一、雏形构建
先给大家看下这小节的效果图:
自定义一个对话框,内容是四个ImageView横排;

1、Dialog布局
根据上图的对话框样式,我们看一下Dialog的布局定义(custom_dialog.xml)
1. <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2.
3. <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
4. android:id="@+id/log_in_layout"
5. android:layout_width="fill_parent"
6. android:layout_height="wrap_content"
7. android:orientation="horizontal">
8.
9. <ImageView
10. android:layout_width="match_parent"
11. android:layout_height="100dip"
12. android:src="@drawable/animal1"
13. android:clickable="true"
14. android:layout_weight="1"/>
15. <ImageView
16. android:layout_width="match_parent"
17. android:layout_height="100dip"
18. android:src="@drawable/animal2"
19. android:clickable="true"
20. android:layout_weight="1"/>
21. <ImageView
22. android:layout_width="match_parent"
23. android:layout_height="100dip"
24. android:src="@drawable/animal3"
25. android:clickable="true"
26. android:layout_weight="1"/>
27. <ImageView
28. android:layout_width="match_parent"
29. android:layout_height="100dip"
30. android:src="@drawable/animal4"
31. android:clickable="true"
32. android:layout_weight="1"/>
33.
34. </LinearLayout>
2、从Dialog派生对话框类
有关构造函数:有三种构造函数,现在我这里使用重写了两个,这里只需要使用第一个,即传进去context即可;
有关OnCreate()
在OnCreate()时,利用LayoutInflater获取我们对话框的View,然后利用SetContentView指定为我们CustomDialog类的布局。
1. public class CustomDialog extends Dialog {
2. Context mContext;
3. public CustomDialog (Context context){
4. super(context);
5. mContext = context;
6. }
7. public CustomDialog(Context context, int theme) {
8. super(context, theme);
9. mContext = context;
10. }
11.
12. @Override
13. protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
14. super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
15.
16. LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater) mContext
17. .getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
18. null);
19. this.setContentView(layout);
20. }
21. }
3、主函数(MainActivity)
在MainActivity中,我们写一个Button,当用户点击的时候弹出我们自定义的对话框实例
MainActivity的布局:(activity_main.xml)
1. <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
2. xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
3. android:layout_width="match_parent"
4. android:layout_height="match_parent"
5. tools:context=".MainActivity">
6.
7. <Button
8. android:id="@+id/btn_pop_dialog"
9. android:layout_width="fill_parent"
10. android:layout_height="wrap_content"
11. android:text="弹出对话框"/>
12.
13. </RelativeLayout>
代码中的处理:(MainActivity.java)
在点击Btn的时候,创建CustomDialog类的实例,并显示
1. public class MainActivity extends Activity {
2.
3. @Override
4. protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
5. super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
6. setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
7.
8. Button btn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_pop_dialog);
9. new View.OnClickListener() {
10. @Override
11. public void onClick(View view) {
12. new CustomDialog(MainActivity.this);
13. dialog.show();
14. }
15. });
16. }
17.
18. }二、定义对话框样式
这里再回头看看上面弹出的对话框:

在布局中,我们只定义了一个水平布局,里面放了四个ImageView,即那四个小动物,那上面那一坨是哪来的呢(我用红笔圈出来的那块)?能不能去掉?这节,我们就说说有关样式的问题。
第一个问题,只所有上面那一坨,是因为我们没有指定对话框样式,系统会使用默认样式,那一坨就是标题栏。
要去掉的话,我们就需要自定义样式。
1、自定义样式
我们的样式是写在res/values文件夹下的style.xml文件中的,如图,如果没有style.xml,自已新建一个,位置如图:

这里定义的样式代码是这样的:
1. <style name="dialog" parent="android:Theme.Dialog">
2. <item name="android:windowFrame">@null</item>
3. <item name="android:windowIsFloating">true</item>
4. <item name="android:windowContentOverlay">@null</item>
5. <item name="android:windowNoTitle">true</item>
6. </style>
先对这几个参数解释一下:
android:windowFrame:界面对应的前景图片;
android:windowIsFloating:表示浮在屏幕上的,如果在这里使用了,整个layout就会在 屏幕中心,相当于浮在屏幕上,所以这个只适用于dialog
android:windowContentOverlay:表示标题栏的阴影部分的样式,使用图片或者颜色
android:windowNoTitle:标题栏是否隐藏,这就是我们上面显示的标题栏
有关样式的内容很多很杂,这里有篇文章大家可以参考下《Andriod中Style/Theme原理以及Activity界面文件选取过程浅析》,有机会给大家总结一下有关样式和主题的内容,到时再细讲,这里不是本篇的重点,就不再细讲了。
2、使用样式
方法一:
这里有两种方法来使用样式,主要还是利用构造函数,还记得我们上面说过,对话框的两个构造函数:
1. public class CustomDialog extends Dialog {
2. Context mContext;
3.
4. public CustomDialog(Context context) {
5. super(context);
6. mContext = context;
7. }
8.
9. public CustomDialog(Context context, int theme) {
10. super(context, theme);
11. mContext = context;
12. }
13.
14. …………
15. }
看第二个就是我们的Theme样式,所以第一种使用样式的方法是在构造时直接将样式传进来,如果这样使用,那我们在构造对话框时应该是这样的“:
1. public class MainActivity extends Activity {
2.
3. @Override
4. protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
5. super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
6. setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
7.
8. Button btn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_pop_dialog);
9. new View.OnClickListener() {
10. @Override
11. public void onClick(View view) {
12. new CustomDialog(MainActivity.this,R.style.dialog);
13. dialog.show();
14. }
15. });
16. }
17. }
即在新建CustomDialog实例时,第二个参数传进来我们上面定义的样式。
方法二:
第二种方法,就是我们在构造时,不让别人传样式,只让传进来Context,但在内部,我们利用Super(context,theme)来指定样式,代码如下:
1. public class CustomDialog extends Dialog {
2. Context mContext;
3.
4. public CustomDialog(Context context) {
5. super(context,R.style.dialog);
6. mContext = context;
7. }
8.
9. …………
10. }
这种情况一般用在我们封装代码时,不让其它人在外部改变我们的样式时使用的。
无论使用哪种方法,我们就已经指定我我们的对话框样式,现在的效果是这样的:

看到了没,上面的标题栏没了,下面再看看有关参数传递的问题
三、参数传递
这里涉及到两个问题:传进去和传出来;
传进去:下面有两个按钮,当用户点第一个按钮时,在对话框中显示"From btn 1",如果用户点击第二个按钮,在对话框中显示“From btn 2”
传出来:这四个图片都是可以点击的,当用户点击任何一个图片,把它的ID传出来,并设置到我们的MainActivity中;
这里为了好理解,更改了对话框的布局,将水平布局改成了垂直布局。并且在MainActiviy下面加了一个ImageView.
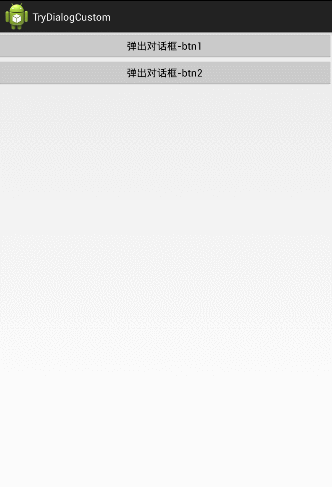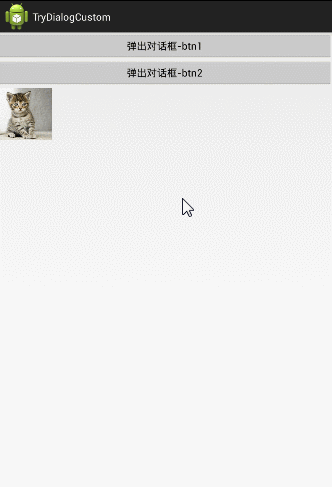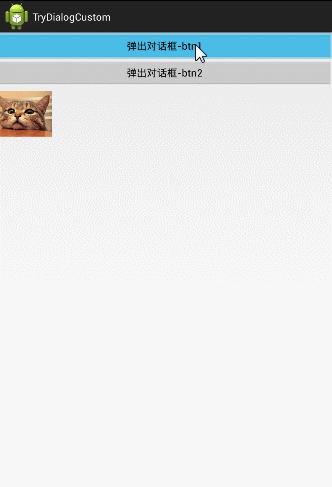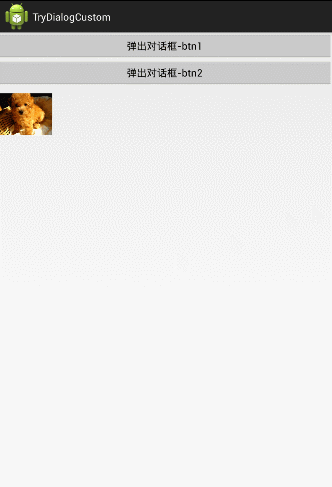
1、传进去
往对话框里传参数,一般就是利用构造函数来完成的,很简单,即在对话框的构造函数上加上我们自己想要传的参数,这里我们需要额外传一个字符串,来表示从哪个BTN来的。
所以对话框的构造函数就变成了这样:
1. public class CustomDialog extends Dialog{
2. private Context mContext;
3. private String mStr;
4.
5. public CustomDialog(Context context, String str, int theme) {
6. super(context, theme);
7. mContext = context;
8. mStr = str;
9. }
10.
11. …………
12. }
在使用的时候,也很简单:
1. Button btn2 = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_pop_dialog_2);
2. btn2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
3. @Override
4. public void onClick(View view) {
5. new CustomDialog(MainActivity.this,"From btn 2",R.style.dialog);
6. dialog.show();
7. }
8. });
直接利用构造函数传参即可
2、传出来
利用构造函数传参数大家都知道,但要怎么把用户的操作信息传出来就不是那么简单了,这里就要利用回调来实现了!
回调函数的使用主要依照下面这些步骤:
在对话框中:
1. public class CustomDialog extends Dialog {
2.
3. // 利用interface来构造一个回调函数
4. public interface ICustomDialogEventListener {
5. public void customDialogEvent(int valueYouWantToSendBackToTheActivity);
6. }
7.
8. private ICustomDialogEventListener onCustomDialogEventListener;
9.
10. // 在构造函数中,设置进去回调函数
11. public CustomDialog(Context context,
12. ICustomDialogEventListener onCustomDialogEventListener) {
13. super(context);
14. this.onCustomDialogEventListener = onCustomDialogEventListener;
15. }
16.
17. //当你想把值传回去的时候,调用回调函数将值设置进去
18. @Override
19. public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
20. {
21. Button btnOk = (Button) findViewById(R.id.customDialogButton);
22. new Button.OnClickListener()
23. {
24. public void onClick(View v) {
25. onCustomDialogEventListener.customDialogEvent(valueYouWantToSendBackToTheActivity);
26. dismiss();
27. }
28. });
29. }
30. }
在构造对话框时:
1. final CustomDialog dialog = new CustomDialog(this, new ICustomDialogEventListener() {
2. public void customDialogEvent(int value) {
3. //在这里就获取到了从对话框传回来的值
4. }
5. });
大致使用流程就是这样的,下面就把我们上面的效果利用回调函数实现出来;
首先在对话框中新建一个回调函数(接口),并且在对话框的构造方法中把回调函数传进来:
1. public class CustomDialog extends Dialog implements View.OnClickListener {
2.
3. //增加一个回调函数,用以从外部接收返回值
4. public interface ICustomDialogEventListener {
5. public void customDialogEvent(int id);
6. }
7.
8. private ICustomDialogEventListener mCustomDialogEventListener;
9. private Context mContext;
10. private String mStr;
11. //把回调函数传进来
12. public CustomDialog(Context context, String str, ICustomDialogEventListener listener, int theme) {
13. super(context, theme);
14. mContext = context;
15. mStr = str;
16. mCustomDialogEventListener = listener;
17. }
18.
19. …………
20. }
然后在OnCreate() 函数中设定ImageView的点击事件,我们将CustomDialog类继承View.OnClickListener接口,对点击事件统一处理:
1. private void bindImageClickEvent(View layout){
2. ImageView img1 = (ImageView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_image1);
3. ImageView img2 = (ImageView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_image2);
4. ImageView img3 = (ImageView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_image3);
5. ImageView img4 = (ImageView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_image4);
6. this);
7. this);
8. this);
9. this);
10. }
11.
12. @Override
13. protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
14. super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
15.
16. LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater) mContext
17. .getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
18. null);
19.
20. TextView tv = (TextView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_text);
21. tv.setText(mStr);
22.
23. //绑定ImageView点击事件
24.
25. this.setContentView(layout);
26. }
在OnCreate()中,首先将传进来的String字符串设置到对话框的TextView中;然后绑定各个ImageView的点击事件
然后 就是在OnClick中的处理:
主要是根据用户当前点击的ImageView的ID,把这个ImageView所用的图片的DrawableID返回给MainActivity,代码如下:
1. public void onClick(View view) {
2. int id = view.getId();
3. int drawableID = -1;
4. switch (id){
5. case R.id.dialog_image1:
6. drawableID = R.drawable.animal1;
7. break;
8. case R.id.dialog_image2:
9. drawableID = R.drawable.animal2;
10. break;
11. case R.id.dialog_image3:
12. drawableID = R.drawable.animal3;
13. break;
14. case R.id.dialog_image4:
15. drawableID = R.drawable.animal4;
16. break;
17. }
18. if (drawableID != -1) {
19. mCustomDialogEventListener.customDialogEvent(drawableID);
20. }
21. dismiss();
22. }
这样就把对话框的构造过程讲完了,完整的对话框代码是这样的:
1. public class CustomDialog extends Dialog implements View.OnClickListener{
2.
3. //增加一个回调函数,用以从外部接收返回值
4. public interface ICustomDialogEventListener {
5. public void customDialogEvent(int id);
6. }
7.
8. private ICustomDialogEventListener mCustomDialogEventListener;
9. private Context mContext;
10. private String mStr;
11.
12. public CustomDialog(Context context) {
13. super(context);
14. mContext = context;
15. }
16.
17. public CustomDialog(Context context, String str,ICustomDialogEventListener listener,int theme) {
18. super(context, theme);
19. mContext = context;
20. mStr = str;
21. mCustomDialogEventListener = listener;
22. }
23. private void bindImageClickEvent(View layout){
24. ImageView img1 = (ImageView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_image1);
25. ImageView img2 = (ImageView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_image2);
26. ImageView img3 = (ImageView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_image3);
27. ImageView img4 = (ImageView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_image4);
28. this);
29. this);
30. this);
31. this);
32. }
33.
34. @Override
35. protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
36. super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
37.
38. LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater) mContext
39. .getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
40. null);
41.
42. TextView tv = (TextView)layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_text);
43. tv.setText(mStr);
44.
45. bindImageClickEvent(layout);
46.
47. this.setContentView(layout);
48. }
49.
50. @Override
51. public void onClick(View view) {
52. int id = view.getId();
53. int drawableID = -1;
54. switch (id){
55. case R.id.dialog_image1:
56. drawableID = R.drawable.animal1;
57. break;
58. case R.id.dialog_image2:
59. drawableID = R.drawable.animal2;
60. break;
61. case R.id.dialog_image3:
62. drawableID = R.drawable.animal3;
63. break;
64. case R.id.dialog_image4:
65. drawableID = R.drawable.animal4;
66. break;
67. }
68. if (drawableID != -1) {
69. mCustomDialogEventListener.customDialogEvent(drawableID);
70. }
71. dismiss();
72. }
73. }
下面就是构造对话框的过程了:
在MainAcitivity中,当点击一个按钮时,new一个ICustomDialogEventListener实例来接收传过来的值;
1. Button btn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_pop_dialog_1);
2. btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
3. @Override
4. public void onClick(View view) {
5. new CustomDialog(MainActivity.this,"From btn 1",new CustomDialog.ICustomDialogEventListener() {
6. @Override
7. public void customDialogEvent(int id) {
8. ImageView imageView = (ImageView)findViewById(R.id.main_image);
9. imageView.setImageDrawable(getResources().getDrawable(id));
10. }
11. },R.style.dialog);
12. dialog.show();
13. }
14. });
在我们收到传过来的DrawableID时,把它设置gc主页面ImageVIew里显示出来,这就完成了我们上面的功能。





















