1、添加依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.session</groupId> <artifactId>spring-session-data-redis</artifactId> <version>1.2.1.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> <version>2.8.1</version> </dependency>
2、配置
spring-mvc.xml:
<bean id="redisHttpSessionConfiguration"
class="org.springframework.session.data.redis.config.annotation.web.http.RedisHttpSessionConfiguration">
<property name="maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds" value="600"/>
</bean>
<bean id="jedisPoolConfig" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig">
<property name="maxTotal" value="100" />
<property name="maxIdle" value="10" />
</bean>
<bean id="jedisConnectionFactory"
class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory" destroy-method="destroy">
<property name="hostName" value="${redis_hostname}"/>
<property name="port" value="${redis_port}"/>
<property name="password" value="${redis_pwd}" />
<property name="timeout" value="3000"/>
<property name="usePool" value="true"/>
<property name="poolConfig" ref="jedisPoolConfig"/>
</bean>web.xml添加拦截器: 放前面
<filter> <filter-name>springSessionRepositoryFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>springSessionRepositoryFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping>
3、使用spring-session
只要使用标准的servlet api调用session,在底层就会通过Spring Session得到的,并且会存储到Redis或其他你所选择的数据源中。
这里是我写的一个demo:
/**
* @author fengzp
* @date 17/2/23下午3:19
* @email fengzp@gzyitop.com
* @company 广州易站通计算机科技有限公司
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "index")
public class IndexController {
private final Gson gson = new GsonBuilder().setDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmss").create();
@RequestMapping(value = "login")
public String login(HttpServletRequest request, String username){
request.getSession().setAttribute("user", gson.toJson(new User(username,"123456")));
return "login";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "index")
public String index(HttpServletRequest request, Model model){
User user = gson.fromJson(request.getSession().getAttribute("user").toString(), User.class);
model.addAttribute("user", user);
return "index";
}
}index.jsp:
第一个tomcat
<html>
<body>
<h2>Hello World!</h2>
<p>${user.username}</p>
</body>
</html>第二个tomcat
<html>
<body>
<h2>Hello World! i am the second!</h2>
<p>${user.username}</p>
</body>
</html>测试
这里利用上一篇nginx负载配置的两个tomcat来测试。
首先访问 http://192.168.99.100/feng/index/login.htm?username=nginx 来触发生成session。
查看redis,发现session已经保存到redis。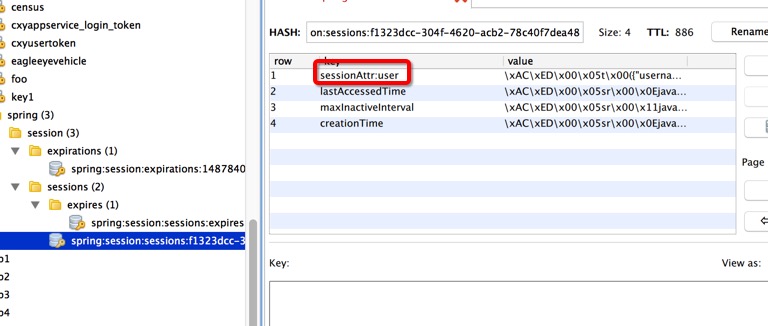
访问 http://192.168.99.100/feng/index/index.htm 来读取session, 并刷新多次。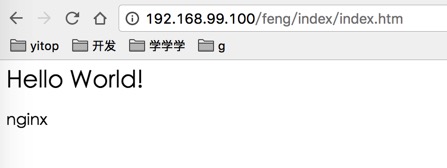

发现在负载的情况下读取session没问题,并且是同一个session,成功实现负载+session共享!
以上是转再:https://www.cnblogs.com/andyfengzp/p/6434287.html
下面是自己实现: 通过nginx负载均衡 分发到两个tomcat上
tomcat1:

tomcat2
redis:






















