上篇文章阐述了Fast RCNN网络模型,介于Faster RCNN属于RCNN系列的经典模型,以及是目前项目暂使用的目标检测模型,本篇文章会结合论文以及tensorflow版本的代码实现详细的阐述该模型。【可能篇幅会很长,毕竟经典模型,慎重】
Faster RCNN论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.01497
Faster RCNN论文翻译:https://alvinzhu.xyz/2017/10/12/faster-r-cnn/
一、概述
Faster RCNN(Fast Regions with CNN features)相对于Fast RCNN是一种更快速的目标检测模型。相对于Fast RCNN 66%的mAP,其不仅在缩减训练、测试时长的情况下,也提高了准确度。(主干网络VGG16, mAP70.7%, resnet101 mAP75%)。
【Faster RCNN目标检测模型提出了与RCNN、SPPNet、Fast RCNN(选择搜索算法)不一样的区域提取模式RPN网络模型,该模型优化了Fast RCNN在时间上的性能瓶颈。RPN网络和检测网络共享全图的卷积,并且可以在每个位置同时预测目标边界和objectness得分。】
二、Faster RCNN网络模型

主体结构

网络细节
Faster RCNN物体检测系统由三个模块组成:
- 特征提取网络
- RPN网络
- 区域归一化、物体分类以及边框回归
1、特征提取网络
Faster RCNN提取特征的主干网络可以是VGG16的前13层,13Conv+4次池化。

VGG16
2、RPN网络
RPN(Region Proposal Network) 区域提案网络,较之Fast RCNN单独的Selective Search选择搜索算法提取候选框,将候选框提取融合到整个网络中。
区域提案网络(Region Proposal Network, RPN),它和检测网络共享全图的卷积特征,使得区域提案几乎不花时间。RPN是一个全卷积网络,在每个位置同时预测目标边界和objectness得分。RPN是端到端训练的,生成高质量区域提案框,用于Fast R-CNN来检测。我们通过共享其卷积特征进一步将RPN和Fast R-CNN合并到一个网络中。使用最近流行的神经网络术语“注意力”机制,RPN模块将某块anchor box打分比较高,则后面的网络对其进行训练。
说到RPN网络,则需要提到锚点(anchor)和 边框回归。

【Anchor】
【原理】滑动窗口在特征图上滑动,每经过一个anchor点就会产生3种尺度和3种长宽比K(K = 9)个提案框。每个提案框包含2类信息,一个是该提案框是否包含物体,二是该提案框的坐标编码。每个anchor在cls分类层(softmax二分类)会输出2*K个分类得分(每个anchor box 前景背景得分),在reg回归层(线性回归)会产生4K个输出(每个anchor box都有4个坐标),对于大小为H*W的卷积特征映射,总共会产生W*H*K个anchor boxes。
【属性】使用Anchor提取候选区域具有一些属性:
1、平移不变性,即图片中物体的也会被其它的anchor的anchor box框选到;
2、基于参照多个尺度和纵横比设计的锚点,可以简单地使用单尺度图像上的卷积特征,无需额外的成本来缩放尺寸。
(a) 图像金字塔 (b)卷积金字塔 (d)参考框金字塔(RPN)
【边框回归】
【摘要】RCNN、Fast RCNN、Faster RCNN都需要用到边界框回归来预测物体的目标检测框。边界框回归要做的就是利用某种映射关系,使得候选目标框经过映射后更加接近于真实目标框。
Anchor与预测
Anchro边框、预测边框、真实边框
【原理】
设Anchor的坐标 预测边框G'的坐标 真实边框G的坐标
边框回归就是寻找一种变换
, 使得
A和G'之间的关系:
【平移】:
【缩放】:
边框回归需要【学习】的就是:
【当anchor A与GT相差较小时(在进行线性回归时会筛选anchor和gt IOU在一定范围内的anchor,这也就保证了anchor与GT的相差不会很大),可以认为这种变换时一种线性变换,则可以用线性回归建模。即Y = WX】
【Y = WX 】输入的X是 cnn feature map,定义为
,那么:
【
表示的是Anchor的坐标和预测的贴近真实框的预测的坐标的线性关系,而Anchor的坐标和真实框的坐标的线性关系是怎么样呢,这两个关系又是什么关系呢,是否是学习与被学习的关系。】
根据上面Anchor和预测G’的坐标关系可知Anchor坐标和GT坐标的关系是:
【通过上面的公式,可得知
就是要
拟合
(变成)
】,
,所以整个线性回归其实就是学习一组
优化目标为:
是正则项防止过拟合
Smooth_L1损失函数:
【Propoasl层】
Proposal层输入三个参数,anchor box前景、背景打分,以及anchor box偏移关系和im_Info(原图信息),那该层的作用:
对于所有的anchor boxes,结合输入的偏移关系,进行回归,也就是将偏移叠加到anchor boxes上修正原始anchor boxes,
利用anchor box的打分情况和NMS筛选出一定数目的偏移后的anchor boxes。
【RPN】
RPN主要作用是生成区域提案,里面设计了分类和边框回归。
【分类】:anchor产生的anchor box 通过softmax二分类网络判断该区域提案为前景(包含目标)和背景(不包含)的得分。基于该分类的得分,可以作为筛选过多anchor的手段。
【边框回归】:
,来优化anchor和预测边框(其实在这里预测边框是不存在,是anchor叠加回归输出的偏移)的关系
,边框回归输出的不是坐标而是一种关系,也就是anchor和预测边框之间的偏移情况,在Propoasl层才将回归输出的偏移叠加到anchor坐标上,来修正anchor坐标,这也是对anchor的第一次修正,后面还有第二次修正。
边框回归的偏移关系
,
输入是
特征向量
,所以边框回归要学习的是参数
,
也就是通过不同目标的特征,分别学习针对该目标特征对应的
参数,也就是该参数的维度应该是包含可以检测的所有物体类别数目。
【输出】
RPN网络最终得到训练(256)、测试(300)对应的anchor box的前景、后景得分情况,以及该anchor box的坐标。
3、区域归一化、物体分类以及边框回归
区域归一化、物体分类以及边框回归这里的结构就和Fast RCNN基本一致了,在此就不做阐述了。
三、Faster RCNN代码解析

该图来自:
下面就结合上面的图,针对代码一步一步分析:
代码的主体结构在_build_network函数里。
def _build_network(self, is_training=True):
"""
该函数总体流程:
1、通过分类网络(vgg16、resnet)得到特征net_cov
2、将net_cov送入rpn网络得到候选区域anchors,训练则筛选出2000个anchor,测试则筛选出
300个anchors,在进一步筛选出256个anchors用于分类
3、将256个anchors进行rois_pooling操作得到pool5的7*7的特征图
4、将pool5通过两个fc得到fc7得到21维的cls_score和21*4的bbox_pred
:param is_training:
:return:
"""
# 是否使用截断正态分布
if cfg.TRAIN.TRUNCATED:
initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(mean=0.0, stddev=0.01)
initializer_bbox = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(mean=0.0, stddev=0.001)
else:
initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(mean=0.0, stddev=0.01)
initializer_bbox = tf.random_normal_initializer(mean=0.0, stddev=0.001)
# 分类网络处理生成特征图
net_conv = self._image_to_head(is_training)
with tf.variable_scope(self._scope, self._scope):
# 为特征图创建anchors(特征图是原图/16,anchors的个数是特征图像素数*9,而每个
#anchor是在原图上的坐标,该函数返回anchors的坐标矩阵和anchors数量 )
self._anchor_component()
# RPN网络对特征进行处理,最终得到256(训练)个anchors对应类别以及坐标或者300(测
#试)个anchors对应类别以及坐标
rois = self._region_proposal(net_conv, is_training, initializer)
# roi pooling层将特征向量resize到指定大小
if cfg.POOLING_MODE == 'crop':
pool5 = self._crop_pool_layer(net_conv, rois, "pool5")
else:
raise NotImplementedError
fc7 = self._head_to_tail(pool5, is_training)
with tf.variable_scope(self._scope, self._scope):
# region classification
cls_prob, bbox_pred = self._region_classification(fc7, is_training,
initializer,initializer_bbox)
self._score_summaries.update(self._predictions)
"""
rois: 256个anchors的类别
cls_prob: 256个anchor中每一类别的概率
bbox_pred: 预测位置的偏移
"""
return rois, cls_prob, bbox_predself._image_to_head() 提取输入图片特征
def _image_to_head(self, is_training, reuse=None):
with tf.variable_scope(self._scope, self._scope, reuse=reuse):
net = slim.repeat(self._image, 2, slim.conv2d, 64, [3, 3],
trainable=False, scope='conv1')
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], padding='SAME', scope='pool1')
net = slim.repeat(net, 2, slim.conv2d, 128, [3, 3],
trainable=False, scope='conv2')
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], padding='SAME', scope='pool2')
net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d, 256, [3, 3],
trainable=is_training, scope='conv3')
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], padding='SAME', scope='pool3')
net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d, 512, [3, 3],
trainable=is_training, scope='conv4')
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], padding='SAME', scope='pool4')
net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d, 512, [3, 3],
trainable=is_training, scope='conv5')
self._act_summaries.append(net)
self._layers['head'] = net
return netself._anchor_component()生成anchor boxdef _anchor_component(self):
with tf.variable_scope('ANCHOR_' + self._tag) as scope:
# 获取图片的形状
height = tf.to_int32(tf.ceil(self._im_info[0] /
np.float32(self._feat_stride[0]))) # 特征图的高(原图的1/16)
width = tf.to_int32(tf.ceil(self._im_info[1] /
np.float32(self._feat_stride[0]))) # 特征图的宽(原图的1/16)
# 配置端到端
if cfg.USE_E2E_TF:
anchors, anchor_length = generate_anchors_pre_tf(
height,
width,
self._feat_stride,
self._anchor_scales,
self._anchor_ratios)
else:
anchors, anchor_length = tf.py_func(generate_anchors_pre,
[height, width,
self._feat_stride,
self._anchor_scales,
self._anchor_ratios],
[tf.float32, tf.int32],
name="generate_anchors")
anchors.set_shape([None, 4])
anchor_length.set_shape([])
self._anchors = anchors
self._anchor_length = anchor_length
def generate_anchors_pre_tf(height, width, feat_stride=16, anchor_scales=(8, 16, 32),
anchor_ratios=(0.5, 1, 2)):
shift_x = tf.range(width) * feat_stride # width
shift_y = tf.range(height) * feat_stride # height
shift_x, shift_y = tf.meshgrid(shift_x, shift_y)
sx = tf.reshape(shift_x, shape=(-1,))
sy = tf.reshape(shift_y, shape=(-1,))
shifts = tf.transpose(tf.stack([sx, sy, sx, sy]))
K = tf.multiply(width, height)
shifts = tf.transpose(tf.reshape(shifts, shape=[1, K, 4]), perm=(1, 0, 2))
"生成anchor"
anchors = generate_anchors(ratios=np.array(anchor_ratios),
scales=np.array(anchor_scales))
A = anchors.shape[0]
anchor_constant = tf.constant(anchors.reshape((1, A, 4)), dtype=tf.int32)
length = K * A
anchors_tf = tf.reshape(tf.add(anchor_constant, shifts), shape=(length, 4))
return tf.cast(anchors_tf, dtype=tf.float32), length
def generate_anchors(base_size=16, ratios=[0.5, 1, 2],
scales=2 ** np.arange(3, 6)):
"""
在(0, 0, 15, 15) 的基准窗口上,通过不同尺度、比例变换获得9个anchor boxes.
"""
base_anchor = np.array([1, 1, base_size, base_size]) - 1
ratio_anchors = _ratio_enum(base_anchor, ratios)
anchors = np.vstack([_scale_enum(ratio_anchors[i, :], scales)
for i in range(ratio_anchors.shape[0])])
"""
anchors = array(
[
[ -83., -39., 100., 56.],
[-175., -87., 192., 104.],
[-359., -183., 376., 200.],
[ -55., -55., 72., 72.],
[-119., -119., 136., 136.],
[-247., -247., 264., 264.],
[ -35., -79., 52., 96.],
[ -79., -167., 96., 184.],
[-167., -343., 184., 360.]
])
"""
return anchorsself._region_proposal(net_conv, is_training, initializer)通过RPN网络产生对应数量分类和第一次回归的anchor坐标和得分。def _region_proposal(self, net_conv, is_training, initializer):
"特征提取网络返回的特征再经历个3*3的卷积"
rpn = slim.conv2d(net_conv, cfg.RPN_CHANNELS, [3, 3],
trainable=is_training,
weights_initializer=initializer,
scope="rpn_conv/3x3")
self._act_summaries.append(rpn)
"1*1的卷积"
rpn_cls_score = slim.conv2d(rpn, self._num_anchors * 2, [1, 1],
trainable=is_training,
weights_initializer=initializer,
padding='VALID', activation_fn=None,
scope='rpn_cls_score')
"重新定义符合caffe数据格式的特征向量"
rpn_cls_score_reshape = self._reshape_layer(rpn_cls_score, 2,
'rpn_cls_score_reshape')
"softmax二分类,给前景、后景打分"
rpn_cls_prob_reshape = self._softmax_layer(rpn_cls_score_reshape,
"rpn_cls_prob_reshape")
"得到该anchor的预测(属于前景还是后景)"
rpn_cls_pred = tf.argmax(tf.reshape(rpn_cls_score_reshape, [-1, 2]), axis=1,
name="rpn_cls_pred")
"重新改为原来的数据格式"
rpn_cls_prob = self._reshape_layer(rpn_cls_prob_reshape, self._num_anchors * 2,
"rpn_cls_prob")
"边框偏移预测"
rpn_bbox_pred = slim.conv2d(rpn, self._num_anchors * 4, [1, 1],
trainable=is_training,
weights_initializer=initializer,
padding='VALID', activation_fn=None,
scope='rpn_bbox_pred')
"训练生成256个anchor boxes坐标信息、类别标签"
if is_training:
"""
通过回归预测的偏移,分类的得分和原始坐标,得到2000个修正后的anchor box边框和得分
"""
rois, roi_scores = self._proposal_layer(rpn_cls_prob, rpn_bbox_pred, "rois")
"对比真实框判断图片中对应的修正后的anchor是正样本、负样本、还是不关注"
rpn_labels = self._anchor_target_layer(rpn_cls_score, "anchor")
"训练批次大小是256,该函数产生256个anchor boxes,里面包含坐标信息,类别标签(前后景)"
with tf.control_dependencies([rpn_labels]):
rois, _ = self._proposal_target_layer(rois, roi_scores, "rpn_rois")
"测试生成300个anchor boxes坐标信息、类别标签"
else:
"cfg[TEST].RPN_POST_NMS_TOP_N = 300"
if cfg.TEST.MODE == 'nms':
rois, _ = self._proposal_layer(rpn_cls_prob, rpn_bbox_pred, "rois")
elif cfg.TEST.MODE == 'top':
rois, _ = self._proposal_top_layer(rpn_cls_prob, rpn_bbox_pred, "rois")
else:
raise NotImplementedError
self._predictions["rpn_cls_score"] = rpn_cls_score "anchor前后景的得分情况"
self._predictions["rpn_cls_score_reshape"] = rpn_cls_score_reshape "得分重定义结构"
self._predictions["rpn_cls_prob"] = rpn_cls_prob "分类前后景概率"
self._predictions["rpn_cls_pred"] = rpn_cls_pred "预测为前景或者后景"
self._predictions["rpn_bbox_pred"] = rpn_bbox_pred "预测回归偏移"
self._predictions["rois"] = rois
return roisself._crop_pool_layer(net_conv, rois, "pool5")将特征向量resize到固定大小def _crop_pool_layer(self, bottom, rois, name):
"""
将256个archors从特征图中裁剪出来缩放到14*14,并进一步max pool到7*7的固定大小,方便rcnn网
络分类及回归坐标。
"""
with tf.variable_scope(name) as scope:
"类别"
batch_ids = tf.squeeze(tf.slice(rois, [0, 0], [-1, 1], name="batch_id"), [1])
"获取边界框的标准化坐标"
bottom_shape = tf.shape(bottom)
height = (tf.to_float(bottom_shape[1]) - 1.) * np.float32(self._feat_stride[0])
width = (tf.to_float(bottom_shape[2]) - 1.) * np.float32(self._feat_stride[0])
x1 = tf.slice(rois, [0, 1], [-1, 1], name="x1") / width
y1 = tf.slice(rois, [0, 2], [-1, 1], name="y1") / height
x2 = tf.slice(rois, [0, 3], [-1, 1], name="x2") / width
y2 = tf.slice(rois, [0, 4], [-1, 1], name="y2") / height
bboxes = tf.stop_gradient(tf.concat([y1, x1, y2, x2], axis=1))
pre_pool_size = cfg.POOLING_SIZE * 2
crops = tf.image.crop_and_resize(bottom, bboxes, tf.to_int32(batch_ids),
[pre_pool_size, pre_pool_size],
name="crops")
return slim.max_pool2d(crops, [2, 2], padding='SAME')self._head_to_tail(pool5, is_training)添加fc6、fc7以及防止过拟合的dropoutdef _head_to_tail(self, pool5, is_training, reuse=None):
with tf.variable_scope(self._scope, self._scope, reuse=reuse):
pool5_flat = slim.flatten(pool5, scope='flatten')
fc6 = slim.fully_connected(pool5_flat, 4096, scope='fc6')
if is_training:
fc6 = slim.dropout(fc6, keep_prob=0.5, is_training=True,
scope='dropout6')
fc7 = slim.fully_connected(fc6, 4096, scope='fc7')
if is_training:
fc7 = slim.dropout(fc7, keep_prob=0.5, is_training=True,
scope='dropout7')
return fc7self._region_classification()分类和回归def _region_classification(self, fc7, is_training, initializer, initializer_bbox):
"21类分类得分"
cls_score = slim.fully_connected(fc7, self._num_classes,
weights_initializer=initializer,
trainable=is_training,
activation_fn=None, scope='cls_score')
"类别概率"
cls_prob = self._softmax_layer(cls_score, "cls_prob")
"预测类别"
cls_pred = tf.argmax(cls_score, axis=1, name="cls_pred")
"预测边框偏移,和在rpn网络里面一样都是预测的偏移"
bbox_pred = slim.fully_connected(fc7, self._num_classes * 4,
weights_initializer=initializer_bbox,
trainable=is_training,
activation_fn=None, scope='bbox_pred')
self._predictions["cls_score"] = cls_score
self._predictions["cls_pred"] = cls_pred
self._predictions["cls_prob"] = cls_prob
self._predictions["bbox_pred"] = bbox_pred
return cls_prob, bbox_predself._add_losses()损失函数,该模型的损失包括rpn网络的损失和rcnn网络的损失,在rpn和rcnn中都包含分类损失和回归损失,分类损失用的交叉熵损失,回归损失用的是smooth l1 损失。【边框回归的原理及推导过程在前面有提及】
def _add_losses(self, sigma_rpn=3.0):
with tf.variable_scope('LOSS_' + self._tag) as scope:
"RPN --> class loss 分类损失"
rpn_cls_score = tf.reshape(self._predictions['rpn_cls_score_reshape'], [-1, 2])
rpn_label = tf.reshape(self._anchor_targets['rpn_labels'], [-1])
rpn_select = tf.where(tf.not_equal(rpn_label, -1))
rpn_cls_score = tf.reshape(tf.gather(rpn_cls_score, rpn_select), [-1, 2])
rpn_label = tf.reshape(tf.gather(rpn_label, rpn_select), [-1])
"预测前后景的得分和前后景真正类别交叉熵损失"
rpn_cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=rpn_cls_score,
labels=rpn_label))
"RPN --> bbox loss 回归损失"
rpn_bbox_pred = self._predictions['rpn_bbox_pred']
rpn_bbox_targets = self._anchor_targets['rpn_bbox_targets']
rpn_bbox_inside_weights = self._anchor_targets['rpn_bbox_inside_weights']
rpn_bbox_outside_weights = self._anchor_targets['rpn_bbox_outside_weights']
"预测偏移和anchor与gt真实偏移的smooth l1 损失"
rpn_loss_box = self._smooth_l1_loss(rpn_bbox_pred, rpn_bbox_targets,
rpn_bbox_inside_weights,
rpn_bbox_outside_weights,
sigma=sigma_rpn, dim=[1, 2, 3])
"RCNN --> class loss 分类损失"
cls_score = self._predictions["cls_score"]
label = tf.reshape(self._proposal_targets["labels"], [-1])
"预测目标类别得分和目标真正类别交叉熵损失"
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=cls_score,
labels=label))
"RCNN --> bbox loss 回归损失"
bbox_pred = self._predictions['bbox_pred']
bbox_targets = self._proposal_targets['bbox_targets']
bbox_inside_weights = self._proposal_targets['bbox_inside_weights']
bbox_outside_weights = self._proposal_targets['bbox_outside_weights']
"""
预测偏移和anchor与gt真实偏移的smooth l1 损失(注意两次边框回归都是和anchor和gt真实偏移
进行回归,因为两次都是为了修正anchor使之更接近gt)
"""
loss_box = self._smooth_l1_loss(bbox_pred, bbox_targets, bbox_inside_weights,
bbox_outside_weights)
self._losses['cross_entropy'] = cross_entropy
self._losses['loss_box'] = loss_box
self._losses['rpn_cross_entropy'] = rpn_cross_entropy
self._losses['rpn_loss_box'] = rpn_loss_box
"总损失为四个损失之和"
loss = cross_entropy + loss_box + rpn_cross_entropy + rpn_loss_box
regularization_loss = tf.add_n(tf.losses.get_regularization_losses(), 'regu')
"总损失添加正则项"
self._losses['total_loss'] = loss + regularization_loss
self._event_summaries.update(self._losses)
return loss【上面只是介绍了特征提取、产生anchor、rpn网络、crop_pooling层、添加fc和dropout、分类和回归以及额外添加的loss主体函数,每个主体函数里面还调用许多主体函数的具体实现过程,Faster RCNN的代码量比较大,在此就不在阐述,可以参考源码自己细化理解。也可以参考博客】
四、创新与挑战
1、创新
Faster RCNN就是RPN + Fast RCNN,RPN内部的分类网络可以生成高质量的区域提案框,内部的回归层可以优化、修正区域提案框。
在多任务损失训练添加了RPN网络里面的分类和回归损失。
2、挑战
Faster RCNN一张图片的处理速度还不是很快。
总结:Faster RCNN是RCNN系列的一个阶段性成果,RPN网络的创新,使得区域提案不再是时间性能瓶颈,边框偏移的两次优化提高了整体目标检测的预测性能。




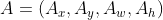
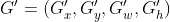
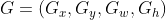
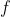
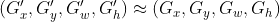
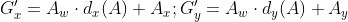
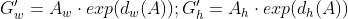
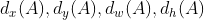
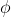
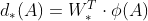
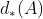
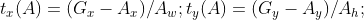
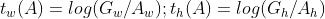
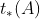
![W_*[W_x,W_y,W_w,W_y] fastrcnn结构框架 faster rcnn介绍_fastrcnn结构框架_24](https://s2.51cto.com/images/blog/202403/19040806_65f89f26f3a0143894.gif)
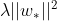
![W_*^[W_x,W_y,W_w,W_h] fastrcnn结构框架 faster rcnn介绍_fastrcnn结构框架_29](https://s2.51cto.com/images/blog/202403/19040811_65f89f2b8928543751.gif)




















