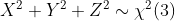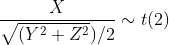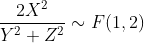接上
参考文档:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/110207817
https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy-1.0.0/reference/generated/scipy.stats.f.html
目录
- t 分布
- F分布
- 例子
一 t 分布
1.1 定义
如果随机变量X,Y条件独立,且
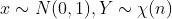
则 随机变量T

服从自由度为n的t 分布,
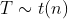
1.2 概率密度
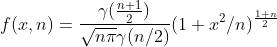
当
;
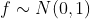
1.3 上

分位数 给定

,

如果
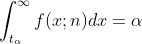
则
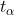
称为上

分位数

python里面的给出的分位数如下
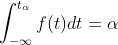
,跟书上定义的不一样,但是是对称的
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Thu Mar 18 17:17:59 2021
@author: chengxf2
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.stats import t
#Percent point function (inverse of cdf) at q of the given RV.累积分布函数的反函数。
#q=0.01时,ppf就是p(X<x)=0.01时的x值。
#因为对称关系
def DrawAlaph():
alpha_list = [0.95,0.05]
print("\n ===enter=======")
for alpha in alpha_list:
t_alpha = -t.ppf(alpha,100)
print("\n 上alaph 分位数: ",t_alpha)
#上alpha 分位数
DrawAlaph()
==========================
===enter=======
上alaph 分位数: -1.66023432607
上alaph 分位数: 1.66023432607 通过图形的对称性可以看到

1.4 图形

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Thu Mar 18 16:44:20 2021
@author: chengxf2
"""
import numpy as np
from scipy.stats import norm
from scipy.stats import t
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
'''
norm: 标准正太分布
t分布: t 分布
'''
def DrawT():
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
x = np.linspace( -3, 3, 100)
print('比较t-分布与标准正态分布')
plt.plot(x, t.pdf(x,1),color='b', label='n=1')
plt.plot(x, t.pdf(x,2),color='g', label='n=2')
plt.plot(x, t.pdf(x,100), color='r',linewidth=5,label = 'n=100')
#r颜色 v 正太分布的图标
plt.plot( x[::5], norm.pdf(x[::5]),'rv', label='normal')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
DrawT()二 F 分布

2.1 定义
假设
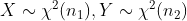
,X,Y独立 则
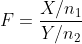
, 服从自由度为(
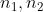
)的F 分布
性质
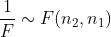
2.2 概率密度

B 由伽玛函数组成,是常数
2.3 上

分位数 假设
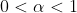
,
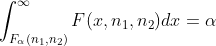
则
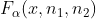
称为上

分位数 性质:
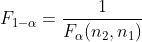
证明:
记住分位数是一个常数
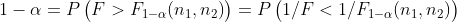
...1
由2.1性质

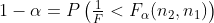
....2
比较1,2得到

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Fri Mar 19 10:42:00 2021
@author: chengxf2
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.stats import f
#rvs:随机变量
#pdf:概率密度函数
#cdf:累积分布函数 cdf(x, dfn, dfd, loc=0, scale=1)
#sf:(1-CDF)sf(x, dfn, dfd, loc=0, scale=1)
#ppf:下分位数(CDF的逆 ppf(q, loc=0, scale=1) 百分比点函数(的倒数cdf—百分位数)。
#isf:Inverse survival functionisf(q, dfn, dfd, loc=0, scale=1)
#moment(n, dfn, dfd, loc=0, scale=1) Non-central moment of order n
#stats(dfn, dfd, loc=0, scale=1, moments='mv') Mean(‘m’), variance(‘v’), skew(‘s’), and/or kurtosis(‘k’).
#统计信息:返回均值,方差,(费舍尔)偏度或(费舍尔)峰度
'''
rvs(n1,n2,loc=0,scale=1) #产生随机变量
pdf(x,n1,n2,loc=0, scale=1) #概率密度函数
cdf(x,n1,n2, loc=0,scale=1) #分布函数
sf(x,n1,n2,loc=0,scale=1) #1-cdf ,可以求出alpah值
moments :[可选]由字母['mvsk']组成;
“ m” =均值
“ v” =方差,
“ s” = Fisher的偏度,
“ k” = Fisher的峰度。 (默认=“ MV”)。
'''
def Examples():
print("\n enter===> ")
n1,n2 = 5,10
fig ,ax = plt.subplots(1,1)
#均值,方差等参数
mean, var ,skew,kurt = f.stats(n1,n2,moments='mvsk')
#print("\n ----------- ",mean, var,skew, kurt)
QuantileL= f.ppf(0.01, n1,n2)
QuantileH = f.ppf(0.99,n1,n2)
# print("\n QuantileL ",QuantileL, "\t QuantileH ",QuantileH)
# 在上下分位数之间产生一百数
x = np.linspace(QuantileL,QuantileH,100 )
y = f.pdf(x,n1,n2) #这个是概率密度函数,非分布函数
#颜色,rgbw #00800
#风格符号: - -- -. :
#标识符 。 , 0,v^ > <
#markersize 标记尺寸
#markerfacecolor 标记颜色
#marker 标记风格
ax.plot(x,y,color='r',linewidth=5, alpha=0.6, label='n1=5;n2=10')
#加上图例
plt.legend()
plt.title("F_distribution")
#plt.show()
#print("\n x : ",x)
'''
根据分布表检查该函数
'''
def Check(n1,n2,alpha):
#第一个参数为概率值,后面两个为自由度
ppf = f.ppf(alpha,n1,n2) #求下分位数
print("\n 下分位数值: ",ppf)
cf = f.cdf(ppf,n1,n2) #累积积分,可以看到算出来的就是alpha 值
print("累积积分:%2.1f"%cf)
#求上alpha 分位点
isf = f.isf(alpha,n1,n2)
#验证性质2.2.3
reciprocal = f.isf(1-alpha,n2,n1)
n= isf*reciprocal
#reciprocal 值
m = f.sf(isf, n1,n2)
print("\n 上分位点 %5.2f"%isf,"\t 概率alpha: ",m,"\t 乘积为1? : ",n)
'''
看拟合程度
args:
n1: 自由度1
n2: 自由度2
'''
def Example2(n1,n2):
fig,ax = plt.subplots(1,1)
n1= 5;n2=10
left= f.ppf(0.01, n1,n2)
right = f.ppf(0.99,n1,n2)
x = np.linspace(left, right,100)
y = f.pdf(x,n1,n2)
ax.plot(x,y,'r-',lw=2, label='r pdf')
rv = f(n1,n2)
y = rv.pdf(x)
ax.plot(x,y,'g-',lw=3,label='frozen pdf')
plt.legend()
'''
检查精度
args:
n1: 自由度1
n2: 自由度2
'''
def CheckAccuracy(n1,n2):
alphaList = np.arange(0.01,0.999,0.1)
quantile = f.ppf(alphaList,n1,n2) #分位数列表
cdf = f.cdf(quantile, n1,n2) #计算分布函数的概率
bSame = np.allclose(alphaList, cdf)
#def allclose(a, b, rtol=1.e-5, atol=1.e-8, equal_nan=False):
print("相同: ",bSame)
def Example4(n1,n2):
fig,ax = plt.subplots(1,1)
#产生符合F分布的随机变量
r = f.rvs(n1,n2,size=1000)
rv =f(n1,n2)
left= f.ppf(0.01, n1,n2)
right = f.ppf(0.99,n1,n2)
x = np.linspace(left, right,100)
y = rv.pdf(x)
ax.plot(x,y,'r-',lw=3,label='frozen pdf')
ax.hist(r,normed=True, histtype='stepfilled', alpha=0.2)
ax.legend(loc='best', frameon=False)
plt.show()
#Examples()
Example4(5,10)2.4 图形

三 例子
如果X,Y,Z 相互独立,都服从N(0,1)分布,则下面公式成立