
通常大家做出来的图表,绝大部分都是静态的,有时会显得不够吸引人。
今天就给大家介绍一下,如何用Python绘制动态图表。
主要是使用到Matplotlib+imageio,其中Matplotlib就有一个Animation类,可以生成动图GIF,不过使用起来学习成本较高,还是有一定难度的。

这里我将先创建静态图表的图片,然后使用Imageio创建一个GIF(动态图表)。
一共给大家介绍三种动态图表的绘制,折线图,条形图,散点图。
01 折线图
先来绘制一个简单的折线图看看。
import os
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import imageio
# 生成40个取值在30-40的数
y = np.random.randint(30, 40, size=(40))
# 绘制折线
plt.plot(y)
# 设置y轴最小值和最大值
plt.ylim(20, 50)
# 显示
plt.show()
使用Numpy创建一个数值范围在30到40之间的随机整数列表,结果如下。

下面将对整数列表进行切片,生成不同阶段的图表。
# 第一张图
plt.plot(y[:-3])
plt.ylim(20, 50)
plt.savefig('1.png')
plt.show()
# 第二张图
plt.plot(y[:-2])
plt.ylim(20, 50)
plt.savefig('2.png')
plt.show()
# 第三张图
plt.plot(y[:-1])
plt.ylim(20, 50)
plt.savefig('3.png')
plt.show()
# 第四张图
plt.plot(y)
plt.ylim(20, 50)
plt.savefig('4.png')
plt.show()
得到x轴为0:36、0:37、0:38、0:39四个折线图表。

有了这四张图,我们就可以使用Imageio生成GIF了。
# 生成Gif
with imageio.get_writer('mygif.gif', mode='I') as writer:
for filename in ['1.png', '2.png', '3.png', '4.png']:
image = imageio.imread(filename)
writer.append_data(image)
动图来了。

一个会动的折线图表就制作出来了,不过不是从x轴坐标为0的时候开始的。
filenames = []
num = 0
for i in y:
num += 1
# 绘制40张折线图
plt.plot(y[:num])
plt.ylim(20, 50)
# 保存图片文件
filename = f'{num}.png'
filenames.append(filename)
plt.savefig(filename)
plt.close()
# 生成gif
with imageio.get_writer('mygif.gif', mode='I') as writer:
for filename in filenames:
image = imageio.imread(filename)
writer.append_data(image)
# 删除40张折线图
for filename in set(filenames):
os.remove(filename)
绘制出40张折线图,并且保存图片,生成GIF。

可以看到折线图的x坐标从0一直到了40。
02 条形图
上面的折线图每次只有一个y值即可,而条形图则需要所有的y值,如此所有的条形才能同时移动。
给X轴创建固定值,Y轴创建列表,并使用Matplotlib的条形图函数。
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
coordinates_lists = [[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[10, 30, 60, 30, 10],
[70, 40, 20, 40, 70],
[10, 20, 30, 40, 50],
[50, 40, 30, 20, 10],
[75, 0, 75, 0, 75],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
filenames = []
for index, y in enumerate(coordinates_lists):
# 条形图
plt.bar(x, y)
plt.ylim(0, 80)
# 保存图片文件
filename = f'{index}.png'
filenames.append(filename)
# 重复最后一张图形15帧(数值都为0),15张图片
if (index == len(coordinates_lists) - 1):
for i in range(15):
filenames.append(filename)
# 保存
plt.savefig(filename)
plt.close()
# 生成gif
with imageio.get_writer('mygif.gif', mode='I') as writer:
for filename in filenames:
image = imageio.imread(filename)
writer.append_data(image)
# 删除20张柱状图
for filename in set(filenames):
os.remove(filename)
有数值的条形图图片是5张,没数值的图片是2+15=17张。

GIF结束段,添加了15帧空白图片。所以在结束的时候会显示一段时间的空白。
可以设置一下条形图当前位置到下个位置的速度,让过渡变得平滑。
将当前位置和下一个位置之间的距离除以过渡帧数。
n_frames = 10
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
coordinates_lists = [[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[10, 30, 60, 30, 10],
[70, 40, 20, 40, 70],
[10, 20, 30, 40, 50],
[50, 40, 30, 20, 10],
[75, 0, 75, 0, 75],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
print('生成图表\n')
filenames = []
for index in np.arange(0, len(coordinates_lists) - 1):
# 获取当前图像及下一图像的y轴坐标值
y = coordinates_lists[index]
y1 = coordinates_lists[index + 1]
# 计算当前图像与下一图像y轴坐标差值
y_path = np.array(y1) - np.array(y)
for i in np.arange(0, n_frames + 1):
# 分配每帧的y轴移动距离
# 逐帧增加y轴的坐标值
y_temp = (y + (y_path / n_frames) * i)
# 绘制条形图
plt.bar(x, y_temp)
plt.ylim(0, 80)
# 保存每一帧的图像
filename = f'images/frame_{index}_{i}.png'
filenames.append(filename)
# 最后一帧重复,画面停留一会
if (i == n_frames):
for i in range(5):
filenames.append(filename)
# 保存图片
plt.savefig(filename)
plt.close()
print('保存图表\n')
# 生成GIF
print('生成GIF\n')
with imageio.get_writer('mybars.gif', mode='I') as writer:
for filename in filenames:
image = imageio.imread(filename)
writer.append_data(image)
print('保存GIF\n')
print('删除图片\n')
# 删除图片
for filename in set(filenames):
os.remove(filename)
print('完成')
看起来是平滑了许多。

好了,接下来我们更改一下图表相关的配置参数,让图表变得好看。
n_frames = 10
bg_color = '#95A4AD'
bar_color = '#283F4E'
gif_name = 'bars'
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
coordinates_lists = [[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[10, 30, 60, 30, 10],
[70, 40, 20, 40, 70],
[10, 20, 30, 40, 50],
[50, 40, 30, 20, 10],
[75, 0, 75, 0, 75],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
print('生成图表\n')
filenames = []
for index in np.arange(0, len(coordinates_lists) - 1):
y = coordinates_lists[index]
y1 = coordinates_lists[index + 1]
y_path = np.array(y1) - np.array(y)
for i in np.arange(0, n_frames + 1):
y_temp = (y + (y_path / n_frames) * i)
# 绘制条形图
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 4))
ax.set_facecolor(bg_color)
plt.bar(x, y_temp, width=0.4, color=bar_color)
plt.ylim(0, 80)
# 移除图表的上边框和右边框
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
# 设置虚线网格线
ax.set_axisbelow(True)
ax.yaxis.grid(color='gray', linestyle='dashed', alpha=0.7)
# 保存每一帧的图像
filename = f'images/frame_{index}_{i}.png'
filenames.append(filename)
# 最后一帧重复,画面停留一会
if (i == n_frames):
for i in range(5):
filenames.append(filename)
# 保存图片
plt.savefig(filename, dpi=96, facecolor=bg_color)
plt.close()
print('保存图表\n')
# 生成GIF
print('生成GIF\n')
with imageio.get_writer(f'{gif_name}.gif', mode='I') as writer:
for filename in filenames:
image = imageio.imread(filename)
writer.append_data(image)
print('保存GIF\n')
print('删除图片\n')
# 删除图片
for filename in set(filenames):
os.remove(filename)
print('完成')
给图表添加了背景色、条形图上色、去除边框、增加网格线等。
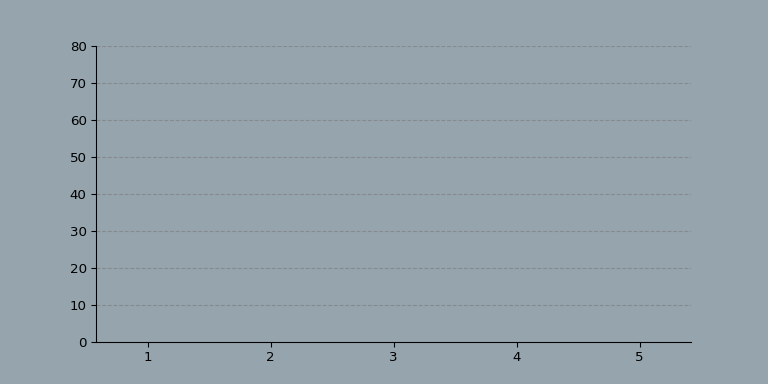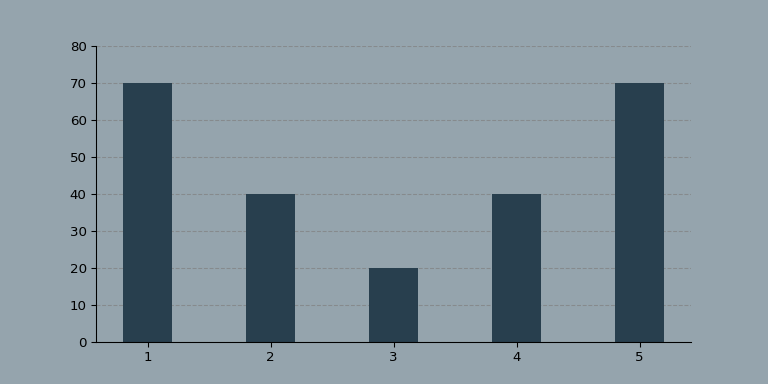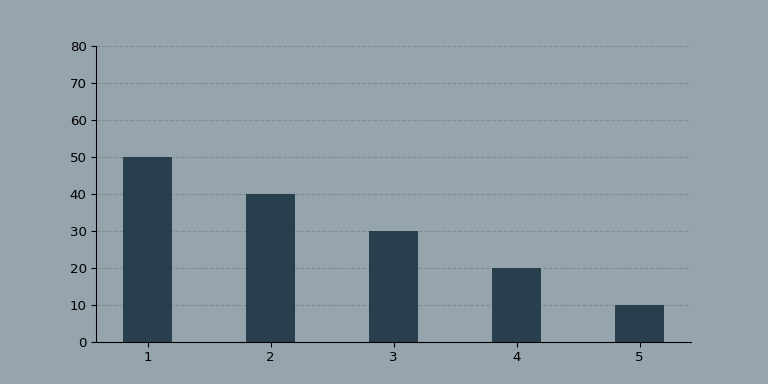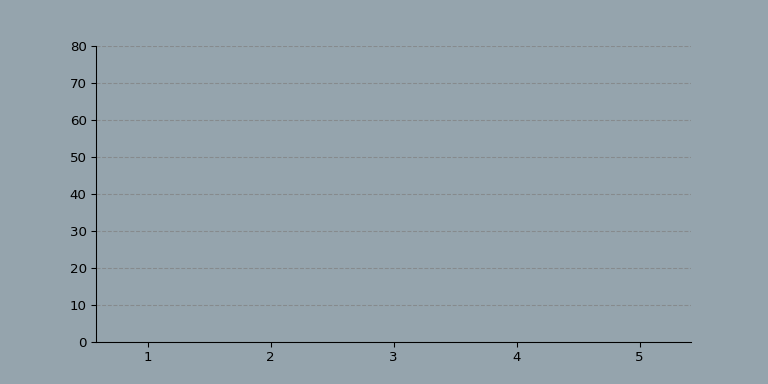
看起来,效果还不错!
当然也有一些值得改进的地方,比如添加标题。通过插值的方式来使过渡变得更平滑,甚至可以让条形图在x轴上移动。
这里大家就可以自行去研究啦。
03 散点图
要绘制动态散点图,则需要同时考虑x轴和y轴的值。
这里不一定要在每帧上显示相同数量的点,因此需要对其进行校正来进行过渡。
coordinates_lists = [[[0], [0]],
[[100, 200, 300], [100, 200, 300]],
[[400, 500, 600], [400, 500, 600]],
[[400, 500, 600, 400, 500, 600], [400, 500, 600, 600, 500, 400]],
[[500], [500]],
[[0], [0]]]
gif_name = 'movie'
n_frames = 10
bg_color = '#95A4AD'
marker_color = '#283F4E'
marker_size = 25
print('生成图表\n')
filenames = []
for index in np.arange(0, len(coordinates_lists) - 1):
# 获取当前图像及下一图像的x与y轴坐标值
x = coordinates_lists[index][0]
y = coordinates_lists[index][1]
x1 = coordinates_lists[index + 1][0]
y1 = coordinates_lists[index + 1][1]
# 查看两点差值
while len(x) < len(x1):
diff = len(x1) - len(x)
x = x + x[:diff]
y = y + y[:diff]
while len(x1) < len(x):
diff = len(x) - len(x1)
x1 = x1 + x1[:diff]
y1 = y1 + y1[:diff]
# 计算路径
x_path = np.array(x1) - np.array(x)
y_path = np.array(y1) - np.array(y)
for i in np.arange(0, n_frames + 1):
# 计算当前位置
x_temp = (x + (x_path / n_frames) * i)
y_temp = (y + (y_path / n_frames) * i)
# 绘制图表
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6), subplot_kw=dict(aspect="equal"))
ax.set_facecolor(bg_color)
plt.scatter(x_temp, y_temp, c=marker_color, s=marker_size)
plt.xlim(0, 1000)
plt.ylim(0, 1000)
# 移除边框线
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
# 网格线
ax.set_axisbelow(True)
ax.yaxis.grid(color='gray', linestyle='dashed', alpha=0.7)
ax.xaxis.grid(color='gray', linestyle='dashed', alpha=0.7)
# 保存图片
filename = f'images/frame_{index}_{i}.png'
filenames.append(filename)
if (i == n_frames):
for i in range(5):
filenames.append(filename)
# 保存
plt.savefig(filename, dpi=96, facecolor=bg_color)
plt.close()
print('保存图表\n')
# 生成GIF
print('生成GIF\n')
with imageio.get_writer(f'{gif_name}.gif', mode='I') as writer:
for filename in filenames:
image = imageio.imread(filename)
writer.append_data(image)
print('保存GIF\n')
print('删除图片\n')
# 删除图片
for filename in set(filenames):
os.remove(filename)
print('完成')
效果如下。

当然还有更有趣的散点图变化,比如字母变化。
使用OpenCV从图像创建mask,绘制填充有随机x/y坐标的图,并过滤mask内的点。
使用Matplotlib绘制散点图,使用ImageIO生成gif。
import os
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import imageio
import random
import cv2
# 根据字母的形状, 将字母转化为多个随机点
def get_masked_data(letter, intensity=2):
# 多个随机点填充字母
random.seed(420)
x = []
y = []
for i in range(intensity):
x = x + random.sample(range(0, 1000), 500)
y = y + random.sample(range(0, 1000), 500)
if letter == ' ':
return x, y
# 获取图片的mask
mask = cv2.imread(f'images/letters/{letter.upper()}.png', 0)
mask = cv2.flip(mask, 0)
# 检测点是否在mask中
result_x = []
result_y = []
for i in range(len(x)):
if (mask[y[i]][x[i]]) == 0:
result_x.append(x[i])
result_y.append(y[i])
# 返回x,y
return result_x, result_y
# 将文字切割成一个个字母
def text_to_data(txt, repeat=True, intensity=2):
print('将文本转换为数据\n')
letters = []
for i in txt.upper():
letters.append(get_masked_data(i, intensity=intensity))
# 如果repeat为1时,重复第一个字母
if repeat:
letters.append(get_masked_data(txt[0], intensity=intensity))
return letters
def build_gif(coordinates_lists, gif_name='movie', n_frames=10, bg_color='#95A4AD',
marker_color='#283F4E', marker_size=25):
print('生成图表\n')
filenames = []
for index in np.arange(0, len(coordinates_lists) - 1):
# 获取当前图像及下一图像的x与y轴坐标值
x = coordinates_lists[index][0]
y = coordinates_lists[index][1]
x1 = coordinates_lists[index + 1][0]
y1 = coordinates_lists[index + 1][1]
# 查看两点差值
while len(x) < len(x1):
diff = len(x1) - len(x)
x = x + x[:diff]
y = y + y[:diff]
while len(x1) < len(x):
diff = len(x) - len(x1)
x1 = x1 + x1[:diff]
y1 = y1 + y1[:diff]
# 计算路径
x_path = np.array(x1) - np.array(x)
y_path = np.array(y1) - np.array(y)
for i in np.arange(0, n_frames + 1):
# 计算当前位置
x_temp = (x + (x_path / n_frames) * i)
y_temp = (y + (y_path / n_frames) * i)
# 绘制图表
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6), subplot_kw=dict(aspect="equal"))
ax.set_facecolor(bg_color)
plt.xticks([]) # 去掉x轴
plt.yticks([]) # 去掉y轴
plt.axis('off') # 去掉坐标轴
plt.scatter(x_temp, y_temp, c=marker_color, s=marker_size)
plt.xlim(0, 1000)
plt.ylim(0, 1000)
# 移除框线
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
# 网格线
ax.set_axisbelow(True)
ax.yaxis.grid(color='gray', linestyle='dashed', alpha=0.7)
ax.xaxis.grid(color='gray', linestyle='dashed', alpha=0.7)
# 保存图片
filename = f'images/frame_{index}_{i}.png'
if (i == n_frames):
for i in range(5):
filenames.append(filename)
filenames.append(filename)
# 保存
plt.savefig(filename, dpi=96, facecolor=bg_color)
plt.close()
print('保存图表\n')
# 生成GIF
print('生成GIF\n')
with imageio.get_writer(f'{gif_name}.gif', mode='I') as writer:
for filename in filenames:
image = imageio.imread(filename)
writer.append_data(image)
print('保存GIF\n')
print('删除图片\n')
# 删除图片
for filename in set(filenames):
os.remove(filename)
print('完成')
coordinates_lists = text_to_data('Python', repeat=True, intensity=50)
build_gif(coordinates_lists,
gif_name='Python',
n_frames=7,
bg_color='#52A9F0',
marker_color='#000000',
marker_size=0.2)
生成一个Python单词字母的动态散点图。

三个主要的函数。
# 创建一个随机的x/y坐标列表,并使用mask对其进行过滤。
get_masked_data()
# 将文本转化为数据
text_to_data()
# 使用坐标点生成散点图, 保存GIF
build_gif()
这里小F给大家提供了26个字母,大伙可以自行组合。

当然其他图形也是可以的,就是需要自己作图。
图片的大小应为1000x1000像素,mask着色为黑色,背景为白色。
然后将png文件保存在images/letters文件夹中,单独一个字符命名。
coordinates_lists = text_to_data('mac_', repeat=True, intensity=50)
build_gif(coordinates_lists,
gif_name='mac',
n_frames=7,
bg_color='#F5B63F',
marker_color='#000000',
marker_size=0.2)结果如下,最后一张是个人物像。

好了,本期的分享就到此结束了。





















