文章目录
Android中的线程通信:消息机制
【消息机制】
消息机制的本质是子线程在执行过程中,发送消息给主线程,主线程对消息进行处理。
消息机制中的角色:
Message:消息的载体,用于封装消息的相关数据
Handler:消息的发送者与处理者,用于发送消息,并处理消息
【基本使用】
1、当需要更新 UI 时,在子线程中创建 Message 的对象,并在该对象中封装必要的数据,然后调用 Handler 对象的 sendMessage(Message)发送消息
2、自定义 Handler 的子类,重写 void handleMessage(Message)方法,该方法的参数 Message 对象即此前发送时的 Message 对象,所以,可以根据参数获取此前封装的数据,实现 UI 的更新。
【Message】
Message 是在线程之间传递的消息,它可以在内部携带少量的信息,用于在不同线 程之间交换数据 。Message 的 what 字段可以区分信息类型,除此之外还可以使 用 arg1和 arg2字段来携带一些整型数据,使用 obj字段携带一个 Object 对象
栗子:进度条更新
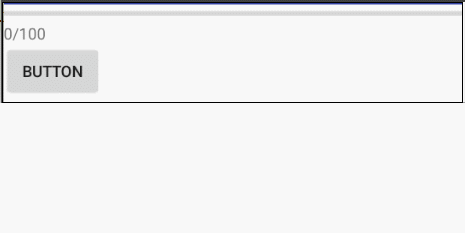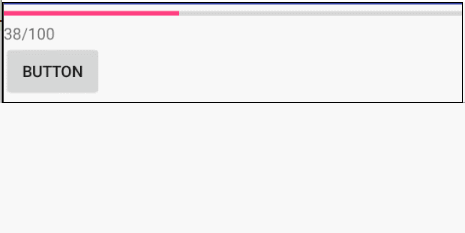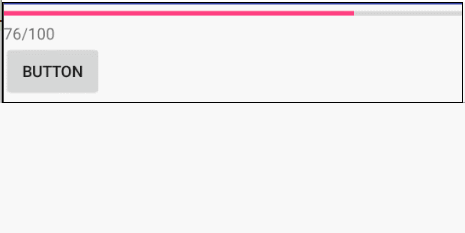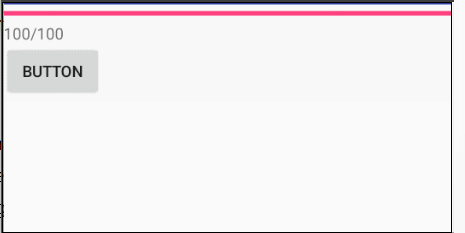
xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progressBar"
style="?android:progressBarStyleHorizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_show_progress"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="0/100" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button" />
</LinearLayout>
MainActivity
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private ProgressBar progressBar;
private Button button;
private TextView textView;
private Handler handler;
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
progressBar = findViewById(R.id.progressBar);
button = findViewById(R.id.button);
textView = findViewById(R.id.tv_show_progress);
button.setOnClickListener(this);
handler = new InnerHandler();
}
public void onClick(View view) {
InnerThread thread = new InnerThread();
thread.start();
}
private class InnerHandler extends Handler {
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
progressBar.setProgress(msg.arg1);
textView.setText(msg.arg1 + "/100");
}
}
private class InnerThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
//发消息,通知主线程更新UI
Message msg = new Message();
msg.arg1 = i;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
之前的写过进度条更新的一个栗子,这两个的实现方法有所区别:
1、【达内课程】Thread中ANR 中,开启了一个线程,在线程中使用runOnUiThread来更新 view
2、这里的栗子中,同样是开启了一个线程,我们通过 Handler 来发送 Message来 更新 view
Message 类
之前我们说过循环中尽量不要创建新对象,但在刚才的例子中,for 循环里我们在一直 new Message,如果我们把创建 Message 的代码写在 for 循环外面:
Message msg = new Message();
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
//发消息,通知主线程更新UI
......
}
这样是不行的。
子线程有 100 次循环,所以它会发 100 次消息
主线程根据子线程的 msg 进行消息处理时,需要一定的时间,可能第一条消息还没处理完,第二条消息已经到达,而第一个消息对象还在被使用着,所以用同一个消息对象是有问题的,所以消息对象一定是不同的
解决之前我们先了解 Message 类
【Message类】
当需要消息对象时,应该使用 Message 类的静态方法 obtain()获取消息对象,而不要使用 new Message()语法自行创建新的消息对象。
【Message类属性】
int arg1用于在消息对象中封装 int 类型数据
int arg2同上
Object obj用于在消息对象中封装任何类型的数据,例如一次需要封装 3 个 int 类型数据时,则可以自定义数据类型中放入 3 个 int 属性,然后在消息对象中封装自定义数据类型的对象。
int what用于标识消息的类型,通常对应某个 int 类型的常量
我们解决刚才说的问题。对上面栗子进行优化。
MainActivity
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private ProgressBar progressBar;
private Button button;
private TextView textView;
private Handler handler;
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
progressBar = findViewById(R.id.progressBar);
button = findViewById(R.id.button);
textView = findViewById(R.id.tv_show_progress);
button.setOnClickListener(this);
handler = new InnerHandler();
}
public void onClick(View view) {
InnerThread thread = new InnerThread();
thread.start();
}
private class InnerHandler extends Handler {
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.what == MESSAGE_UPDATE_PROGRESS) {
progressBar.setProgress(msg.arg1);
textView.setText(msg.arg1 + "/100");
} else if (msg.what == MESSAGE_UPDATE_COMPLETE) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "更新进度完成", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
}
public static final int MESSAGE_UPDATE_PROGRESS = 999;
public static final int MESSAGE_UPDATE_COMPLETE = 998;
private class InnerThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
//发消息,通知主线程更新UI
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = MESSAGE_UPDATE_PROGRESS;
msg.arg1 = i;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//发出消息,标识更新进度完成
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = MESSAGE_UPDATE_COMPLETE;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
}
}
运行程序:
如果使用 Message 的 obtain()方法中指定了 Handler 对象做为参数,则发送消息时应该调用 Message 对象的 sendToTarget()方法。
在 Handler 类中,也有一系列 obtainMessage()方法获取 Message 对象,这些方法都是基于 Message 类的 obtain() 方法实现的,且这些 obtainMessage()方法中都使用了 Handler 对象作为参数。





















