LeetCode题集三
- 简单题
- 100. 相同的树
- 101. 对称二叉树
- 104. 二叉树的最大深度
- 107. 二叉树的层次遍历 II
- 108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
- 110. 平衡二叉树
- 111. 二叉树的最小深度
- 112. 路径总和
- 119. 杨辉三角 II
- 119. 杨辉三角 II
简单题
100. 相同的树
题目:

思路:
树结构常用到递归,这里使用递归来实现。深度优先探索结点是否相同。
解法:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isSameTree(self, p: TreeNode, q: TreeNode) -> bool:
# 当同一个位置都为空的时候,返回True
if not p and not q:
return True
# 深度优先
if p and q and p.val==q.val:
l = self.isSameTree(p.left, q.left)
r = self.isSameTree(p.right, q.right)
return l and r
# 剩余的情况均为False
return False101. 对称二叉树
题目:

思路:
递归:使用额外的函数来对比左右结点,之后进行递归;
迭代:使用队列来实现,将两个对称的结点一组加入队列,然后取出进行对比判断。
解法:
- 递归
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def isSymmetric(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
if not root:
return True
return self.cmp_node(root.left, root.right)
def cmp_node(self, node_1, node_2):
if not node_1 and not node_2:
return True
elif not node_1 or not node_2:
return False
elif node_1.val != node_2.val:
return False
return self.cmp_node(node_1.left, node_2.right) and self.cmp_node(node_1.right, node_2.left)- 迭代
class Solution:
def isSymmetric(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
if not root:
return True
# 使用队列
queue = collections.deque()
queue.append((root.left,root.right))
while queue:
left, right = queue.popleft()
if not left and not right:
continue
if not left or not right:
return False
if left.val != right.val:
return False
queue.append((left.left, right.right))
queue.append((left.right, right.left))
return True104. 二叉树的最大深度
题目:

思路:
递归:深度优先,如果不为空的话,深度至少是1,递归查找左右子结点可以得到答案;
迭代:广度优先,将一排结点加入到队列中然后查找他们是否存在直接点来进行计算。
解法:
- 递归(DFS)
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
left = 1 + self.maxDepth(root.left)
right = 1 + self.maxDepth(root.right)
return max(left, right)- 迭代(BFS)
# BFS
def maxDepth(self, root):
if not root:
return 0
res = 0
queue = [root]
while queue:
for _ in range(len(queue)):
node = queue.pop(0)
if node.left:
queue.append((node.left))
if node.right:
queue.append((node.right))
res += 1
return res107. 二叉树的层次遍历 II
题目:

思路:
递归:参考了别人的实现,主要还是深度优先实现。
迭代:与球二叉树的最大深度类似,不过最后需要的是结点的值,而不是整个结点。
解法:
- 递归
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def levelOrderBottom(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
def dfs(root, depth):
if not root:
return []
if len(res) < depth+1:
res.append([])
res[depth].append(root.val)
dfs(root.left, depth+1)
dfs(root.right, depth+1)
dfs(root, 0)
return res[::-1]- 迭代
class Solution:
def levelOrderBottom(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
if not root:
return []
queue = [root]
res = []
while queue:
node_values = []
for _ in range(len(queue)):
node = queue.pop(0)
if node.left:
queue.append((node.left))
if node.right:
queue.append((node.right))
node_values.append(node.val)
# 插在前面一层的前面
res.insert(0, node_values)
return res108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
题目:

思路:
递归:找到根节点(中心位置)后,将左右两边继续递归,递归! 永远的神!
解法:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def sortedArrayToBST(self, nums: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
if not nums:
return None
mid = len(nums) // 2
root = TreeNode(nums[mid])
root.left = self.sortedArrayToBST(nums[:mid])
root.right = self.sortedArrayToBST(nums[mid+1:])
return root110. 平衡二叉树
题目:

思路:
递归:计算左右子树,如果左右子树是平衡二叉树的话,再看他们的左右子树
解法:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
# 计算二叉树深度
def cal_height(self, root):
if not root:
return 0
return max(self.cal_height(root.left), self.cal_height(root.right)) + 1
def isBalanced(self, root):
if not root:
return True
if abs(self.cal_height(root.left) - self.cal_height(root.right)) <= 1:
# 判断两个子树是否都是平衡二叉树
return self.isBalanced(root.left) and self.isBalanced(root.right)
else:
return False111. 二叉树的最小深度
题目:

思路:
递归:子结点为空的时候为0,子结点非空的时候为1,其他情况递归。
迭代:和层次遍历类似,一层层向下遍历,当某个结点左右子结点都为空的时候,可以跳出循环返还这个深度了。
解法:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
# 递归
class Solution:
def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
if not root.left and not root.right:
return 1
res = inf
if root.left:
res = min(res, self.minDepth(root.left))
if root.right:
res = min(res, self.minDepth(root.right))
return res+1- 迭代:
class Solution:
def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
res = 1
queue = [root]
while queue:
for i in range(len(queue)):
node = queue.pop(0)
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
if not node.left and not node.right:
return res
res += 1
return res112. 路径总和
题目:

思路:
递归遍历,通过逐渐减少sum值去比较。
迭代也是一样的思路,不过得使用一个栈。
解法:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> bool:
if not root:
return 0
if not root.left and not root.right:
return root.val == sum
return self.hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) or self.hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val)- 迭代
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self,root,sum):
if not root:
return False
stack = [(root,sum)]
while stack:
node, val = stack.pop()
if not node.left and not node.right and node.val == val:
return True
if node.right:
stack.append((node.right,val-node.val))
if node.left:
stack.append((node.left,val-node.val))
return False119. 杨辉三角 II
题目:
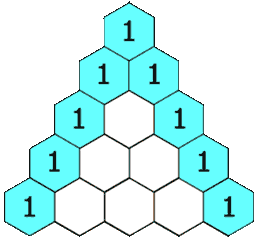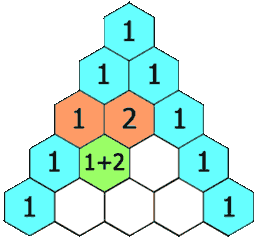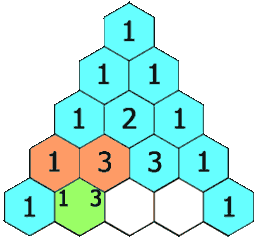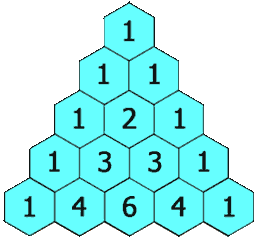

思路:
:按照给的规律直接暴力求解
巧妙求解:参考了别人的答案,可以错位相加求解
解法:
- 暴力求解
class Solution:
def generate(self, numRows: int) -> List[List[int]]:
if not numRows:
return []
res = [[1]]
for i in range(1, numRows):
tmp = [1, 1]
for j in range(1, i):
num = res[i - 1][j - 1] + res[i - 1][j]
tmp.insert(j, num)
res.append(tmp)
return res- 巧妙求解
class Solution:
def generate(self, numRows: int) -> List[List[int]]:
if numRows == 0:
return []
res = [[1]]
while len(res) < numRows:
newRow = [a+b for a, b in zip([0]+res[-1], res[-1]+[0])]
res.append(newRow)
return res119. 杨辉三角 II
题目:

思路:
在上那个一题的基础上修改实现。
解法:
class Solution:
def getRow(self, rowIndex: int) -> List[int]:
res = [[1]]
while len(res) <= rowIndex:
newRow = [a + b for a, b in zip([0]+res[-1], res[-1]+[0])]
res.append(newRow)
return res[rowIndex]





















