1.为什么要使用memcache
由于网站的高并发读写需求,传统的关系型数据库开始出现瓶颈,例如:
1)对数据库的高并发读写:
关系型数据库本身就是个庞然大物,处理过程非常耗时(如解析SQL语句,事务处理等)。如果对关系型数据库进行高并发读写(每秒上万次的访问),那么它是无法承受的。
2)对海量数据的处理:
对于大型的SNS网站,每天有上千万次的数据产生(如twitter, 新浪微博)。对于关系型数据库,如果在一个有上亿条数据的数据表种查找某条记录,效率将非常低。
使用memcache能很好的解决以上问题。
在实际使用中,通常把数据库查询的结果保存到Memcache中,下次访问时直接从memcache中读取,而不再进行数据库查询操作,这样就在很大程度上减少了数据库的负担。
保存在memcache中的对象实际放置在内存中,这也是memcache如此高效的原因。

2.memcache的安装和使用
这个网上有太多教程了,不做赘言。
3.基于libevent的事件处理
libevent是个程序库,它将Linux的
epoll、BSD类操作系统的kqueue等事件处理功能 封装成统一的接口。即使对服务器的连接数增加,也能发挥O(1)的性能。
memcached使用这个libevent库,因此能在Linux、BSD、Solaris等操作系统上发挥其高性能。
参考:
- libevent: http://www.monkey.org/~provos/libevent/
- The C10K Problem: http://www.kegel.com/c10k.html
4.memcache使用实例:
[php] view plain copy
- <?php
- $mc = new
- $mc->connect('127.0.0.1', 11211);
- $uid = (int)$_GET['uid'];
- $sql = "select * from users where uid='uid' ";
- $key = md5($sql);
- if(!($data = $mc->get($key))) {
- $conn = mysql_connect('localhost', 'test', 'test');
- 'test');
- $result = mysql_fetch_object($result);
- while($row = mysql_fetch_object($result)) {
- $data[] = $row;
- }
- $mc->add($key, $datas);
- }
- var_dump($datas);
- ?>
5.memcache如何支持高并发(此处还需深入研究)
memcache使用多路复用I/O模型,如(epoll, select等),传统I/O中,系统可能会因为某个用户连接还没做好I/O准备而一直等待,知道这个连接做好I/O准备。这时如果有其他用户连接到服务器,很可能会因为系统阻塞而得不到响应。
而多路复用I/O是一种消息通知模式,用户连接做好I/O准备后,系统会通知我们这个连接可以进行I/O操作,这样就不会阻塞在某个用户连接。因此,memcache才能支持高并发。
此外,memcache使用了多线程机制。可以同时处理多个请求。线程数一般设置为CPU核数,这研报告效率最高。
6.使用Slab分配算法保存数据
slab分配算法的原理是:把固定大小(1MB)的内存分为n小块,如下图所示:
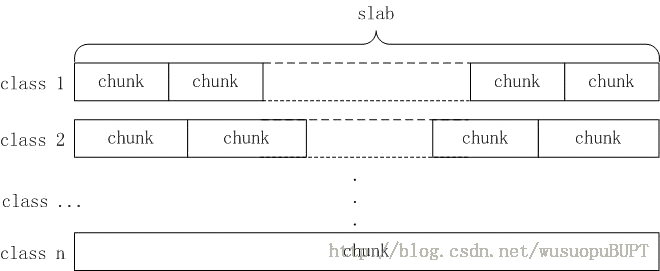
slab分配算法把每1MB大小的内存称为一个slab页,每次向系统申请一个slab页,然后再通过分隔算法把这个slab页分割成若干个小块的chunk(如上图所示),然后把这些chunk分配给用户使用,分割算法如下(在slabs.c文件中):
(注:memcache的github项目地址:https://github.com/wusuopubupt/memcached)
[cpp] view plain copy
- /**
- * Determines the chunk sizes and initializes the slab class descriptors
- * accordingly.
- */
- void slabs_init(const size_t limit, const double factor, const bool
- int
- int size = sizeof(item) + settings.chunk_size;
- mem_limit = limit;
- if
- /* Allocate everything in a big chunk with malloc 通过malloc的方式申请内存*/
- mem_base = malloc(mem_limit);
- if
- mem_current = mem_base;
- mem_avail = mem_limit;
- else
- "Warning: Failed to allocate requested memory in"
- " one large chunk.\nWill allocate in smaller chunks\n");
- }
- }
- sizeof(slabclass));
- while
- /* Make sure items are always n-byte aligned 注意这里的字节对齐*/
- if
- size += CHUNK_ALIGN_BYTES - (size % CHUNK_ALIGN_BYTES);
- slabclass[i].size = size;
- slabclass[i].perslab = settings.item_size_max / slabclass[i].size;
- //以1.25为倍数增大chunk
- if
- "slab class %3d: chunk size %9u perslab %7u\n",
- i, slabclass[i].size, slabclass[i].perslab);
- }
- }
- power_largest = i;
- slabclass[power_largest].size = settings.item_size_max;
- slabclass[power_largest].perslab = 1;
- if
- "slab class %3d: chunk size %9u perslab %7u\n",
- i, slabclass[i].size, slabclass[i].perslab);
- }
- /* for the test suite: faking of how much we've already malloc'd */
- {
- char *t_initial_malloc = getenv("T_MEMD_INITIAL_MALLOC");
- if
- size_t)atol(t_initial_malloc);
- }
- }
- if
- slabs_preallocate(power_largest);
- }
- }
上面代码中的slabclass是一个类型为slabclass_t结构的数组,其定义如下:
[cpp] view plain copy
- typedef struct
- int size; /* sizes of items */
- int perslab; /* how many items per slab */
- void **slots; /* list of item ptrs */
- int sl_total; /* size of previous array */
- int sl_curr; /* first free slot */
- void *end_page_ptr; /* pointer to next free item at end of page, or 0 */
- int end_page_free; /* number of items remaining at end of last alloced page */
- int slabs; /* how many slabs were allocated for this class */
- void **slab_list; /* array of slab pointers */
- int list_size; /* size of prev array */
- int killing; /* index+1 of dying slab, or zero if none */
- size_t requested; /* The number of requested bytes */
- } slabclass_t;
借用别人的一张图说明slabclass_t结构:

由分割算法的源代码可知,slab算法按照不同大小的chunk分割slab页,而不同大小的chunk以factor(默认是1.25)倍增大。
使用memcache -u root -vv 命令查看内存分配情况(8字节对齐):

找到大小最合适的chunk分配给请求缓存的数据:
[cpp] view plain copy
- /*
- * Figures out which slab class (chunk size) is required to store an item of
- * a given size.
- *
- * Given object size, return id to use when allocating/freeing memory for object
- * 0 means error: can't store such a large object
- */
- unsigned int slabs_clsid(const size_t
- int res = POWER_SMALLEST;// 初始化为最小的chunk
- if
- return
- while (size > slabclass[res].size) //逐渐增大chunk size,直到找到第一个比申请的size大的chunk
- if (res++ == power_largest) /* won't fit in the biggest slab */
- return
- return
- }
内存分配:
(此处参考:http://slowsnail.com.cn/?p=20)
[cpp] view plain copy
- static void *do_slabs_alloc(const size_t size, unsigned int
- slabclass_t *p;
- void
- item *it = NULL;
- if (id < POWER_SMALLEST || id > power_largest) {//判断id是否会导致slabclass[]数组越界
- MEMCACHED_SLABS_ALLOCATE_FAILED(size, 0);
- return
- }
- //获取slabclass[id]的引用
- //判断slabclass[id]是否有剩余的chunk
- if (! (p->sl_curr != 0 || do_slabs_newslab(id) != 0)) {//如果slabclass[id]中已经没有空余chunk并且试图向系统申请一个“页”(slab)的chunk失败,则返回NULL
- /* We don't have more memory available */
- ret = NULL;
- else if (p->sl_curr != 0) {//slabclass[id]的空闲链表中还有chunk,则直接将其分配出去
- //获取空闲链表的头指针
- //将头结点指向下一个结点(取下头结点)
- if (it->next) it->next->prev = 0;//将新头结点的prev指针置空
- //减少slabclass[id]空闲链表中的chunk计数
- void *)it;//将头结点赋给ret指针
- }
- if (ret) {//请求成功
- //更新slabclass[id]所分配的内存总数
- MEMCACHED_SLABS_ALLOCATE(size, id, p->size, ret);
- else
- MEMCACHED_SLABS_ALLOCATE_FAILED(size, id);
- }
- return
- }
do_slabs_allc()函数首先尝试从slot列表(被回收的chunk)中获取可用的chunk,如果有可用的就返回,否则从空闲的chunk列表中获取可用的chunk并返回。
删除过期item:
延迟删除过期item到查找时进行,可以提高memcache的效率,因为不必每时每刻检查过期item,从而提高CPU工作效率
使用LRU(last recently used)算法淘汰数据:
[cpp] view plain copy
- /*
- * try to get one off the right LRU
- * don't necessariuly unlink the tail because it may be locked: refcount>0
- * search up from tail an item with refcount==0 and unlink it; give up after 50
- * tries
- */
- if
- itemstats[id].outofmemory++;
- return
- }
- for
- if (search->refcount == 0) { //refount==0的情况,释放掉
- if
- itemstats[id].evicted++;
- itemstats[id].evicted_time = current_time - search->time;
- STATS_LOCK();
- stats.evictions++;
- STATS_UNLOCK();
- }
- do_item_unlink(search);
- break;
- }
- }
- it = slabs_alloc(ntotal, id);
- if
- itemstats[id].outofmemory++;
- /* Last ditch effort. There is a very rare bug which causes
- * refcount leaks. We've fixed most of them, but it still happens,
- * and it may happen in the future.
- * We can reasonably assume no item can stay locked for more than
- * three hours, so if we find one in the tail which is that old,
- * free it anyway.
- */
- tries = 50;
- for
- if (search->refcount != 0 && search->time + 10800 < current_time) { //最近3小时没有被访问到的情况,释放掉
- itemstats[id].tailrepairs++;
- search->refcount = 0;
- do_item_unlink(search);
- break;
- }
- }
- it = slabs_alloc(ntotal, id);
- if
- return
- }
- }
从item列表的尾部开始遍历,找到refcount==0的chunk,调用do_item_unlink()函数释放掉,另外,search->time+10800<current_time(即最近3小时没有被访问过的item),也释放掉--这就是LRU算法的原理。
附:阿里2014笔试题一道:
某缓存系统采用 LRU淘汰算法,假定缓存容量为4,并且初始为空,那么在顺序访问一下数据项的时候:1,5,1,3,5,2,4,1,2出现缓存直接命中的次数是?,最后缓存中即将准备淘汰的数据项是?
答案:3, 5
解答:
- 1调入内存 1
- 5调入内存 1 5
- 1调入内存 5 1(命中 1,更新次序)
- 3调入内存 5 1 3
- 5调入内存 1 3 5 (命中5)
- 2调入内存 1 3 5 2
- 4调入内存(1最久未使用,淘汰1) 3 5 2 4
- 1调入内存(3最久未使用,淘汰3) 5 2 4 1
- 2调入内存 5 4 1 2(命中2)
因此,直接命中次数是3,最后缓存即将准备淘汰的数据项是5





















