二叉排序树(Binary Sort Tree,简称BST),又称二叉查找树,是红黑树、AVL树等的基础。它或是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的一棵二叉树:
1. 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值
2. 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于它的根节点的值
3. 它的左右子树也分别为二叉排序树
很明显,对二叉排序树进行中序遍历,便可得到一个有序序列,该有序序列中的各元素按照从小到大的顺序排列,因此一个无序序列可以通过构造一棵二叉排序树而变成一个有序序列。
二叉排序树通常采用二叉链表作为存储结构。中序遍历二叉排序树可得到一个依据关键字的有序序列,一个无序序列可以通过构造一棵二叉排序树变成一个有序序列,构造树的过程即是对无序序列进行排序的过程。每次插入的新的结点都是二叉排序树上新的叶子结点,在进行插入操作时,不必移动其它结点,只需改动某个结点的指针,由空变为非空即可。搜索、插入、删除的时间复杂度等于树高,期望O(logn),最坏O(n)(数列有序,树退化成线性表,如右斜树)。
虽然二叉排序树的最坏效率是O(n),但它支持动态查找,且有很多改进版的二叉排序树可以使树高为O(logn),如AVL、红黑树等。
二叉排序树性能分析
每个结点的Ci为该结点的层次数。最好的情况是二叉排序树的形态和折半查找的判定树相同,其平均查找长度和logn成正比(O(log2(n)))。最坏情况下,当先后插入的关键字有序时,构成的二叉排序树为一棵斜树,树的深度为n,其平均查找长度为(n + 1) / 2。也就是时间复杂度为O(n),等同于顺序查找。因此,如果希望对一个集合按二叉排序树查找,最好是把它构建成一棵平衡的二叉排序树(平衡二叉树)。
个人认为可以用于排序, 查找 [在建树输入存在符合构造出比较平衡的二叉树的前提下]
用一个有序列表构造平衡二叉树 : 取中间的结点为根节点, 左边的数据作为左子树, 右边的数据作为右子树递归建树
然后 在这样的一颗树中查找一个数据, 你会发现寻找的思路 和在原有序列表中进行二分查找的是一致的
难点
增加数据 : 如果root结点为null, 则插入的val作为root结点的值,
否则 找到val结点的父节点 进行插入[如果已存在, 这里的处理方式是打印日志]
查找值为给定的数据的结点 : 从root结点开始比较[node]
如果val小于node.val 则进入左子树比较,
否则val大于node.val 则进入右子树比价,
否则 当前结点即为所找结点, 如果找到叶子结点都还没有找到 则说明无所找结点
删除数据 : 首先找到该节点, 如果没有该元素 打印日志
如果该节点为root结点[如果选用下面的方式1的话需要更新root结点] 特殊处理,
如果root结点没有子节点 直接将其置空
如果root结点有左子节点 则将左子树中最大的值替换掉 root结点的值 并将该节点的左子树接到该结点的父节点上
如果root结点有有右子节点 则将右子树中最小的值替换掉root结点的值 并将该节点右子树接到该节点的父节点上
否则该结点非root结点
如果该节点是叶子结点 直接令该节点的父节点相应的孩子为null
如果 该节点左右子孩子均不为空
方式一 : 将node结点的右子树[或者左子树] 放在node结点左子树的最大的结点的右子树上[右子树的最小的结点], 然后将node结点的左子树接到node结点的父节点上
方式二 : 将node结点的左子树的最大结点[或者右子树的最小节点] 替换掉node, 然后该结点的左子树接到该节点的父节点上
否则 如果该节点左孩子不为空 则将该结点的左孩子接到父节点上
否则 如果该节点右孩子不为空 则将该结点的右孩子接到父节点上
综上 : 删除一个结点的花样最多, 不过都是为了维护其性质
存在左右子树删除方式一 :
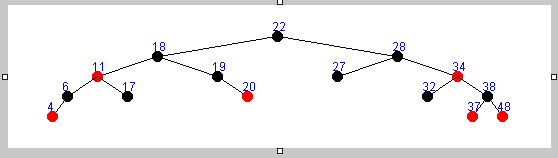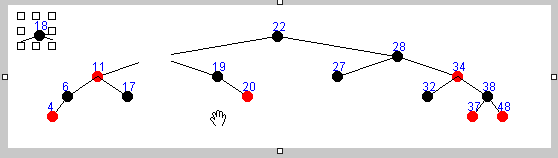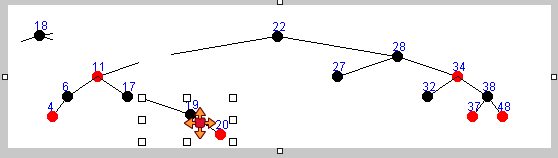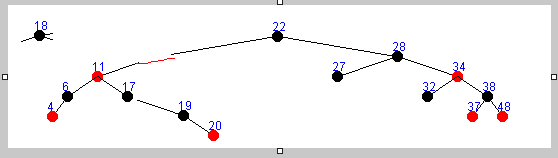
存在左右子树删除方式二 :
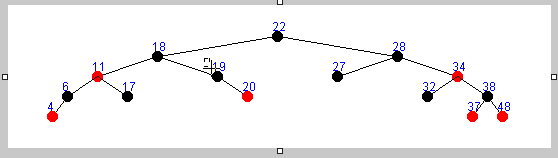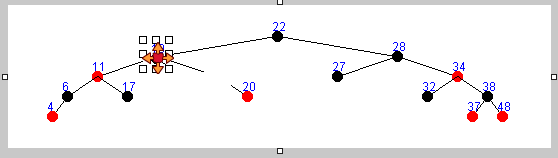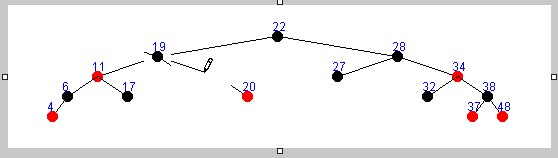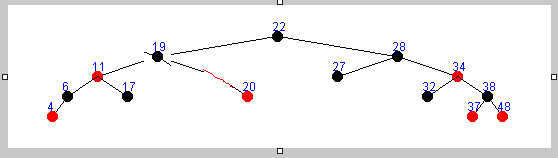
只存在左子树的情况 :
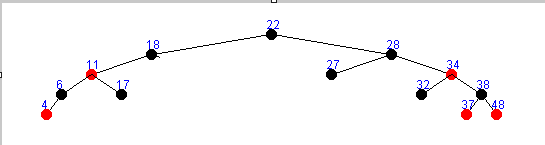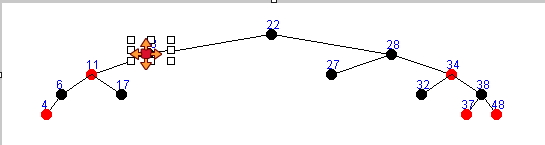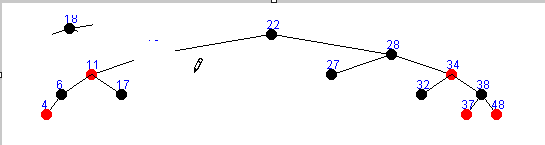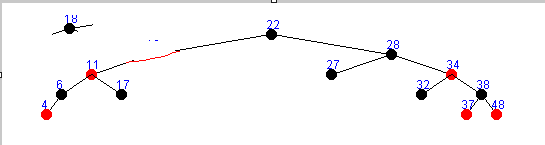
参考代码
/**
* file name : Test17BinarySortTree.java
* created at : 4:39:55 PM Jun 1, 2015
* created by 970655147
*/
package com.hx.test04;
import com.hx.util.Log;
public class Test17BinarySortTree {
// 二叉排序树
// 参考 :
public static void main(String []args) {
BinarySortTree bst = new BinarySortTree();
bst.add(3);
bst.add(1);
bst.add(33);
Log.log(bst);
bst.remove(1);
bst.remove(3);
bst.remove(33);
Log.log(bst);
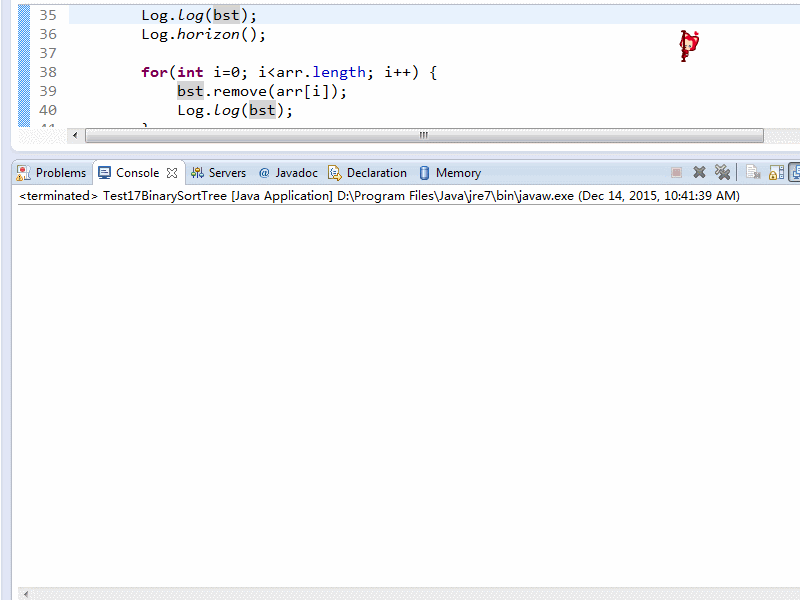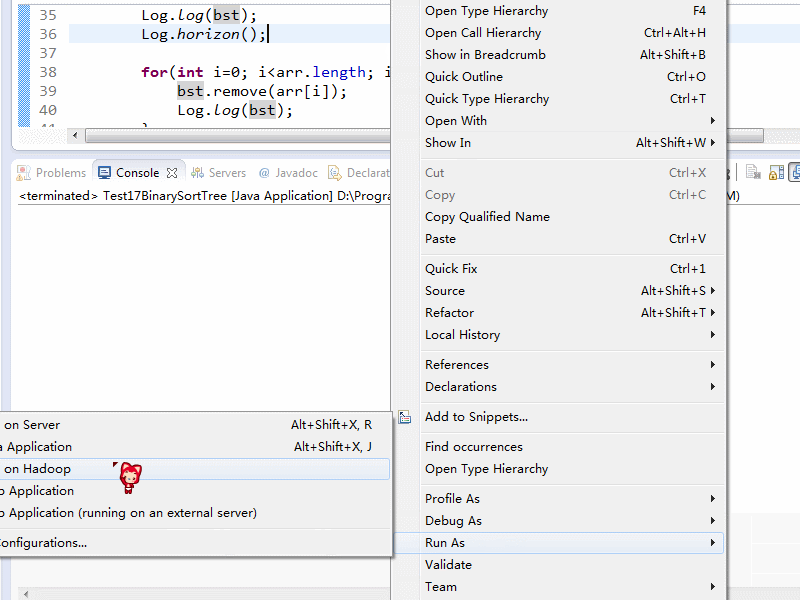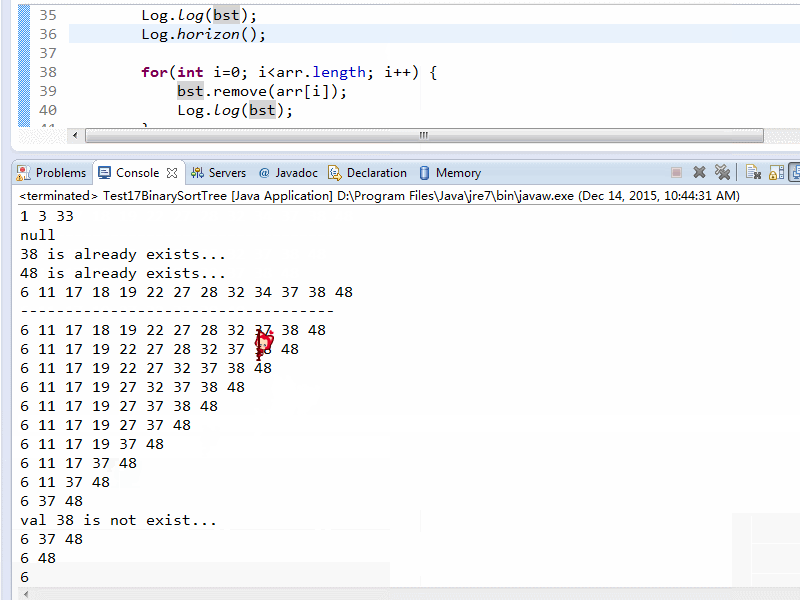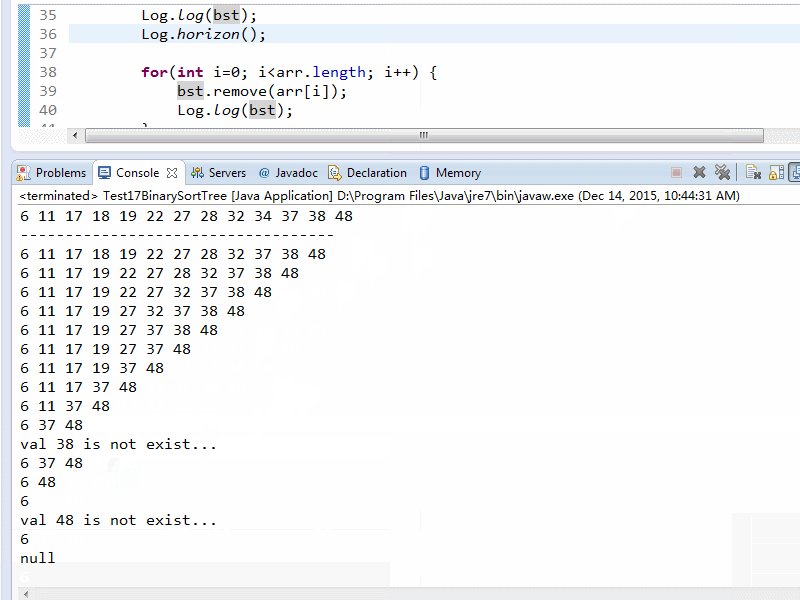
int[] arr = new int[] {34, 18, 28, 22, 32, 38, 27, 19, 17, 11, 38, 37, 48, 48, 6 };
// int[] arr = new int[] {27, 19, 17, 11, 38, 37};
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++) {
bst.add(arr[i]);
}
Log.log(bst);
Log.horizon();
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++) {
bst.remove(arr[i]);
Log.log(bst);
}
}
// 二叉排序树
public static class BinarySortTree {
// 根节点
Node root;
// 初始化
public BinarySortTree() {
root = null;
}
// 获取root结点
public Node root() {
return root;
}
// 添加一个元素
// 如果root结点为null, 则插入的val作为root结点的值
// 否则 找到val结点的父节点 进行插入[如果已存在 : 这里的处理方式是打印日志]
public void add(int val) {
if(root == null) {
root = new Node();
root.val = val;
} else {
Node node = root;
Node last = null;
while(node != null) {
last = node;
if(val < node.val ) {
node = node.left;
} else if(val > node.val ) {
node = node.right;
} else {
Log.log(val + " is already exists...");
return ;
}
}
if(val < last.val) {
last.left = new Node(last, val);
} else {
last.right = new Node(last, val);
}
}
}
// 遍历树 获取val对应的结点
// 从root结点开始比较[node]
// 如果val小于node.val 则进入左子树比较
// 否则val大于node.val 则进入右子树比价
// 否则 当前结点即为所找结点
private Node get(int val) {
Node node = root;
while(node != null) {
if(val < node.val ) {
node = node.left;
} else if(val > node.val ) {
node = node.right;
} else {
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
// 删除val对应的结点
// 如果没有该元素 打印日志
// 对于root结点 特殊处理
// 如果root结点没有子节点 直接将其置空
// 如果root结点有左子节点 则将左子树中最大的值替换掉 root结点的值 并将该节点的左子树接到该结点的父节点上
// 如果root结点有有右子节点 则将右子树中最小的值替换掉root结点的值 并将该节点右子树接到该节点的父节点上
// 否则该结点非root结点
// 如果该节点是叶子结点 直接令该节点的父节点相应的孩子为null
// 如果 该节点左右子孩子均不为空
// 方式一 : 将node结点的右子树[或者左子树] 放在node结点左子树的最大的结点的右子树上[右子树的最小的结点], 然后将node结点的左子树接到node结点的父节点上
// 方式一 : 将node结点的左子树的最大结点[或者右子树的最小节点] 替换掉node, 然后该结点的左子树接到该节点的父节点上
// 否则 如果该节点左孩子不为空 则将该结点的左孩子接到父节点上
// 否则 如果该节点右孩子不为空 则将该结点的右孩子接到父节点上
public void remove(int val) {
Node node = get(val);
if(node == null) {
Log.log("val " + val + " is not exist...");
return ;
}
// root 结点
if(node.parent == null) {
if(isLeaf(node)) {
root = null;
} else if(node.left != null) {
removeForRoot0(node);
} else if(node.right != null) {
removeForRoot1(node);
}
return ;
// 非root 结点
} else {
if(isLeaf(node)) {
if(isLeftChild(node)) {
node.parent.left = null;
} else {
node.parent.right = null;
}
} else if(node.left != null && node.right != null) {
// remove0(node);
remove1(node);
} else if(node.left != null) {
// 方式1 [更新涉及的引用]
if(isLeftChild(node)) {
node.parent.left = node.left;
node.left.parent = node.parent;
} else {
node.parent.right = node.left;
node.left.parent = node.parent;
}
// 方式2 [更新数据, 以及部分引用]
// node.val = node.left.val;
// node.left = node.left.left;
// node.right = node.left.right;
// if(node.left != null) {
// node.left.parent = node;
// }
// if(node.right != null) {
// node.right.parent = node;
// }
} else if(node.right != null) {
if(isLeftChild(node)) {
node.parent.left = node.right;
node.right.parent = node.parent;
} else {
node.parent.right = node.right;
node.right.parent = node.parent;
}
}
}
}
// 移除结点node
// 方式一 : 将node结点的右子树 放在node结点左子树的最大的结点的右子树上, 然后将node结点的左子树接到node结点的父节点上
// 或者 反之亦可
private void remove0(Node node) {
removeForNode0Left(node);
// removeForNode0Right(node);
}
// 移除结点node
// 方式二 : 将node结点的左子树的最大结点[或者右子树的最小节点] 替换掉node, 然后该结点的左子树接到该节点的父节点上
// 或者将node结点的右子树的最小节点替换node结点
private void remove1(Node node) {
removeForNode1Left(node);
// removeForNode1Right(node);
}
// 删除结点方式一(1): 将node结点的右子树 放在node结点左子树的最大的结点的右子树上, 然后将node结点的左子树接到node结点的父节点上
private void removeForNode0Left(Node node) {
Node nodeLeftMax = getMaxNode(node.left);
nodeLeftMax.right = node.right;
if(node.right != null) {
node.right.parent = nodeLeftMax;
}
node.parent.left = node.left;
if(node.left != null) {
node.left.parent = node.parent;
}
}
// 删除结点方式一(2) : 将node结点的左子树 放在node结点右子树的最小的结点的左子树上, 然后将node结点的右子树接到node结点的父节点上
private void removeForNode0Right(Node node) {
Node nodeRightMinx = getMinNode(node.right);
nodeRightMinx.left = node.left;
if(node.left != null) {
node.left.parent = nodeRightMinx;
}
node.parent.right = node.right;
if(node.right != null) {
node.right.parent = node.parent;
}
}
// 删除root结点 方式一 : 找出root结点左孩子的最大值 替换掉root结点, 然后该结点的左子树接到该节点的父节点上
private void removeForRoot0(Node node) {
removeForNode1Left(root);
}
// 删除root结点 方式二 : 将root结点的右子树的最小结点 替换掉root, 然后该结点的右子树接到该节点的父节点上
private void removeForRoot1(Node node) {
removeForNode1Right(root);
}
// 删除结点 方式二(1) : 找出左孩子的最大值 替换掉删除结点, 然后该结点的左子树接到该节点的父节点上
// 分为两种情况
// 如果node.left没有右孩子 则直接令nodeLeftMax.left接到node上面
// 否则 将nodeLeftMax.left接到nodeLeftMax.parent上面
private void removeForNode1Left(Node node) {
Node nodeLeftMax = getMaxNode(node.left);
node.val = nodeLeftMax.val;
if(nodeLeftMax.parent == node) {
node.left = nodeLeftMax.left;
} else {
nodeLeftMax.parent.right = nodeLeftMax.left;
}
if(nodeLeftMax.left != null) {
nodeLeftMax.left.parent = nodeLeftMax.parent;
}
}
// 删除root结点 方式二(2) : 将node结点的右子树的最小结点 替换掉node, 然后该结点的右子树接到该节点的父节点上
// 分为两种情况
// 如果node.right没有左孩子 则直接令nodeLeftMax.right接到node上面
// 否则 将nodeLeftMax.right接到nodeLeftMax.parent上面
private void removeForNode1Right(Node node) {
Node nodeRightMin = getMinNode(node.right);
node.val = nodeRightMin.val;
if(nodeRightMin.parent == node) {
node.right = nodeRightMin.right;
} else {
nodeRightMin.parent.left = nodeRightMin.right;
}
if(nodeRightMin.right != null) {
nodeRightMin.right.parent = nodeRightMin.parent;
}
}
// 判断node是否是node.parent的左孩子
private boolean isLeftChild(Node node) {
return node.val < node.parent.val;
}
// 判断node是否是树叶结点
private boolean isLeaf(Node node) {
return node.left == null && node.right == null;
}
// 获取node结点的最大子节点
private Node getMaxNode(Node node) {
Node tmp = node;
while(tmp.right != null) {
tmp = tmp.right;
}
return tmp;
}
// 获取node结点的最小子节点
private Node getMinNode(Node node) {
Node tmp = node;
while(tmp.left != null) {
tmp = tmp.left;
}
return tmp;
}
// 中序遍历 获取node的子树的字符串表示[得到的是一个有序序列] 存于sb中
public void headFirstForString(Node node, StringBuilder sb) {
if(node == null) {
sb.append("null");
} else {
if(node.left != null) {
headFirstForString(node.left, sb);
}
sb.append(node.val + " ");
if(node.right != null) {
headFirstForString(node.right, sb);
}
}
}
// for debug
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
headFirstForString(root, sb);
return sb.toString();
}
}
// 树结点
public static class Node {
// val 表示数据, parent表示该节点的父节点
// left, right 表示该节点的左孩子, 右孩子
int val;
Node parent;
Node left;
Node right;
// 初始化
public Node() {
}
public Node(Node parent, int val) {
this.parent = parent;
this.val = val;
}
public Node(Node parent, Node left, Node right, int val) {
set(parent, left, right, val);
}
public Node(Node node) {
set(node.parent, node.left, node.right, node.val);
}
// getter & setter
public Node getLeft() {
return left;
}
public Node getRight() {
return right;
}
public void set(Node parent, Node left, Node right, int val) {
this.parent = parent;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.val = val;
}
public void setLeft(Node left) {
this.left = left;
}
public void setRight(Node right) {
this.right = right;
}
// for debug
public String toString() {
return "val : " + val;
}
}
}效果
–2015.06.01






















