 : 100ms, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了 94.27%的用户.
参考资料:
Eratosthenes筛法(埃式筛法)时间复杂度分析 - Gavin_Nicholas的博客 - CSDN
https://blog.csdn.net/Gavin_Nicholas/article/details/88974079
系列文章
- LeetCode面试系列 第3天:No.67 - 二进制数求和
- LeetCode面试系列 第2天:No.136 - 只出现一次的数
- Leetcode面试系列 第1天:Leetcode 89 - 格雷码
- 第20天:Python 之装饰器
第10天:Python 类与对象
第9天:Python Tupple第8天:Python List第7天:Python 数据结构--序列
第6天:Python 模块和包第5天:Python 函数第4天:Python 流程控制第3天:Python 变量与数据类型第2天:Python 基础语法第1天:Python 环境搭建





















