Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
原文链接 作者:Jakob Jenkov 译者:黄忠 校对:丁一
Java NIO 管道是2个线程之间的单向数据连接。Pipe有一个source通道和一个sink通道。数据会被写到sink通道,从source通道读取。
这里是Pipe原理的图示:
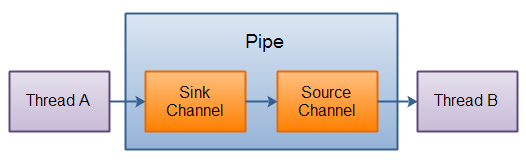
创建管道
通过Pipe.open()方法打开管道。例如:
Pipe pipe = Pipe.open();
向管道写数据
要向管道写数据,需要访问sink通道。像这样:
Pipe.SinkChannel sinkChannel = pipe.sink();
通过调用SinkChannel的write()方法,将数据写入SinkChannel,像这样:
String newData = "New String to write to file..." + System.currentTimeMillis();
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
buf.clear();
buf.put(newData.getBytes());
buf.flip();
while(buf.hasRemaining()) {
sinkChannel.write(buf);
}从管道读取数据
从读取管道的数据,需要访问source通道,像这样:
Pipe.SourceChannel sourceChannel = pipe.source();
调用source通道的read()方法来读取数据,像这样:
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48); int bytesRead = sourceChannel.read(buf);
read()方法返回的int值会告诉我们多少字节被读进了缓冲区。
原创文章,转载请注明: 转载自并发编程网 – ifeve.com
本文链接地址: Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe





















