一. Lottie能做什么
回答这个问题前,我们先想想下面这些动画需要怎么实现:
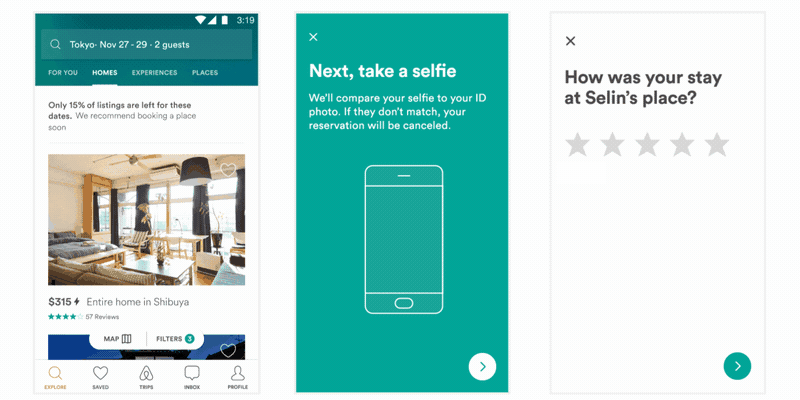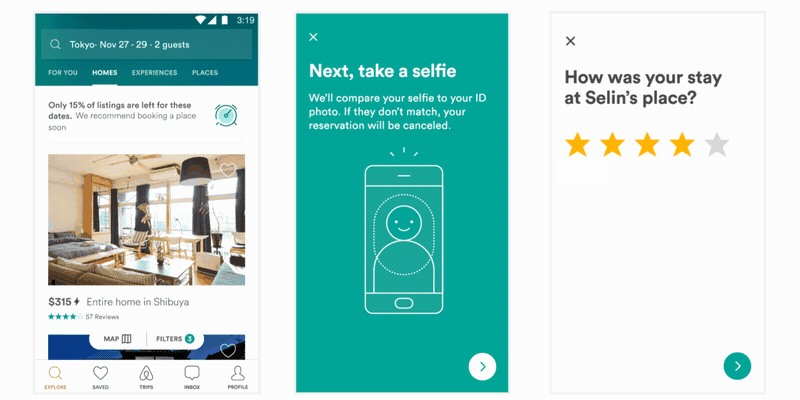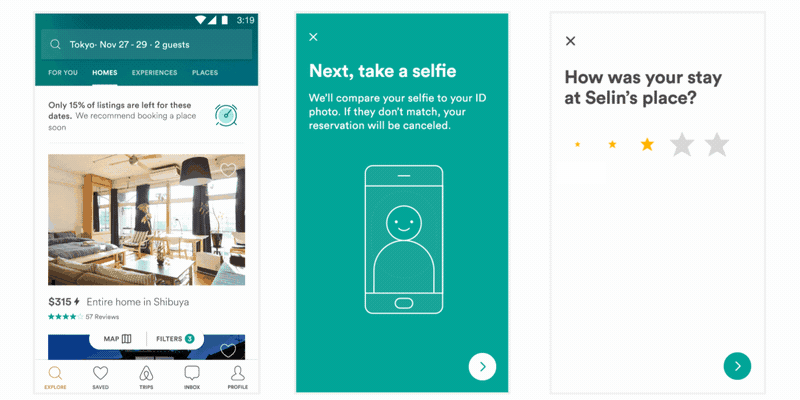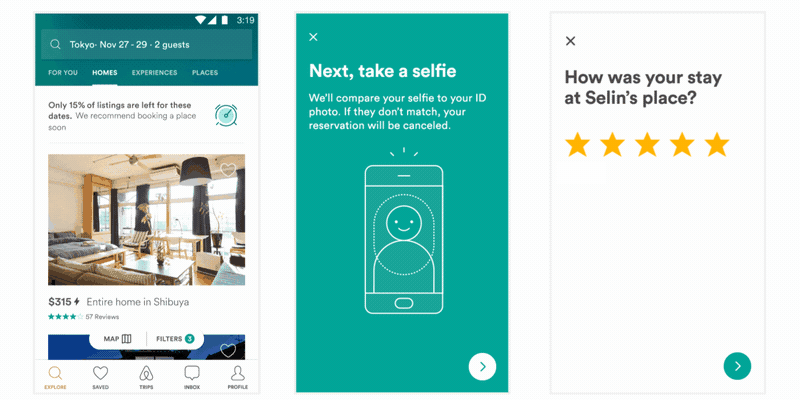

是不是一脸懵逼,如果不懵逼是不是感觉压力山大?传统方式实现动画,无非以下几种方式:
- 使用Animation/Animator。这种方式固然可行,但是要么需要添加多张图片,要么需要针对单个控件写一大堆动画,无论是从apk体积方面考虑还是从开发效率上来说都得不偿失势;
- 使用 GIF。同样面临的问题是所占体积较大,而且需要为各种屏幕尺寸、分辨率做适配,并且Android本是不支持GIF直接展示的;
- Android 5.0 Lollipop 之后提供了对 SVG 的支持,通过 VectorDrawable、AnimatedVectorDrawable 的结合可以实现一些稍微复杂的动画,但是同样面临上述问题。
那么有什么方法既可以高效的实现动画,又不需要占用过多空间,还能同时支持多个系统环境呢?Lottie应运而生。
Lottie 是Airbnb开源的动画实现项目,支持Android、iOS、ReactNaitve三大平台,Github原文内容请点击这里。Lottie 的使用前提是需要先通过插件 bodymovin 将 Adobe After Effects (AE)生成的 aep 动画工程文件转换为通用的 json 格式描述文件( bodymovin 插件本身是用于网页上呈现各种AE效果的一个开源库)。Lottie 所做的事情就是实现在不同移动端平台上呈现AE动画的方式,从而达到动画文件的一次绘制、一次转换,随处可用的效果。
本文主要侧重于讲解 Lottie 在Android 中的使用方式及源码实现过程
二. 使用过程
1.添加依赖
现有版本已升级到2.0.0-rc1
dependencies {
compile 'com.airbnb.android:lottie:2.0.0-rc1'
}
2. 使用
Lottie支持ICS (API 14)及以上的系统版本, 最简单的使用方式是直接在布局文件中添加:
<com.airbnb.lottie.LottieAnimationView
android:id="@+id/animation_view"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:lottie_fileName="hello-world.json"
app:lottie_loop="true"
app:lottie_autoPlay="true" />你也可以选择使用 Java 代码的方式进行动画加载,从app/src/main/assets获取json文件:
LottieAnimationView animationView = (LottieAnimationView)
findViewById(R.id.animation_view);
animationView.setAnimation("hello-world.json");
animationView.loop(true);//设置动画是否循环播放,true表示循环播放,false表示只播放一次
animationView.playAnimation();这种方式会在后台进行一次性的异步文件加载和动画渲染工作 。
如果你想重复利用一个动画效果,例如在列表的每个项目中,或者从一个网络请求的返回中解析JSONObject对象,你可以采用如下方式先生成一个Cancellable, 然后进行设置:
LottieAnimationView animationView = (LottieAnimationView) findViewById(R.id.animation_view);
...
Cancellable compositionCancellable = LottieComposition.Factory.fromJson(getResources(), jsonObject,
new OnCompositionLoadedListener() {
@Override public void onCompositionLoaded(LottieComposition composition) {
animationView.setComposition(composition);
animationView.playAnimation();
}
});
// Cancel to stop asynchronous loading of composition
// compositionCancellable.cancel();你可以通过如下方式控制动画或者添加监听:
animationView.addAnimatorUpdateListener(//监听动画进度
new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
// Do something.
}
});
animationView.playAnimation();//开始动画
...
animationView.cancelAnimation();//结束动画
...
animationView.pauseAnimation();//暂停动画
...
animationView.resumeAnimation();//重启动画
...
animationView.setScaleX(0.5f);//设置X轴方向上的缩放比例,0f为不可见,1f原始大小 Ps.原setScale方法在2.0.0版本后已弃用
animationView.setScaleY(0.5f);//设置Y轴方向上的缩放比例
...
if (animationView.isAnimating()) {//动画正在进行中
// Do something.
}
...
animationView.setProgress(0.5f);//手动设置动画进度
...
// Custom animation speed or duration.
ValueAnimator animator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0f, 1f)//自定义一个属性动画
.setDuration(500);
animator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
animationView.setProgress(animation.getAnimatedValue());
}
});
animator.start();
...你可以给整个动画、一个特定的图层或者一个图层的特定内容添加一个颜色过滤器:
// 任何符合颜色过滤界面的类
final PorterDuffColorFilter colorFilter = new PorterDuffColorFilter(Color.RED, PorterDuff.Mode.LIGHTEN);
// 在整个视图中添加一个颜色过滤器
animationView.addColorFilter(colorFilter);
//在特定的图层中添加一个颜色滤镜
animationView.addColorFilterToLayer("hello_layer", colorFilter);
// 添加一个彩色过滤器特效“hello_layer”上的内容
animationView.addColorFilterToContent("hello_layer", "hello", colorFilter);
// 清除所有的颜色滤镜
animationView.clearColorFilters();你也可以在布局文件中为动画控件添加一个颜色过滤器:
<com.airbnb.lottie.LottieAnimationView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:lottie_fileName="hello-world.json"
app:lottie_colorFilter="@color/blue" />注意:颜色过滤器只适用于图层,如图像层和实体层,以及包含填充、描边或组内容的内容。
在内部, LottieAnimationView 使用 LottieDrawable 作为其代理的方式呈现其动画,您甚至可以直接使用 drawable 表单:
LottieDrawable drawable = new LottieDrawable();
LottieComposition.Factory.fromAssetFileName(getContext(), "hello-world.json",
new OnCompositionLoadedListener() {
@Override public void onCompositionLoaded(LottieComposition composition) {
drawable.setComposition(composition);
}
});如果你的动画会经常重用,LottieAnimationView内置了一个可选的缓存策略。使用LottieAnimationView .setAnimation(String,CacheStrategy)。CacheStrategy可以为Strong, Weak, 或者None。LottieAnimationView对加载和解析的动画持有强引用或弱引用,弱或强表示缓存中组合的回收对象的优先级。
三. Image 支持
如果你的动画是从assets中加载的,并且你的图像文件位于assets 的子目录中,那么你可以对图像进行动画处理。你可以使用 LottieAnimationView 或者 LottieDrawable 对象调用 setImageAssetsFolder(String) 方法读取assets目录中的文件,确保图像 bodymovin 生成的图像文件所保存的文件夹以 img_ 开头。如果直接使用 LottieDrawable, 当你完成时您必须调用 recycleBitmaps方法。
如果你需要提供你自己的位图,如果你从网络或其他地方下载,你可以提供一个委托来做这个工作:
animationView.setImageAssetDelegate(new ImageAssetDelegate() {
@Override public Bitmap fetchBitmap(LottieImageAsset asset) {
getBitmap(asset);
}
});
四. 实现原理
Lottie使用json文件来作为动画数据源,json文件是通过 AE 插件 Bodymovin 导出的,查看sample中给出的json文件,其实就是把图片中的元素进行来拆分,并且描述每个元素的动画执行路径和执行时间。Lottie的功能就是读取这些数据,然后绘制到屏幕上。
现在思考如果我们拿到一份json格式动画如何展示到屏幕上:首先要解析json,建立数据到对象的映射(LottieComposition),然后根据数据对象创建合适的 Drawable (LottieDrawable)并绘制到 View (LottieAnimationView)上,动画的实现可以通过操作读取到的元素完成,如下图所示:

1. json文件到对象的映射
在分析映射过程之前,我们先来看看由 Bodymovin导出的 json 文件的格式:
{
"assets": [
],
"layers": [
{
"ddd": 0,
"ind": 0,
"ty": 1,
"nm": "MASTER",
"ks": {
"o": {
"k": 0
},
"r": {
"k": 0
},
"p": {
"k": [
164.457,
140.822,
0
]
},
"a": {
"k": [
60,
60,
0
]
},
"s": {
"k": [
100,
100,
100
]
}
},
"ao": 0,
"sw": 120,
"sh": 120,
"sc": "#ffffff",
"ip": 12,
"op": 179,
"st": 0,
"bm": 0,
"sr": 1
},
……
],
"v": "4.4.26",
"ddd": 0,
"ip": 0,
"op": 179,
"fr": 30,
"w": 325,
"h": 202
}层级非常丰富,除了包含动画宽、高、帧率等基本属性外,还包含了重要的的图层信息layers,以及包含其他动画信息的递归子集assets。
然后我们在来观察 LottieComposition 这个类的结构:

可以看到startFrame、endFrame、duration、scale等都是动画中常见的属性,Factory是静态内部类(后文会进行分析),剩余的几个属性就值得玩味了:
- precomps:存储assets递归子集的 Layer 类型属性的HashMap集合;
- images:存储assets递归子集中的 LottieImageAsset 类型属性的HashMap集合;
- layerMap:存储外层layers中的Layer类型属性的LongSparseArray集合。
我们再看静态内部类 Factory ,首先从命名上我们可以看到他有如下几个入口:

经过梳理发现这几个函数的调用关系如下:

也就是入口函数实际只有这三个:
- fromAssetFileName(Context context, String fileName, OnCompositionLoadedListener loadedListener);
- fromFileSync(Context context, String fileName);
- fromJson(Resources res, JSONObject json, OnCompositionLoadedListener loadedListener)。
正是通过这三个入口接收json文件、json流,然后通过AsynTask进行异步处理,最终核心处理都是在 fromJsonSync 中进行json数据的解析。
再来看fromJsonSync函数中的处理过程:
首先获取动画区域的宽高:
...
int width = json.optInt("w", -1);
int height = json.optInt("h", -1);
...然后根据缩放比例换算实际所需要的宽高:
...
int scaledWidth = (int) (width * scale);
int scaledHeight = (int) (height * scale);
...再根据实际宽高得到一块矩形区域
...
bounds = new Rect(0, 0, scaledWidth, scaledHeight);
...然后获取动画的初始帧,结束帧和帧率,并初始化 LottieComposition对象:
...
long startFrame = json.optLong("ip", 0);
long endFrame = json.optLong("op", 0);
int frameRate = json.optInt("fr", 0);
LottieComposition composition =
new LottieComposition(bounds, startFrame, endFrame, frameRate, scale);
...最后去解析assets 层级中的 LottieImageAsset属性并存储在images属性中,解析assets层级中的Layer属性并存储在precomps属性中,解析外层的Layer属性并存储在layers属性中,返回 LottieComposition 对象:
...
JSONArray assetsJson = json.optJSONArray("assets");
parseImages(assetsJson, composition);
parsePrecomps(assetsJson, composition);
parseLayers(json, composition);
return composition;
...
2. 根据对象创建drawable并绘制到View上
当LottieCompostion 返回后,会回调 LottieAnimationView.setComposition 方法。LottieAnimationView则通过代理属性--一个LottieDrawable对象,调用其内部的 setComposition 方法:
...
boolean isNewComposition = lottieDrawable.setComposition(composition);
if (!isNewComposition) {
// We can avoid re-setting the drawable, and invalidating the view, since the composition
// hasn't changed.
return;
}
...我们看到 LottieDrawable 中的 setComposition 方法:
/**
* @return True if the composition is different from the previously set composition, false otherwise.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess") public boolean setComposition(LottieComposition composition) {
if (getCallback() == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"You or your view must set a Drawable.Callback before setting the composition. This " +
"gets done automatically when added to an ImageView. " +
"Either call ImageView.setImageDrawable() before setComposition() or call " +
"setCallback(yourView.getCallback()) first.");
}
if (this.composition == composition) {
return false;
}
clearComposition();
this.composition = composition;
setSpeed(speed);
setScale(1f);
updateBounds();
buildCompositionLayer();
applyColorFilters();
setProgress(progress);
if (playAnimationWhenCompositionAdded) {
playAnimationWhenCompositionAdded = false;
playAnimation();
}
if (reverseAnimationWhenCompositionAdded) {
reverseAnimationWhenCompositionAdded = false;
reverseAnimation();
}
return true;
}可以看到 LottieDraw 先清理了旧的 compositionLayer 对象,重新建立了对 compostion 对象的引用,设置了 speed、setScale 等属性,然后通过 buildCompositionLayer 方法重新创建 compostionLayer 对象。
看一看 buildCompositionLayer 方法做了什么:
private void buildCompositionLayer() {
compositionLayer = new CompositionLayer(
this, Layer.Factory.newInstance(composition), composition.getLayers(), composition);
}通过 compostion 创建了一个 Layer 对象,并将自身、 compostion 对象中的 layers 属性及 composition 对象作为参数初始化了一个 CompositionLayer 对象:
CompositionLayer(LottieDrawable lottieDrawable, Layer layerModel, List<Layer> layerModels,
LottieComposition composition) {
super(lottieDrawable, layerModel);
LongSparseArray<BaseLayer> layerMap =
new LongSparseArray<>(composition.getLayers().size());
BaseLayer mattedLayer = null;
for (int i = layerModels.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
Layer lm = layerModels.get(i);
BaseLayer layer = BaseLayer.forModel(lm, lottieDrawable, composition);
if (layer == null) {
continue;
}
layerMap.put(layer.getLayerModel().getId(), layer);
if (mattedLayer != null) {
mattedLayer.setMatteLayer(layer);
mattedLayer = null;
} else {
layers.add(0, layer);
switch (lm.getMatteType()) {
case Add:
case Invert:
mattedLayer = layer;
break;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < layerMap.size(); i++) {
long key = layerMap.keyAt(i);
BaseLayer layerView = layerMap.get(key);
BaseLayer parentLayer = layerMap.get(layerView.getLayerModel().getParentId());
if (parentLayer != null) {
layerView.setParentLayer(parentLayer);
}
}
}大致就是将lottieDrawable、Layer传递给了Parent class, 并将外部 layer 都转换为 BaseLayer 并存储到了一个LongSparseArray中,并为所有BaseLayer设置了他的父亲 BaseLayer属性。
然而 CompositionLayer 又继承于 BaseLayer, 我们来看看它的 draw 方法:
@Override
public void draw(Canvas canvas, Matrix parentMatrix, int parentAlpha) {
if (!visible) {
return;
}
buildParentLayerListIfNeeded();
matrix.reset();
matrix.set(parentMatrix);
for (int i = parentLayers.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
matrix.preConcat(parentLayers.get(i).transform.getMatrix());
}
int alpha = (int)
((parentAlpha / 255f * (float) transform.getOpacity().getValue() / 100f) * 255);
if (!hasMatteOnThisLayer() && !hasMasksOnThisLayer()) {
matrix.preConcat(transform.getMatrix());
drawLayer(canvas, matrix, alpha);
return;
}
rect.set(0, 0, 0, 0);
getBounds(rect, matrix);
intersectBoundsWithMatte(rect, matrix);
matrix.preConcat(transform.getMatrix());
intersectBoundsWithMask(rect, matrix);
rect.set(0, 0, canvas.getWidth(), canvas.getHeight());
canvas.saveLayer(rect, contentPaint, Canvas.ALL_SAVE_FLAG);
// Clear the off screen buffer. This is necessary for some phones.
clearCanvas(canvas);
drawLayer(canvas, matrix, alpha);
if (hasMasksOnThisLayer()) {
applyMasks(canvas, matrix);
}
if (hasMatteOnThisLayer()) {
canvas.saveLayer(rect, mattePaint, SAVE_FLAGS);
clearCanvas(canvas);
//noinspection ConstantConditions
matteLayer.draw(canvas, parentMatrix, alpha);
canvas.restore();
}
canvas.restore();
}可以看到 BaseLayer 先绘制了最底层的内容,然后开始绘制包含的 layers 的内容,这个过程类似与界面中的 ViewGroup 嵌套绘制,其中需要用到 drawLayer 来进行layers的绘制,那我们再回到 CompostionLayer中的 drawLayer方法:
@Override void drawLayer(Canvas canvas, Matrix parentMatrix, int parentAlpha) {
canvas.getClipBounds(originalClipRect);
newClipRect.set(0, 0, layerModel.getPreCompWidth(), layerModel.getPreCompHeight());
parentMatrix.mapRect(newClipRect);
for (int i = layers.size() - 1; i >= 0 ; i--) {
boolean nonEmptyClip = true;
if (!newClipRect.isEmpty()) {
nonEmptyClip = canvas.clipRect(newClipRect);
}
if (nonEmptyClip) {
layers.get(i).draw(canvas, parentMatrix, parentAlpha);
}
}
if (!originalClipRect.isEmpty()) {
canvas.clipRect(originalClipRect, Region.Op.REPLACE);
}
}至此,LottieAnimationView的绘制流程结束。























