本文将详细介绍ID3算法,其也是最经典的决策树分类算法。
1、ID3算法简介及基本原理
ID3算法基于信息熵来选择最佳的测试属性,它选择当前样本集中具有最大信息增益值的属性作为测试属性;样本集的划分则依据测试属性的取值进行,测试属性有多少个不同的取值就将样本集划分为多少个子样本集,同时决策树上相应于该样本集的节点长出新的叶子节点。ID3算法根据信息论的理论,采用划分后样本集的不确定性作为衡量划分好坏的标准,用信息增益值度量不确定性:信息增益值越大,不确定性越小。因此,ID3算法在每个非叶节点选择信息增益最大的属性作为测试属性,这样可以得到当前情况下最纯的划分,从而得到较小的决策树。
设S是s个数据样本的集合。假定类别属性具有m个不同的值:
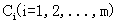
,设
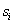
是类
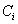
中的样本数。对一个给定的样本,它总的信息熵为
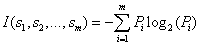
,其中,
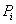
是任意样本属于
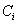
的概率,一般可以用
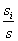
估计。设一个属性A具有k个不同的值
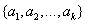
,利用属性A将集合S划分为k个子集
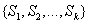
,其中
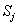
包含了集合S中属性A取
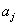
值的样本。若选择属性A为测试属性,则这些子集就是从集合S的节点生长出来的新的叶节点。设
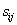
是子集
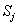
中类别为
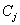
的样本数,则根据属性A划分样本的信息熵为
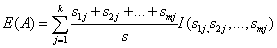
其中,
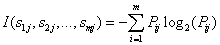
,
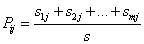
是子集
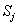
中类别为
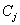
的样本的概率。最后,用属性A划分样本集S后所得的信息增益(Gain)为
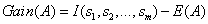
显然
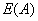
越小,Gain(A)的值就越大,说明选择测试属性A对于分类提供的信息越大,选择A之后对分类的不确定程度越小。属性A的k个不同的值对应的样本集S的k个子集或分支,通过递归调用上述过程(不包括已经选择的属性),生成其他属性作为节点的子节点和分支来生成整个决策树。ID3决策树算法作为一个典型的决策树学习算法,其核心是在决策树的各级节点上都用信息增益作为判断标准来进行属性的选择,使得在每个非叶子节点上进行测试时,都能获得最大的类别分类增益,使分类后的数据集的熵最小。这样的处理方法使得树的平均深度较小,从而有效地提高了分类效率。
2、ID3算法的具体流程
ID3算法的具体流程如下:
1)对当前样本集合,计算所有属性的信息增益;
2)选择信息增益最大的属性作为测试属性,把测试属性取值相同的样本划为同一个子样本集;
3)若子样本集的类别属性只含有单个属性,则分支为叶子节点,判断其属性值并标上相应的符号,然后返回调用处;否则对子样本集递归调用本算法。
数据如图所示
序号 天气 是否周末 是否有促销 销量
1 坏 是 是 高
2 坏 是 是 高
3 坏 是 是 高
4 坏 否 是 高
5 坏 是 是 高
6 坏 否 是 高
7 坏 是 否 高
8 好 是 是 高
9 好 是 否 高
10 好 是 是 高
11 好 是 是 高
12 好 是 是 高
13 好 是 是 高
14 坏 是 是 低
15 好 否 是 高
16 好 否 是 高
17 好 否 是 高
18 好 否 是 高
19 好 否 否 高
20 坏 否 否 低
21 坏 否 是 低
22 坏 否 是 低
23 坏 否 是 低
24 坏 否 否 低
25 坏 是 否 低
26 好 否 是 低
27 好 否 是 低
28 坏 否 否 低
29 坏 否 否 低
30 好 否 否 低
31 坏 是 否 低
32 好 否 是 低
33 好 否 否 低
34 好 否 否 低采用ID3算法构建决策树模型的具体步骤如下:
1)根据公式
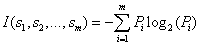
,计算总的信息熵,其中数据中总记录数为34,而销售数量为“高”的数据有18,“低”的有16
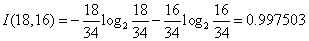
2)根据公式
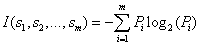
和
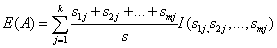
,计算每个测试属性的信息熵。对于天气属性,其属性值有“好”和“坏”两种。其中天气为“好”的条件下,销售数量为“高”的记录为11,销售数量为“低”的记录为6,可表示为(11,6);天气为“坏”的条件下,销售数量为“高”的记录为7,销售数量为“低”的记录为10,可表示为(7,10)。则天气属性的信息熵计算过程如下:
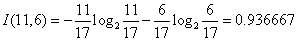
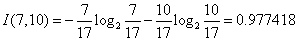
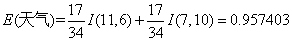
对于是否周末属性,其属性值有“是”和“否”两种。其中是否周末属性为“是”的条件下,销售数量为“高”的记录为11,销售数量为“低”的记录为3,可表示为(11,3);是否周末属性为“否”的条件下,销售数量为“高”的记录为7,销售数量为“低”的记录为13,可表示为(7,13)。则节假日属性的信息熵计算过程如下:
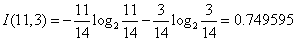
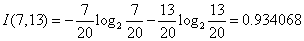
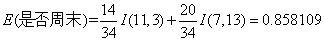
对于是否有促销属性,其属性值有“是”和“否”两种。其中是否有促销属性为“是”的条件下,销售数量为“高”的记录为15,销售数量为“低”的记录为7,可表示为(15,7);其中是否有促销属性为“否”的条件下,销售数量为“高”的记录为3,销售数量为“低”的记录为9,可表示为(3,9)。则是否有促销属性的信息熵计算过程如下:
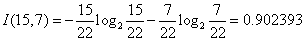
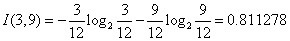
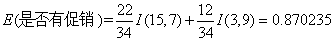
根据公式
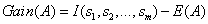
,计算天气、是否周末和是否有促销属性的信息增益值。
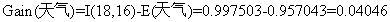


3)由计算结果可以知道是否周末属性的信息增益值最大,它的两个属性值“是”和“否”作为该根节点的两个分支。然后按照上面的步骤继续对该根节点的两个分支进行节点的划分,针对每一个分支节点继续进行信息增益的计算,如此循环反复,直到没有新的节点分支,最终构成一棵决策树。
由于ID3决策树算法采用了信息增益作为选择测试属性的标准,会偏向于选择取值较多的即所谓的高度分支属性,而这类属性并不一定是最优的属性。同时ID3决策树算法只能处理离散属性,对于连续型的属性,在分类前需要对其进行离散化。为了解决倾向于选择高度分支属性的问题,人们采用信息增益率作为选择测试属性的标准,这样便得到C4.5决策树的算法。此外常用的决策树算法还有CART算法、SLIQ算法、SPRINT算法和PUBLIC算法等等。
使用ID3算法建立决策树的MATLAB代码如下所示
ID3_decision_tree.m
%% 使用ID3决策树算法预测销量高低
clear ;
%% 数据预处理
disp('正在进行数据预处理...');
[matrix,attributes_label,attributes] = id3_preprocess();
%% 构造ID3决策树,其中id3()为自定义函数
disp('数据预处理完成,正在进行构造树...');
tree = id3(matrix,attributes_label,attributes);
%% 打印并画决策树
[nodeids,nodevalues] = print_tree(tree);
tree_plot(nodeids,nodevalues);
disp('ID3算法构建决策树完成!');id3_preprocess.m:
function [ matrix,attributes,activeAttributes ] = id3_preprocess( )
%% ID3算法数据预处理,把字符串转换为0,1编码
% 输出参数:
% matrix: 转换后的0,1矩阵;
% attributes: 属性和Label;
% activeAttributes : 属性向量,全1;
%% 读取数据
txt = { '序号' '天气' '是否周末' '是否有促销' '销量'
'' '坏' '是' '是' '高'
'' '坏' '是' '是' '高'
'' '坏' '是' '是' '高'
'' '坏' '否' '是' '高'
'' '坏' '是' '是' '高'
'' '坏' '否' '是' '高'
'' '坏' '是' '否' '高'
'' '好' '是' '是' '高'
'' '好' '是' '否' '高'
'' '好' '是' '是' '高'
'' '好' '是' '是' '高'
'' '好' '是' '是' '高'
'' '好' '是' '是' '高'
'' '坏' '是' '是' '低'
'' '好' '否' '是' '高'
'' '好' '否' '是' '高'
'' '好' '否' '是' '高'
'' '好' '否' '是' '高'
'' '好' '否' '否' '高'
'' '坏' '否' '否' '低'
'' '坏' '否' '是' '低'
'' '坏' '否' '是' '低'
'' '坏' '否' '是' '低'
'' '坏' '否' '否' '低'
'' '坏' '是' '否' '低'
'' '好' '否' '是' '低'
'' '好' '否' '是' '低'
'' '坏' '否' '否' '低'
'' '坏' '否' '否' '低'
'' '好' '否' '否' '低'
'' '坏' '是' '否' '低'
'' '好' '否' '是' '低'
'' '好' '否' '否' '低'
'' '好' '否' '否' '低' }
attributes=txt(1,2:end);
activeAttributes = ones(1,length(attributes)-1);
data = txt(2:end,2:end);
%% 针对每列数据进行转换
[rows,cols] = size(data);
matrix = zeros(rows,cols);
for j=1:cols
matrix(:,j) = cellfun(@trans2onezero,data(:,j));
end
end
function flag = trans2onezero(data)
if strcmp(data,'坏') ||strcmp(data,'否')...
||strcmp(data,'低')
flag =0;
return ;
end
flag =1;
endid3.m:
function [ tree ] = id3( examples, attributes, activeAttributes )
%% ID3 算法 ,构建ID3决策树
...参考:https://github.com/gwheaton/ID3-Decision-Tree
% 输入参数:
% example: 输入0、1矩阵;
% attributes: 属性值,含有Label;
% activeAttributes: 活跃的属性值;-1,1向量,1表示活跃;
% 输出参数:
% tree:构建的决策树;
%% 提供的数据为空,则报异常
if (isempty(examples));
error('必须提供数据!');
end
% 常量
numberAttributes = length(activeAttributes);
numberExamples = length(examples(:,1));
% 创建树节点
tree = struct('value', 'null', 'left', 'null', 'right', 'null');
% 如果最后一列全部为1,则返回“true”
lastColumnSum = sum(examples(:, numberAttributes + 1));
if (lastColumnSum == numberExamples);
tree.value = 'true';
return
end
% 如果最后一列全部为0,则返回“false”
if (lastColumnSum == 0);
tree.value = 'false';
return
end
% 如果活跃的属性为空,则返回label最多的属性值
if (sum(activeAttributes) == 0);
if (lastColumnSum >= numberExamples / 2);
tree.value = 'true';
else
tree.value = 'false';
end
return
end
%% 计算当前属性的熵
p1 = lastColumnSum / numberExamples;
if (p1 == 0);
p1_eq = 0;
else
p1_eq = -1*p1*log2(p1);
end
p0 = (numberExamples - lastColumnSum) / numberExamples;
if (p0 == 0);
p0_eq = 0;
else
p0_eq = -1*p0*log2(p0);
end
currentEntropy = p1_eq + p0_eq;
%% 寻找最大增益
gains = -1*ones(1,numberAttributes); % 初始化增益
for i=1:numberAttributes;
if (activeAttributes(i)) % 该属性仍处于活跃状态,对其更新
s0 = 0; s0_and_true = 0;
s1 = 0; s1_and_true = 0;
for j=1:numberExamples;
if (examples(j,i));
s1 = s1 + 1;
if (examples(j, numberAttributes + 1));
s1_and_true = s1_and_true + 1;
end
else
s0 = s0 + 1;
if (examples(j, numberAttributes + 1));
s0_and_true = s0_and_true + 1;
end
end
end
% 熵 S(v=1)
if (~s1);
p1 = 0;
else
p1 = (s1_and_true / s1);
end
if (p1 == 0);
p1_eq = 0;
else
p1_eq = -1*(p1)*log2(p1);
end
if (~s1);
p0 = 0;
else
p0 = ((s1 - s1_and_true) / s1);
end
if (p0 == 0);
p0_eq = 0;
else
p0_eq = -1*(p0)*log2(p0);
end
entropy_s1 = p1_eq + p0_eq;
% 熵 S(v=0)
if (~s0);
p1 = 0;
else
p1 = (s0_and_true / s0);
end
if (p1 == 0);
p1_eq = 0;
else
p1_eq = -1*(p1)*log2(p1);
end
if (~s0);
p0 = 0;
else
p0 = ((s0 - s0_and_true) / s0);
end
if (p0 == 0);
p0_eq = 0;
else
p0_eq = -1*(p0)*log2(p0);
end
entropy_s0 = p1_eq + p0_eq;
gains(i) = currentEntropy - ((s1/numberExamples)*entropy_s1) - ((s0/numberExamples)*entropy_s0);
end
end
% 选出最大增益
[~, bestAttribute] = max(gains);
% 设置相应值
tree.value = attributes{bestAttribute};
% 去活跃状态
activeAttributes(bestAttribute) = 0;
% 根据bestAttribute把数据进行分组
examples_0= examples(examples(:,bestAttribute)==0,:);
examples_1= examples(examples(:,bestAttribute)==1,:);
% 当 value = false or 0, 左分支
if (isempty(examples_0));
leaf = struct('value', 'null', 'left', 'null', 'right', 'null');
if (lastColumnSum >= numberExamples / 2); % for matrix examples
leaf.value = 'true';
else
leaf.value = 'false';
end
tree.left = leaf;
else
% 递归
tree.left = id3(examples_0, attributes, activeAttributes);
end
% 当 value = true or 1, 右分支
if (isempty(examples_1));
leaf = struct('value', 'null', 'left', 'null', 'right', 'null');
if (lastColumnSum >= numberExamples / 2);
leaf.value = 'true';
else
leaf.value = 'false';
end
tree.right = leaf;
else
% 递归
tree.right = id3(examples_1, attributes, activeAttributes);
end
% 返回
return
endprint_tree.m:
function [nodeids_,nodevalue_] = print_tree(tree)
%% 打印树,返回树的关系向量
global nodeid nodeids nodevalue;
nodeids(1)=0; % 根节点的值为0
nodeid=0;
nodevalue={};
if isempty(tree)
disp('空树!');
return ;
end
queue = queue_push([],tree);
while ~isempty(queue) % 队列不为空
[node,queue] = queue_pop(queue); % 出队列
visit(node,queue_curr_size(queue));
if ~strcmp(node.left,'null') % 左子树不为空
queue = queue_push(queue,node.left); % 进队
end
if ~strcmp(node.right,'null') % 左子树不为空
queue = queue_push(queue,node.right); % 进队
end
end
%% 返回 节点关系,用于treeplot画图
nodeids_=nodeids;
nodevalue_=nodevalue;
end
function visit(node,length_)
%% 访问node 节点,并把其设置值为nodeid的节点
global nodeid nodeids nodevalue;
if isleaf(node)
nodeid=nodeid+1;
fprintf('叶子节点,node: %d\t,属性值: %s\n', ...
nodeid, node.value);
nodevalue{1,nodeid}=node.value;
else % 要么是叶子节点,要么不是
%if isleaf(node.left) && ~isleaf(node.right) % 左边为叶子节点,右边不是
nodeid=nodeid+1;
nodeids(nodeid+length_+1)=nodeid;
nodeids(nodeid+length_+2)=nodeid;
fprintf('node: %d\t属性值: %s\t,左子树为节点:node%d,右子树为节点:node%d\n', ...
nodeid, node.value,nodeid+length_+1,nodeid+length_+2);
nodevalue{1,nodeid}=node.value;
end
end
function flag = isleaf(node)
%% 是否是叶子节点
if strcmp(node.left,'null') && strcmp(node.right,'null') % 左右都为空
flag =1;
else
flag=0;
end
endtree_plot.m
function tree_plot( p ,nodevalues)
%% 参考treeplot函数
[x,y,h]=treelayout(p);
f = find(p~=0);
pp = p(f);
X = [x(f); x(pp); NaN(size(f))];
Y = [y(f); y(pp); NaN(size(f))];
X = X(:);
Y = Y(:);
n = length(p);
if n < 500,
hold on ;
plot (x, y, 'ro', X, Y, 'r-');
nodesize = length(x);
for i=1:nodesize
% text(x(i)+0.01,y(i),['node' num2str(i)]);
text(x(i)+0.01,y(i),nodevalues{1,i});
end
hold off;
else
plot (X, Y, 'r-');
end;
xlabel(['height = ' int2str(h)]);
axis([0 1 0 1]);
endqueue_push.m
function [ newqueue ] = queue_push( queue,item )
%% 进队
% cols = size(queue);
% newqueue =structs(1,cols+1);
newqueue=[queue,item];
endqueue_pop.m
function [ item,newqueue ] = queue_pop( queue )
%% 访问队列
if isempty(queue)
disp('队列为空,不能访问!');
return;
end
item = queue(1); % 第一个元素弹出
newqueue=queue(2:end); % 往后移动一个元素位置
endqueue_curr_size.m
function [ length_ ] = queue_curr_size( queue )
%% 当前队列长度
length_= length(queue);
end





















