本节教程通过 2048 的小游戏快速、完整地呈现了使用 Python 语言编程的过程,将之前介绍的内容有机地结合在了一起 。2048是一款流行于手机、平板等终端设备上的益智小游戏,最早于 2014 年 3 月发行,主界面如图 1 所示。

图 1:2048 小游戏的主界面
其游戏规则是:每次可以选择上下左右其中一个方向去滑动,每滑动一次,所有的数字方块都会往滑动的方向靠拢,系统也会在空白的地方随机出现一个数字方块,相同数字的方块在靠拢、相撞时会相加。系统给予的数字方块不是 2 就是 4,玩家要想办法在这小小的 16 格范围中凑出“2048”这个数字方块。
网友总结的游戏技巧有:
- 最大数尽可能放在角落;
- 数字按顺序紧邻排列;
- 首先满足最大数和次大数在的那一列/行是满的;
- 时刻注意活动较大数(32以上)旁边要有相近的数;
- 以大数所在的一行为主要移动方向;
- 不要急于“清理桌面”;
- 根据游戏规则,可以整理出游戏的流程,如图 2 所示。
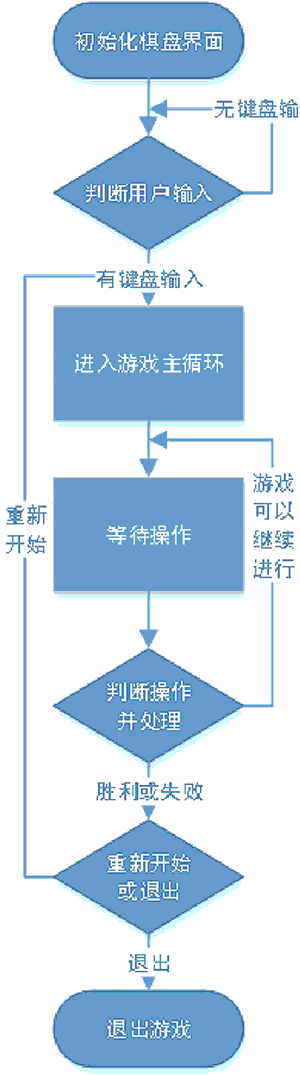
图 2:2048 小游戏的主要流程
根据流程图,可以将整个游戏程序大致分为三个部分:
- 程序初始化;
- 判断用户输入;
- 进入游戏主循环。
其中第三部分可以继续细分为以下三个部分:
- 等待操作;
- 判断操作并处理;
- 重新开始或退出。
为了游戏界面效果美观,这里使用了 pygame 库。安装 pygame 库的命令如下:
- pip install pygame
安装过程如图 3 所示。
图 3:pygame 库安装过程
下面我们继续关注 2048 小游戏。首先来看程序初始化,这里主要完成以下工作:导入所需模块,初始化棋盘和窗口界面,初始化各种组件和变量。根据游戏规则,棋盘大小为 4×4 共 16 格的正方形棋盘,简便起见我们使用二维列表存储每个格子里的数字。
定义棋盘并初始化每个格子存储的数字的语句如下:
board = [[0, 0, 0, 0]
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0]]
以下语句用于初始化窗口的相关属性:
1. #每个格子的边长,单位:像素(下同)
2. box_size = 50
3. #格子之间的间距
4. box_gap = 5
5. #中心棋盘区域上边缘离窗口顶部的距离
6. top_of_window = 100
7. #中心棋盘区域下边缘离窗口底部的距离
8. bottom_of_window = 30
9. #中心棋盘区域左边缘离窗口左边的距离
10. left_of_window = 2 0
11. #窗口宽度
12. window_width = box_size * 4 + box_gap * 5 + left_of_window * 2
13. #窗口高度
14. window_height = top_of_window + box_gap * 5 + box_size * 4 + left_of_window + bottom_of_window
15. #初始化窗口
16. window = pygame.display.set_mode((window_width, window_height), 0, 32)
17. #窗口标题
18. pygame.display.set_caption("2048")
19. #得分
20. score = 0
21. #使用 pygame 内置颜色值定义一些颜色常量
22. OLDLACE = pygame.color.THECOLORS["oldlacen"]
23. IVORY = pygame.color.THECOLORS["ivory3"]
24. BLACK = pygame.color.THECOLORS["black"]
25. RED = pygame.color.THECOLORS["red"]
26. RED2 = pygame.color.THECOLORS["red2"]
27. DARKGOLD = pygame.color.THECOLORS["darkgoldenrodl"]
28. GOLD = pygame.color.THECOLORS["gold"]
29. GRAY = pygame.color.THECOLORS["gray41"]
30. CHOCOLATE = pygame.color.THECOLORS["chocolate"]
31. CHOCOLATE1 = pygame.color.THECOLORS["chocolate1"]
32. CORAL = pygame.color.THECOLORS["coral"]
33. CORAL2 = pygame.color.THECOLORS["coral2"]
34. ORANGED = pygame.color.THECOLORS["orangered"]
35. ORANGED2 = pygame.color.THECOLORS["orangered2"]
36. DARKORANGE = pygame.color.THECOLORS["darkorange"]
37. DARKORANGE2 = pygame.color.THECOLORS["darkorange2"]
38. FORESTGREEN = pygame.color.THECOLORS["forestgreen"]
39. #界面字体
40. FONTNAME = "SimHei"绘制棋盘格子主要由 Box 类和 draw_box( ) 函数完成:
1. class Box:
2. def __init__(self, topleft, text, color):
3. self.topleft = topleft
4. self.text = text
5. self.color = color
6. def render(self, surface):
7. x, y = self.topleft
8. #绘制棋盘格
9. pygame.draw.rect(surface, self.color, (xz y, box_size, box_ size))
10. #定义棋盘格中数字的高度
11. text_height = int(box_size * 0.35)
12. #设置棋盘格中数字使用的字体
13. font_obj = pygame.font.SysFont(FONTNAME, text_height)
14. text_surface = font_obj.render(self.text, True, BLACK)
15. text_rect = text_surface.get_rect()
16. text_rect.center = (x + box_size / 2, y + box_size / 2)
17. surface.blit(text_surface, text_rect)
18. def draw_box():
19. giobal board
20. #定义棋盘上每个格子中不同数字的颜色
21. colors = {0 : (192, 192, 192) , 2 : (176, 224, 230) , 4 : (127, 255, 212), 8 : (135, 206, 235) , 16 : (64, 224, 208),
22. 32 : (0, 255, 255), 64 : (0, 201, 87), 128: (50, 205, 50), 256 : (34, 139, 34),
23. 512 : (0, 255, 127) , 1024 : (61, 145, 64), 2048 : (48, 128, 20), 4096 : (65, 105, 255),
24. 8192 : (8, 46, 84) , 16384 : (11, 23, 70), 32 768: (25, 25, 112), 65536 : (0, 0, 255) }
25. x, y = left_of_window, top_of_window
26. size = box_size * 4 + box gap * 5
27. pygame.draw.rect(window, BLACK, (x, y, size, size))
28. x, y = x + box_gap, y + box_gap
29. #使用嵌套循环绘制棋盘上所有格子
30. for i in range(4):
31. for j in range(4):
32. idx = board. [ i ] [ j ]
33. if idx == 0:
34. text =""
35. else :
36. text = str(idx)
37. if idx > 65536: idx = 65536
38. color = colors[idx]
39. box = Box((x, y), text, color) box.render(window)
40. x += box_size + box_gap
41. x = left_of_window + box_gap
42. y += box_size + box_gap
接下来需要初始化棋盘上开局的数字,来看 set_random_number( ) 函数:对于新手小白想更轻松的学好Python基础,Python爬虫,web开发、大数据,数据分析,人工智能等技术,这里给大家分享系统教学资源,架下我尉(同英): 2763177065 【教程/工具/方法/解疑】
1. def set_random_number():
2. pool =[]
3. for i in range(4):
4. for j in range (4):
5. if board[i][j] == 0:
6. pool. append. ( (if j ))
7. m = random.choice(pool)
8. pool.remove(m)
9. value = random.uniform(0, 1)
10. if value < 0.1:
11. value = 4
12. else :
13. value = 2
14. board[m[0]][m[1]] = value其作用是在棋盘上随机选取两个格子,将其值设置为 2 或 4。
以下代码将绘制游戏窗口其余的界面内容:
1. #显示游戏名称
2. window.blit(write ("2048", height = 45, color = GOLD), (left_of_ window, left_of_window // 2))
3. #显示当前得分
4. window.blit(write("得分", height=14, color=FORESTGREEN), (left_of_window+105, left_of_window//2 + 5))
5. rect1 = pygame.draw.rect(window, FORESTGREEN, (left_of_window+100, left_of_window//2 + 30, 60, 20))
6. text1 = write(str(score), height=14, color=GOLD)
7. text1_rect = text1.get_rect()
8. text1_rect.center = (left_of_window+100+30, left_of_window//2 + 40)
9. window.blit(textlf textl_rect)
10. #显示历史最高分
11. window.blit(write("最高", height=14, color=FORESTGREEN), (left_of_window+175, left_of_window//2 + 5))
12. rect2 = pygame.draw.rect(window, FORESTGREEN, (left_of_window+165, left_of_window//2 + 30, 60, 20))
13. #读取历史最高分
14. best = read_best()
15. if best < score:
16. best = score
17. text2 = write(str(best), height=14, color=GOLD)
18. text2_rect = text2.get_rect()
19. text2_rect.center = (left_of_window+165+30, left_of_window//2 + 40)
20. window.blit(text2, text2_rect)
21. #显示游戏操作提示
22. window.blit(write("使用上下左右方向键控制", height=16, color=GRAY), (left_of_window, window_height - bottom_of_Window))判断用户操作并处理是通过无限循环完成的,代码如下:
1. while True:
2. #通过事件机制获取当前用户操作
3. for event in pygame.event.get():
4. #用户操作为退出窗口或按下ESC键时写入最高分,并退出游戏窗口
5. if event.type == QUIT or (event.type == KEYUP and event.key == K_ESCAPE):
6. write_best(best)
7. pygame.quit ()
8. exit ()
9. #游戏没有正常结束时监听用户的操作
10. elif not gameover:
11. #用户按下键盘上的向上方向键
12. if event.type == KEYUP and event.key == K_UP:
13. up()
14. #用户按下键盘上的向下方向键
15. elif event.type ==KEYUP and event.key == K DOWN:
16. down()
17. #用户按下键盘上的向左方向键
18. elif event.type ==KEYUP and event.key == K_LEFT:
19. left ()
20. # 用户按下键盘上的向右方向键
21. elif event.type ==KEYUP and event.key == K_ RHGHT:
22. right ()
23. #开始新游戏
24. if newboard != board:
25. set_random_number()
26. newboard = deepcopy(board) draw_box()
27. gameover = is_over()
28. rect1 = pygame.draw.rect(window, FORESTGREEN,(left_ of_window+100, left_of_window//2 + 30, 60, 20))
29. text1 = write(str(score), height=14, color=GOLD)
30. text_rect = text1.get_rect()
31. text_rect.center = (left_of_window+100+30Aleft_of_window//2 + 4 0)
32. window.blit(text1, text_rect)
33. rect2 = pygame.draw.rect(window, FORESTGREEN, (left_of_window+165, left_of_window//2 + 30, 60, 20))
34. if best < score:
35. best = score
36. text2 = write(str(best), height=14, color=GOLD)
37. text2_rect = text2.get_rect()
38. text2_rect.center = (left_of_window+l65+30, left_of_window//2 + 4 0)
39. window.blit(text2, text2_rect)
40. #游戏正常结束(即用户合成了 2048或未合成2048但棋盘上已经无法继续下一步操作)
41. else :
42. write_best(best)
43. window.blit(write("游戏结束! ", height = 40, color = FORESTGREEN), (left_of_windowz window_height // 2))为了实现游戏效果,还有几个关键函数需要定义:一是对棋盘上的数字求和,用于当用户按下上下左右操作键后合并棋盘上的数字,代码如下:
1. def combinate(L):
2. glbal score
3. ans = [0, 0, 0 , 0]
4. num =[]
5. for i in L:
6. if i != 0:
7. num. append. (i)
8. length = len(num)
9. #当不为0的数字有4个时
10. if length == 4:
11. if num[0] == num[1]:
12. ans[0] = num[0] + num[1]
13. score += ans[0]
14. if num[2] == num[3]:
15. ans[1] = num[2] + num [3]
16. score += ans[1]
17. else :
18. ans[1]=num[2]
19. ans [2]=num[3]
20. elif num[1] ==num[2]
21. ans [0]= num[0]
22. ans[1]= num[1] + num[2]
23. ans [2]= num[3]
24. score += ans[1]
25. elif num[2] ==num[3]
26. ans [ 0]= num[0]
27. ans[1]= num[1]
28. ans [2]= num[2] + num[3]
29. score += ans[2]
30. else :
31. for i in range(length):
32. ans[i] = num[i]
33. #当不为0的数字有3个时
34. elif length == 3:
35. if num[0] == num[1]:
36. ans[0] = num[0] + num[1]
37. ans[1] = num[2]
38. score += ans[0]
39. elif num[1] == num[2]:
40. ans [0] = num[0]
41. ans[1]=num[1] + num[2]
42. score += ans[1]
43. else :
44. for i in range(length):
45. ans[i] = num[i]
46. #当不为0的数字有2个时
47. elif length == 2:
48. if num[0] == num[1]:
49. ans[0] = num[0] + num[1]
50. score += ans[0]
51. else :
52. for i in range(length):
53. ans[i] = num[i]
54. #当不为0的数字只有1个时
55. elif length == 1:
56. ans[0] = num[0]
57. else :
58. pass
59. return ans二是用户按下上下左右控制键后对应的操作,需要注意的是,我们定义存放棋盘上数字的列表是行式二维列表,故处理左右键相对容易,只需对左右相邻的数字判断是否应该合并即可,而处理上下键时则需要按照对应的列找到目标数字,再判断是否应该合并。代码如下:
1. def left():
2. for i in range(4):
3. temp = combinate (boa:rd [ i ])
4. for j in range (4):
5. board[i][j] = temp[j]
7. def right():
8. for i in range(4):
9. temp = combinate (boaird[i][::-1]
10. for j in range (4):
11. board[i][3-j] = temp[j]
13. def up():
14. for i in range(4):
15. to_comb =[]
16. for j in range (4):
17. to_comb.append(board[j][i])
18. temp = combinate(to_comb)
19. for k in range(4):
20. board[k][i] = temp[k]
22. def down():
23. for i in range(4):
24. to_comb =[]
25. for j in range (4):
26. to_comb.append(board[3-j][i])
27. temp = combina.te(to_comb)
28. for k in range (4):
29. board[3-k][i] = temp[k]三是判断游戏是否结束的函数 is_over( )。按照游戏规则,当棋盘上仍然存在空格,或是同一行/列存在相邻且相同的数字时,游戏方可继续进行,否则游戏结束,该函数可做如下定义:
1. def is_over():
2. #棋盘上仍然存在空格
3. for i in range(4):
4. for j in range(4):
5. if board[i][j]==0:
6. return False
8. #同一行中存在相邻且相同的数字
9. for i in range(4):
10. for j in range(3):
11. if board[i][j] == board[i][j+1]:
12. return False
14. #同一列中存在相邻且相同的数字
15. for i in range(3):
16. for j in range(4):
17. if board[i][j] == board[i+1][j]:
18. return False
20. return True至此,小游戏 2048 的主要内容和关键代码介绍完毕。





















