一:
一.定义:
通俗理解向上转型:
就是子类转型成父类。
classA
{
}
classBextendsA
{
}
A b=new B();这个就是向上转型。
向上转型可以像下面这条语句这么简单:
Shape s =new Circle();
这里,创建一个Circle对象,并把得到的引用立即赋值给S矇,这样做看似错误(将一种类型赋值给别一种类型);但实际上没有问题,因为通过继承,Circle就是一种Shape。因此,编译器认可这条语句,也就不会产生错误信息。
二.注意事项:
(1)向上转型的对象的引用调用的方法是子类的。
(2)但如果调用的方法父类中没有的话则会报错。(意思是只能调用子类中重载父类的方法)
(3)父类的引用可以指向子类的对象,但是子类的引用不能指向父类的对象。
java 转型问题其实并不复杂,只要记住一句话:父类引用指向子类对象。
什么叫父类引用指向子类对象,且听我慢慢道来.
从2个名词开始说起:向上转型(upcasting) 、向下转型(downcasting).
举个例子:有2个类,Father是父类,Son类继承自Father。
Father f1 = new Son(); // 这就叫 upcasting (向上转型)
// 现在f1引用指向一个Son对象
Son s1 = (Son)f1; // 这就叫 downcasting (向下转型)
// 现在f1还是指向Son对象
第2个例子:
Father f2 = new Father();
Son s2 = (Son)f2; // 出错,子类引用不能指向父类对象
你或许会问,第1个例子中:Son s1 = (Son)f1;问什么是正确的呢。
很简单因为f1指向一个子类对象,Father f1 = new Son(); 子类s1引用当然可以指向子类对象了。
而f2 被传给了一个Father对象,Father f2 = new Father();子类s1引用不能指向父类对象。
总结:
1。父类引用指向子类对象,而子类引用不能指向父类对象。
2。把子类对象直接赋给父类引用叫upcasting向上转型,向上转型不用强制转换。
如:Father f1 = new Son();
3。把指向子类对象的父类引用赋给子类引用叫向下转型(downcasting),要强制转换。
如:f1 就是一个指向子类对象的父类引用。把f1赋给子类引用s1即 Son s1 = (Son)f1;
其中f1前面的(Son)必须加上,进行强制转换。
现在再进一步变化,在父类和子类中同时定义和赋值同名的成员变量name,并试图输出该变量的值。

1 public class Father {
2
3 protected String name="父亲属性";
4
5 public void method() {
6 System.out.println("父类方法,对象类型:" + this.getClass());
7 }
8 }
9
10 public class Son extends Father {
11 protected String name="儿子属性";
12
13 public void method() {
14 System.out.println("子类方法,对象类型:" + this.getClass());
15 }
16
17 public static void main(String[] args) {
18 Father sample = new Son();//向上转型
19 System.out.println("调用的成员:"+sample.name);
20 }
21 }
22
23 public class Father {
24
25 protected String name="父亲属性";
26
27 public void method() {
28 System.out.println("父类方法,对象类型:" + this.getClass());
29 }
30 }
31
32 public class Son extends Father {
33 protected String name="儿子属性";
34
35 public void method() {
36 System.out.println("子类方法,对象类型:" + this.getClass());
37 }
38
39 public static void main(String[] args) {
40 Father sample = new Son();//向上转型
41 System.out.println("调用的成员:"+sample.name);
42 }
43 }
44
45
46
47
48

调用的成员:父亲属性
这个结果表明,子类的对象(由父类的引用handle)调用到的是父类的成员变
现在试图调用子类的成员变量name,该怎么做?最简单的办法是将该成员变量封装成方法getter形式。

1 public class Father {
2 protected String name = "父亲属性";
3 public String getName() {
4 return name;
5 }
6 public void method() {
7 System.out.println("父类方法,对象类型:" + this.getClass());
8 }
9 }
10
11 public class Son extends Father {
12 protected String name="儿子属性";
13
14 public String getName() {
15 return name;
16 }
17
18 public void method() {
19 System.out.println("子类方法,对象类型:" + this.getClass());
20 }
21
22 public static void main(String[] args) {
23 Father sample = new Son();//向上转型
24 System.out.println("调用的成员:"+sample.getName());
25 }
26 }
27
28 public class Father {
29 protected String name = "父亲属性";
30 public String getName() {
31 return name;
32 }
33 public void method() {
34 System.out.println("父类方法,对象类型:" + this.getClass());
35 }
36 }
37
38 public class Son extends Father {
39 protected String name="儿子属性";
40
41 public String getName() {
42 return name;
43 }
44
45 public void method() {
46 System.out.println("子类方法,对象类型:" + this.getClass());
47 }
48
49 public static void main(String[] args) {
50 Father sample = new Son();//向上转型
51 System.out.println("调用的成员:"+sample.getName());
52 }
53 }
54
55
56
57

结果4:
调用的成员:儿子属性
三.向上转型的作用:
在父类有多个子类时,利用向上转型减少重复代码量。
二:搜啦个容易理解的例子
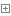
class Chinese
class
Guangdongren
extends
Chinese
{
public static void print(){
System.out.println("this is 广东人 ");
}
}
class
HunanRen
extends
Chinese
{
public static void print(){
System.out.println("this is 湖南人 ");
}
}
class
GuangzhouRen
extends
Guangdongren
{
public static void print(){
System.out.println("this is 广州人 ");
}
}
public
class
Test
{
public static void main(String args[]){
Chinese c=new Chinese();//这样编译可以通过,但运行会抛出异常
HunanRen h=(HunanRen)c;// 这是因为向下转型错误,中国人不一定是湖南人,这里
//是不是可以这样理解要将c强制转换成一个HunanRen
HunanRen h=new HunanRen();//这样就没有问题,这是向上转型,
Chinese c=(Chinese)h; //湖南人一定是中国人这是是否可以理解为将h转换成Cinese
Chinaese h=new HunanRen();//向上转型
h.print();
}
}




















