1. 概述
上次讨论了HashMap的结构,原理和实现,本文来对Map家族的另外一个常用集合HashTable进行介绍。HashTable和HashMap两种集合非常相似,经常被各种面试官问到两者的区别。
对于两者的区别,主要有以下几点:
- HashMap是非同步的,没有对读写等操作进行锁保护,所以是线程不安全的,在多线程场景下会出现数据不一致的问题。而HashTable是同步的,所有的读写等操作都进行了锁(
synchronized)保护,在多线程环境下没有安全问题。但是锁保护也是有代价的,会对读写的效率产生较大影响。 - HashMap结构中,是允许保存
null的,Entry.key和Entry.value均可以为null。但是HashTable中是不允许保存null的。 - HashMap的迭代器(
Iterator)是fail-fast迭代器,但是Hashtable的迭代器(enumerator)不是fail-fast的。如果有其它线程对HashMap进行的添加/删除元素,将会抛出ConcurrentModificationException,但迭代器本身的remove方法移除元素则不会抛出异常。这条同样也是Enumeration和Iterator的区别。 - 2. 原理
- HashTable类中,保存实际数据的,依然是
Entry对象。其数据结构与HashMap是相同的。 - HashTable类继承自
Dictionary类,实现了三个接口,分别是Map,Cloneable和java.io.Serializable,如下图所示。
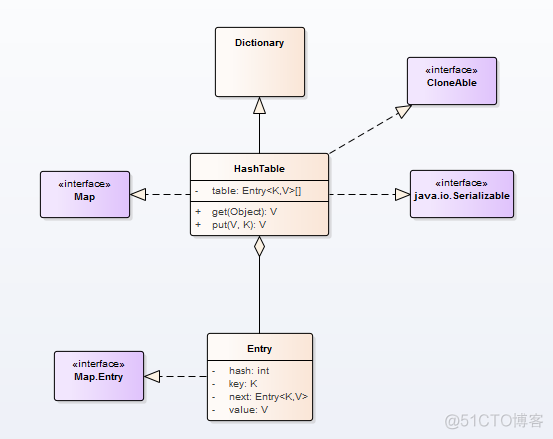
HashTable中的主要方法,如put,get,remove和rehash等,与HashMap中的功能相同,这里不作赘述,可以参考另外一篇文章HashMap原理和底层实现
3. 源码分析
HashTable的主要方法的源码实现逻辑,与HashMap中非常相似,有一点重大区别就是所有的操作都是通过synchronized锁保护的。只有获得了对应的锁,才能进行后续的读写等操作。
1. put方法
put方法的主要逻辑如下:
- 先获取
synchronized锁。 - put方法不允许
null值,如果发现是null,则直接抛出异常。 - 计算
key的哈希值和index - 遍历对应位置的链表,如果发现已经存在相同的hash和key,则更新value,并返回旧值。
- 如果不存在相同的key的Entry节点,则调用
addEntry方法增加节点。 -
addEntry方法中,如果需要则进行扩容,之后添加新节点到链表头部。
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}private void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int index) {
modCount++;
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
if (count >= threshold) {
// Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
rehash();
tab = table;
hash = key.hashCode();
index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
}
// Creates the new entry.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>) tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
}2. get方法
get方法的主要逻辑如下
- 先获取
synchronized锁。 - 计算key的哈希值和index。
- 在对应位置的链表中寻找具有相同hash和key的节点,返回节点的value。
- 如果遍历结束都没有找到节点,则返回
null。
public synchronized V get(Object key) {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return (V)e.value;
}
}
return null;
}3.rehash扩容方法
rehash扩容方法主要逻辑如下:
- 数组长度增加一倍(如果超过上限,则设置成上限值)。
- 更新哈希表的扩容门限值。
- 遍历旧表中的节点,计算在新表中的index,插入到对应位置链表的头部。
protected void rehash() {
int oldCapacity = table.length;
Entry<?,?>[] oldMap = table;
// overflow-conscious code
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {
if (oldCapacity == MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
// Keep running with MAX_ARRAY_SIZE buckets
return;
newCapacity = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
Entry<?,?>[] newMap = new Entry<?,?>[newCapacity];
modCount++;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
table = newMap;
for (int i = oldCapacity ; i-- > 0 ;) {
for (Entry<K,V> old = (Entry<K,V>)oldMap[i] ; old != null ; ) {
Entry<K,V> e = old;
old = old.next;
int index = (e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % newCapacity;
e.next = (Entry<K,V>)newMap[index];
newMap[index] = e;
}
}
}4.remove方法
remove方法主要逻辑如下:
- 先获取synchronized锁。
- 计算key的哈希值和index。
- 遍历对应位置的链表,寻找待删除节点,如果存在,用
e表示待删除节点,pre表示前驱节点。如果不存在,返回null。 - 更新前驱节点的
next,指向e的next。返回待删除节点的value值。
4. 总结
HashTable相对于HashMap的最大特点就是线程安全,所有的操作都是被synchronized锁保护的
作者:道可





















