Python中的排列组合
Python中的排列组合
itertools
Python 提供了直接的方法来查找序列的排列和组合。这些方法存在于 itertools 包中。
排列
首先导入itertools包,在python中实现permutations方法。此方法将列表作为输入并返回包含列表形式的所有排列的元组对象列表。
# A Python program to print all
# permutations using library function
from itertools import permutations
# Get all permutations of [1, 2, 3]
perm = permutations([1, 2, 3])
# Print the obtained permutations
for i in list(perm):
print (i)输出:
(1, 2, 3)
(1, 3, 2)
(2, 1, 3)
(2, 3, 1)
(3, 1, 2)
(3, 2, 1)它生成 n! 如果输入序列的长度为 n,则排列。
如果想要得到长度为 L 的排列,那么以这种方式实现它。
# A Python program to print all
# permutations of given length
from itertools import permutations
# Get all permutations of length 2
# and length 2
perm = permutations([1, 2, 3], 2)
# Print the obtained permutations
for i in list(perm):
print (i)输出:
(1, 2)
(1, 3)
(2, 1)
(2, 3)
(3, 1)
(3, 2)它生成 nCr * r! 如果输入序列的长度为 n 且输入参数为 r,则排列。
组合
此方法将一个列表和一个输入 r 作为输入,并返回一个元组对象列表,其中包含列表形式的长度 r 的所有可能组合。
# A Python program to print all
# combinations of given length
from itertools import combinations
# Get all combinations of [1, 2, 3]
# and length 2
comb = combinations([1, 2, 3], 2)
# Print the obtained combinations
for i in list(comb):
print (i)输出:
(1, 2)
(1, 3)
(2, 3)- 组合按输入的字典排序顺序发出。因此,如果输入列表已排序,则组合元组将按排序顺序生成。
# A Python program to print all
# combinations of a given length
from itertools import combinations
# Get all combinations of [1, 2, 3]
# and length 2
comb = combinations([1, 2, 3], 2)
# Print the obtained combinations
for i in list(comb):
print (i)输出:
(1, 2)
(1, 3)
(2, 3)- 元素根据它们的位置而不是它们的价值被视为唯一的。因此,如果输入元素是唯一的,则每个组合中都不会出现重复值。
# A Python program to print all combinations
# of given length with unsorted input.
from itertools import combinations
# Get all combinations of [2, 1, 3]
# and length 2
comb = combinations([2, 1, 3], 2)
# Print the obtained combinations
for i in list(comb):
print (i)输出:
(2, 1)
(2, 3)
(1, 3)3.如果我们想将相同的元素组合成相同的元素,那么我们使用combinations_with_replacement。
# A Python program to print all combinations
# with an element-to-itself combination is
# also included
from itertools import combinations_with_replacement
# Get all combinations of [1, 2, 3] and length 2
comb = combinations_with_replacement([1, 2, 3], 2)
# Print the obtained combinations
for i in list(comb):
print (i)输出:
(1, 1)
(1, 2)
(1, 3)
(2, 2)
(2, 3)
(3, 3)打印给定字符串的所有排列
排列也称为“排列编号”或“顺序”,是将有序列表 S 的元素重新排列为与 S 本身一一对应的排列。长度为 n 的字符串有 n! 排列。
下面是字符串 ABC 的排列。
ABC ACB BAC BCA CBA CAB
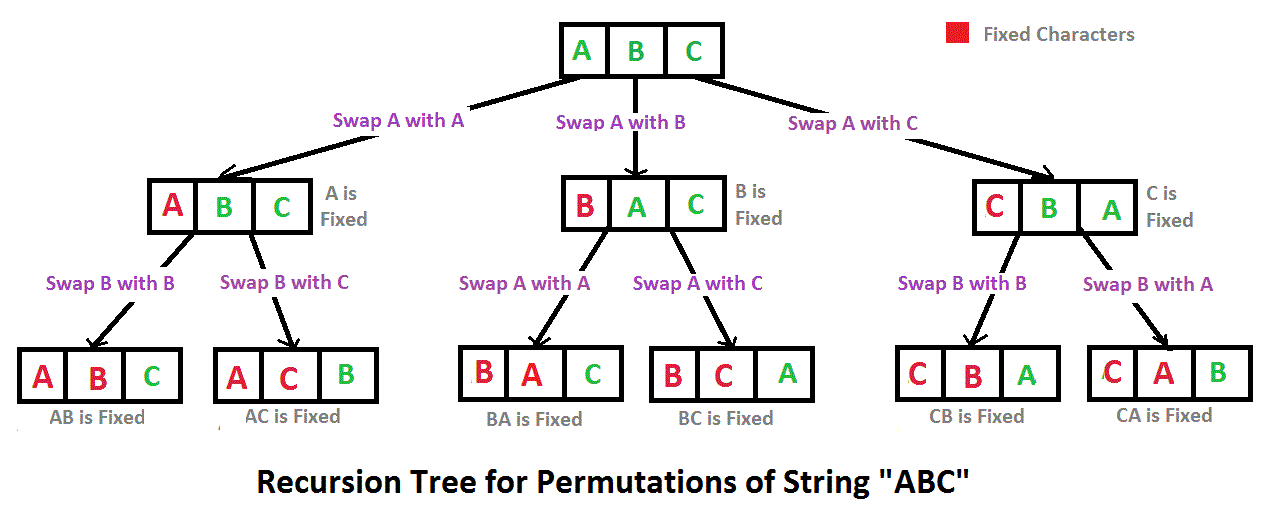
# Python program to print all permutations with
# duplicates allowed
def toString(List):
return ''.join(List)
# Function to print permutations of string
# This function takes three parameters:
# 1. String
# 2. Starting index of the string
# 3. Ending index of the string.
def permute(a, l, r):
if l==r:
print toString(a)
else:
for i in xrange(l,r+1):
a[l], a[i] = a[i], a[l]
permute(a, l+1, r)
a[l], a[i] = a[i], a[l] # backtrack
# Driver program to test the above function
string = "ABC"
n = len(string)
a = list(string)
permute(a, 0, n-1)
# This code is contributed by Bhavya JainOutput:
ABC
ACB
BAC
BCA
CBA
CAB算法范式:回溯
时间复杂度: O(n*n!) 注意有 n! 排列,打印排列需要 O(n) 时间。
辅助空间: O(r – l)
注意:如果输入字符串中有重复字符,上述解决方案会打印重复排列。
另一种方法:
def permute(s, answer):
if (len(s) == 0):
print(answer, end = " ")
return
for i in range(len(s)):
ch = s[i]
left_substr = s[0:i]
right_substr = s[i + 1:]
rest = left_substr + right_substr
permute(rest, answer + ch)
# Driver Code
answer = ""
s = input("Enter the string : ")
print("All possible strings are : ")
permute(s, answer)
# This code is contributed by Harshit Srivastava输出:
输入字符串:abc
所有可能的字符串是:abc acb bac bca cab cba时间复杂度: O(n*n!) 时间复杂度和上面的方法一样,即有n!排列,打印排列需要 O(n) 时间。
辅助空间: O(|s|)
打印具有重复项的给定字符串的所有不同排列
给定一个可能包含重复的字符串,编写一个函数来打印给定字符串的所有排列,以便在输出中没有重复排列。
例子:
输入:str[] = "AB"
输出:AB BA
输入:str[] = "AA"
输出:AA
输入:str[] = "ABC"
输出:ABC ACB BAC BCA CBA CAB
输入:str[] = "ABA"
输出:ABA AAB BAA
输入:str[] = "ABCA"
输出:AABC AACB ABAC ABCA ACBA ACAB BAAC BACA
BCAA CABA CAAB CBAA// Program to print all permutations of a
// string in sorted order.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
/* Following function is needed for library
function qsort(). */
int compare(const void* a, const void* b)
{
return (*(char*)a - *(char*)b);
}
// A utility function two swap two characters
// a and b
void swap(char* a, char* b)
{
char t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
// This function finds the index of the
// smallest character which is greater
// than 'first' and is present in str[l..h]
int findCeil(char str[], char first, int l, int h)
{
// initialize index of ceiling element
int ceilIndex = l;
// Now iterate through rest of the
// elements and find the smallest
// character greater than 'first'
for (int i = l + 1; i <= h; i++)
if (str[i] > first && str[i] < str[ceilIndex])
ceilIndex = i;
return ceilIndex;
}
// Print all permutations of str in sorted order
void sortedPermutations(char str[])
{
// Get size of string
int size = strlen(str);
// Sort the string in increasing order
qsort(str, size, sizeof(str[0]), compare);
// Print permutations one by one
bool isFinished = false;
while (!isFinished) {
// print this permutation
static int x = 1;
printf("%d %s \n", x++, str);
// Find the rightmost character
// which is smaller than its next
// character. Let us call it 'first
// char'
int i;
for (i = size - 2; i >= 0; --i)
if (str[i] < str[i + 1])
break;
// If there is no such character, all
// are sorted in decreasing order,
// means we just printed the last
// permutation and we are done.
if (i == -1)
isFinished = true;
else {
// Find the ceil of 'first char'
// in right of first character.
// Ceil of a character is the
// smallest character greater
// than it
int ceilIndex = findCeil(str,
str[i], i + 1, size - 1);
// Swap first and second characters
swap(&str[i], &str[ceilIndex]);
// Sort the string on right of 'first char'
qsort(str + i + 1, size - i - 1,
sizeof(str[0]), compare);
}
}
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main()
{
char str[] = "ACBC";
sortedPermutations(str);
return 0;
}输出
1 ABCC
2 ACBC
3 ACCB
4 BACC
5 BCAC
6 BCCA
7 CABC
8 CACB
9 CBAC
10 CBCA
11 CCAB
12 CCBA时间复杂度:O(n 2 * n!)
辅助空间:O(1)
上述算法的时间复杂度为 O(n2 * n!) 但我们可以通过一些修改实现 O(n!*n) 的更好时间复杂度,这是在输入中所有不同字符的情况下存在的算法。
有效的方法:在我们的递归函数中找到所有排列,我们可以使用 unordered_set 来处理活动字符串中剩余的重复元素。在迭代字符串的元素时,我们将在 unordered_set 中检查该元素,如果找到,则我们将跳过该迭代,否则我们将将该元素插入到 unordered_set 中。平均而言,所有像 insert() 和 find() 的 unordered_set 操作都在 O(1) 时间内,因此使用 unordered_set 不会改变算法时间复杂度。
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
void printAllPermutationsFast(string s, string l)
{
if (s.length() < 1) {
cout << l + s << endl;
}
unordered_set<char> uset;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (uset.find(s[i]) != uset.end()) {
continue;
}
else {
uset.insert(s[i]);
}
string temp = "";
if (i < s.length() - 1) {
temp = s.substr(0, i) + s.substr(i + 1);
}
else {
temp = s.substr(0, i);
}
printAllPermutationsFast(temp, l + s[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
string s = "ACBC";
sort(s.begin(), s.end());
printAllPermutationsFast(s, "");
return 0;
}Output
ABCC
ACBC
ACCB
BACC
BCAC
BCCA
CABC
CACB
CBAC
CBCA
CCAB
CCBA时间复杂度 - O(n*n!)
辅助空间 - O(n)
总和等于 X 的子集计数
给定一个长度为N的数组arr[]和一个整数X,任务是找到总和等于X的子集的数量。
例子:
Input: arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 3}, X = 6
Output: 3
All the possible subsets are {1, 2, 3},
{1, 2, 3} and {3, 3}
Input: arr[] = {1, 1, 1, 1}, X = 1
Output: 4方法一:
一个简单的方法是通过生成所有可能的子集,然后检查该子集是否具有所需的总和来解决此问题。这种方法将具有指数时间复杂度。但是,对于较小的X值和数组元素,可以使用动态规划解决此问题。
我们先来看递归关系。
此方法对所有整数都有效。
dp[i][C] = dp[i – 1][C – arr[i]] + dp[i – 1][C]
现在让我们了解 DP 的状态。这里,dp[i][C]存储子数组arr[i…N-1]的子集数量,使得它们的总和等于C。
因此,递归是非常微不足道的,因为只有两种选择,即要么考虑子集中的第i个元素,要么不考虑。
# Python3 implementation of the approach
import numpy as np
maxN = 20
maxSum = 50
minSum = 50
base = 50
# To store the states of DP
dp = np.zeros((maxN, maxSum + minSum));
v = np.zeros((maxN, maxSum + minSum));
# Function to return the required count
def findCnt(arr, i, required_sum, n) :
# Base case
if (i == n) :
if (required_sum == 0) :
return 1;
else :
return 0;
# If the state has been solved before
# return the value of the state
if (v[i][required_sum + base]) :
return dp[i][required_sum + base];
# Setting the state as solved
v[i][required_sum + base] = 1;
# Recurrence relation
dp[i][required_sum + base] = findCnt(arr, i + 1,
required_sum, n) + \
findCnt(arr, i + 1,
required_sum - arr[i], n);
return dp[i][required_sum + base];
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__" :
arr = [ 3, 3, 3, 3 ];
n = len(arr);
x = 6;
print(findCnt(arr, 0, x, n));
# This code is contributed by AnkitRai01输出
6方法二:使用制表法:
This method is valid only for those arrays which contains positive elements.
In this method we use a 2D array of size (arr.size() + 1) * (target + 1) of type integer.
Initialization of Matrix:
mat[0][0] = 1 because If the size of sum isif (A[i] > j)
DP[i][j] = DP[i-1][j]
else
DP[i][j] = DP[i-1][j] + DP[i-1][j-A[i]]这意味着如果当前元素的值大于“当前总和值”,我们将复制之前案例的答案
如果当前的总和值大于 'ith' 元素,我们将看到是否有任何先前的状态已经经历过 sum='j' 并且任何先前的状态经历了一个值 'j – A[i]' 这将是我们的目的
def subset_sum(a: list, n: int, sum: int):
# Initializing the matrix
tab = [[0] * (sum + 1) for i in range(n + 1)]
for i in range(1, sum + 1):
tab[0][i] = 0
for i in range(n+1):
# Initializing the first value of matrix
tab[i][0] = 1
for i in range(1, n+1):
for j in range(1, sum + 1):
if a[i-1] <= j:
tab[i][j] = tab[i-1][j] + tab[i-1][j-a[i-1]]
else:
tab[i][j] = tab[i-1][j]
return tab[n][sum]
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = [3, 3, 3, 3]
n = 4
sum = 6
print(subset_sum(a, n, sum))
# This code is contributed by Premansh2001.输出
6时间复杂度: O(sum*n),其中总和是“目标总和”,“n”是数组的大小。
辅助空间: O(sumn),作为二维数组的大小,是sumn。
计算 nCr 值的程序
二项式系数的常见定义:
- A binomial coefficient C(n, k) can be defined as the coefficient of X^k in the expansion of (1 + X)^n.
- A binomial coefficient C(n, k) also gives the number of ways, disregarding order, that k objects can be chosen from among n objects; more formally, the number of k-element subsets (or k-combinations) of an n-element set.
Given two numbers n and r, find value of nCr
nCr = (n!) / (r! * (n-r)!)示例:
Input : n = 5, r = 2
Output : 10
The value of 5C2 is 10
Input : n = 3, r = 1
Output : 3# Python 3 program To calculate
# The Value Of nCr
def nCr(n, r):
return (fact(n) / (fact(r)
* fact(n - r)))
# Returns factorial of n
def fact(n):
res = 1
for i in range(2, n+1):
res = res * i
return res
# Driver code
n = 5
r = 3
print(int(nCr(n, r)))
# This code is contributed
# by SmithaOutput:
10大数阶乘
非负整数的阶乘,是所有小于或等于 n 的整数的乘积。例如 6 的阶乘是 6*5*4*3*2*1,即 720。
Examples :
Input : 100
Output : 933262154439441526816992388562667004-
907159682643816214685929638952175999-
932299156089414639761565182862536979-
208272237582511852109168640000000000-
00000000000000
Input :50
Output : 3041409320171337804361260816606476884-
4377641568960512000000000000方法一: 我们使用数组来存储结果的各个数字。
下面是求阶乘的详细算法:
factorial(n)
- 创建一个最大大小的数组“res[]”,其中 MAX 是输出中的最大位数。
- 将存储在 'res[]' 中的值初始化为 1,并将 'res_size' ('res[]' 的大小) 初始化为 1。
- 对从 x = 2 到 n 的所有数字执行以下操作。
……a) 将 x 与 res[] 相乘并更新 res[] 和 res_size 以存储乘法结果。
如何将数字“x”与存储在 res[] 中的数字相乘?
我们将 x 与 res[] 的每一位数字一一相乘。这里要注意的重点是数字从最右边的数字到最左边的数字相乘。如果我们在 res[] 中以相同的顺序存储数字,那么在没有额外空间的情况下更新 res[] 变得困难。这就是为什么 res[] 以相反的方式维护,即从右到左存储数字。
multiply(res[], x)
- 将进位初始化为 0。
- 对 i = 0 执行以下操作到 res_size – 1
....a) 找到 res[i] * x + 进位的值。让这个价值成为现实。
....b) 通过在其中存储 prod 的最后一位来更新 res[i]。
....c) 通过将剩余数字存储在进位中来更新进位。 - 将进位的所有数字放入 res[] 并通过进位位数增加 res_size。
Example to show working of multiply(res[], x)
A number 5189 is stored in res[] as following.
res[] = {9, 8, 1, 5}
x = 10
Initialize carry = 0;
i = 0, prod = res[0]*x + carry = 9*10 + 0 = 90.
res[0] = 0, carry = 9
i = 1, prod = res[1]*x + carry = 8*10 + 9 = 89
res[1] = 9, carry = 8
i = 2, prod = res[2]*x + carry = 1*10 + 8 = 18
res[2] = 8, carry = 1
i = 3, prod = res[3]*x + carry = 5*10 + 1 = 51
res[3] = 1, carry = 5
res[4] = carry = 5
res[] = {0, 9, 8, 1, 5}注意:在下面的实现中,输出中的最大位数假定为 500。要找到更大数字(> 254)的阶乘,请增加数组的大小或增加 MAX 的值。
# Python program to compute factorial
# of big numbers
import sys
# This function finds factorial of large
# numbers and prints them
def factorial( n) :
res = [None]*500
# Initialize result
res[0] = 1
res_size = 1
# Apply simple factorial formula
# n! = 1 * 2 * 3 * 4...*n
x = 2
while x <= n :
res_size = multiply(x, res, res_size)
x = x + 1
print ("Factorial of given number is")
i = res_size-1
while i >= 0 :
sys.stdout.write(str(res[i]))
sys.stdout.flush()
i = i - 1
# This function multiplies x with the number
# represented by res[]. res_size is size of res[]
# or number of digits in the number represented
# by res[]. This function uses simple school
# mathematics for multiplication. This function
# may value of res_size and returns the new value
# of res_size
def multiply(x, res,res_size) :
carry = 0 # Initialize carry
# One by one multiply n with individual
# digits of res[]
i = 0
while i < res_size :
prod = res[i] *x + carry
res[i] = prod % 10; # Store last digit of
# 'prod' in res[]
# make sure floor division is used
carry = prod//10; # Put rest in carry
i = i + 1
# Put carry in res and increase result size
while (carry) :
res[res_size] = carry % 10
# make sure floor division is used
# to avoid floating value
carry = carry // 10
res_size = res_size + 1
return res_size
# Driver program
factorial(100)
#This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.输出
定数的阶乘是
93326215443944152681699238856266700490715968264381621468592963895217599993229915608941463976156518286253697920827223758251185210916864000000000000000000000000方法二: 也可以使用链表,这种方式不会浪费任何额外的空间。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i <= b; i++)
using namespace std;
// Made a class node containing data and previous pointer as
// we are using tail pointer
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* prev;
Node(int n)
{
data = n;
prev = NULL;
}
};
void Multiply(Node* tail, int n)
{
Node *temp = tail,
*prevNode = tail; // Temp variable for keeping tail
int carry = 0;
while (temp != NULL) {
int data = temp->data * n + carry;
temp->data = data % 10; // stores the last digit
carry = data / 10;
prevNode = temp;
temp = temp->prev; // Moving temp by 1 prevNode will
// now denote temp
}
// If carry is greater than 0 then we create another
// node for it.
while (carry != 0) {
prevNode->prev = new Node((int)(carry % 10));
carry /= 10;
prevNode = prevNode->prev;
}
}
void print(Node* tail)
{
if (tail == NULL) // Using tail recursion
return;
print(tail->prev);
cout
<< tail->data; // Print linked list in reverse order
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 20;
Node tail(1); // Create a node and initialise it by 1
rep(i, 2, n)
Multiply(&tail, i); // Run a loop from 2 to n and
// multiply with tail's i
print(&tail); // Print the linked list
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Kingshuk Deb输出
2432902008176640000























