功能以及显示效果简介
需求:在双屏显示中,把启动的应用从其中一个屏幕中移动到另一个屏幕中。
操作:通过双指按压应用使其移动,如果移动的距离过小,我们就不移动到另一屏幕,否则移动到另一屏。
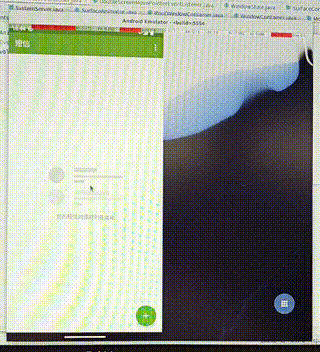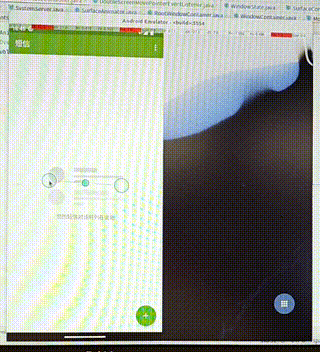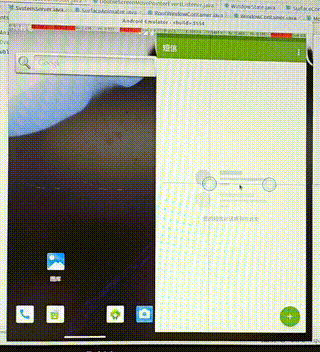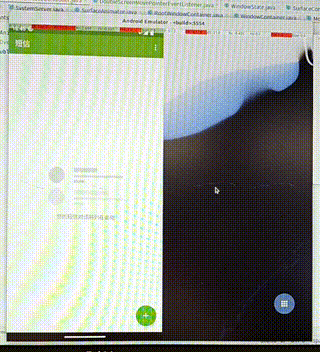
功能分析
多屏中移动应用至另一屏本质就是Task的移动。
从窗口层级结构的角度来说,就是把Display1中的DefaultTaskDisplayArea上的Task,移动到Display2中的DefaultTaskDisplayArea上。
容器结构简化树状图如下所示:

窗口层级结构简化树状图如下所示:

动画分析
动画图层节点

这里以从左往右移动为例,通过DisplayContent的getWindowingLayer()方法获取WindowedMagnification节点,在该节点下创建copyTaskSc节点用于动画过渡。从右往左同理。
图层移动偏移量计算
当移动的偏移量(offsetX)大于一定的数值时向对侧移动,否则回到之前的屏幕。
为保证两屏显示过渡平滑,需要使用到镜像图层。我们拖动那个图层是镜像图层,另一屏显示的为真实图层。需要注意的是,如果真实图层(被复制的图层)发生变化(坐标、缩放等)会导致镜像图层跟着变化(坐标、缩放等)。

如上图所示:图层向右移动时,镜像图层偏移量为offsetX,真实图层的偏移量为-(width-offsetX)。由于我们真实的图层发生了变化,因此当我们镜像图层偏移量为offsetX时,其实际偏移量为镜像图层偏移量加上真实图层的偏移量,即offsetX - (width-offsetX)。所以为保证镜像图层的偏移量为offsetX,需要进行额外的偏移,即offsetX - (width-offsetX) + 额外偏移量 = offsetX 。这里我们可以算出额外偏移量就是width-offsetX,最终我们得出镜像图层的实际偏移量为offsetX + (width-offsetX)。
结论:镜像图层偏移量为offsetX + (width-offsetX),真实图层的偏移量为-(width-offsetX)。

如上图所示:向右偏移时同理,镜像图层偏移量为-offsetX,真实图层的偏移量为width-offsetX。所以经过变化后的镜像图层的实际偏移量为-offset - (width-offsetX)。
关键代码知识点
移动Task至另一屏幕
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/RootWindowContainer.java
/**
* Move root task with all its existing content to specified display.
*
* @param rootTaskId Id of root task to move.
* @param displayId Id of display to move root task to.
* @param onTop Indicates whether container should be place on top or on bottom.
*/
void moveRootTaskToDisplay(int rootTaskId, int displayId, boolean onTop) {
//根据displayId获取DisplayContent
final DisplayContent displayContent = getDisplayContentOrCreate(displayId);
if (displayContent == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("moveRootTaskToDisplay: Unknown displayId="
+ displayId);
}
//调用moveRootTaskToTaskDisplayArea方法
moveRootTaskToTaskDisplayArea(rootTaskId, displayContent.getDefaultTaskDisplayArea(),
onTop);
}入参说明:rootTaskId需要移动的Task的Id。可以通过Task中getRootTaskId()方法获取。displayId需要移动到对应屏幕的Display的Id。可以通过DisplayContent中的getDisplayId()方法获取。onTop移动后的Task是放在容器顶部还是底部。true表示顶部,false表示底部。
代码解释:
这个方法首先通过getDisplayContentOrCreate方法根据displayId获取DisplayContent,然后调用moveRootTaskToTaskDisplayArea方法进行移动。
其中传递参数displayContent.getDefaultTaskDisplayArea(),表示获取DisplayContent下面的DefaultTaskDisplayArea。
/**
* Move root task with all its existing content to specified task display area.
*
* @param rootTaskId Id of root task to move.
* @param taskDisplayArea The task display area to move root task to.
* @param onTop Indicates whether container should be place on top or on bottom.
*/
void moveRootTaskToTaskDisplayArea(int rootTaskId, TaskDisplayArea taskDisplayArea,
boolean onTop) {
//获取Task
final Task rootTask = getRootTask(rootTaskId);
if (rootTask == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("moveRootTaskToTaskDisplayArea: Unknown rootTaskId="
+ rootTaskId);
}
final TaskDisplayArea currentTaskDisplayArea = rootTask.getDisplayArea();
if (currentTaskDisplayArea == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("moveRootTaskToTaskDisplayArea: rootTask=" + rootTask
+ " is not attached to any task display area.");
}
if (taskDisplayArea == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"moveRootTaskToTaskDisplayArea: Unknown taskDisplayArea=" + taskDisplayArea);
}
if (currentTaskDisplayArea == taskDisplayArea) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Trying to move rootTask=" + rootTask
+ " to its current taskDisplayArea=" + taskDisplayArea);
}
//把获取到的task重新挂载到了新display的taskDisplayArea
rootTask.reparent(taskDisplayArea, onTop);
// Resume focusable root task after reparenting to another display area.
//窗口或任务reparent之后,恢复焦点,激活相关任务的活动,并更新活动的可见性,以确保窗口管理器和用户界面的状态一致和正确。
rootTask.resumeNextFocusAfterReparent();
// TODO(multi-display): resize rootTasks properly if moved from split-screen.
}根据前面传递的TaskId获取到Task,在通过rootTask.reparent(taskDisplayArea, onTop);方法,把这个Task重新挂载到了新display的taskDisplayArea上。然后使用rootTask.resumeNextFocusAfterReparent();方法更新窗口焦点显示。
rootTask.reparent(taskDisplayArea, onTop);代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/Task.java
void reparent(TaskDisplayArea newParent, boolean onTop) {
if (newParent == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Task can't reparent to null " + this);
}
if (getParent() == newParent) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Task=" + this + " already child of " + newParent);
}
//通过调用 canBeLaunchedOnDisplay 方法检查任务是否可以在新父区域所在的显示设备上启动。
if (canBeLaunchedOnDisplay(newParent.getDisplayId())) {
//实际执行reparent的操作。
reparent(newParent, onTop ? POSITION_TOP : POSITION_BOTTOM);
//如果Task是一个叶子Task(即没有子Task的Task)
if (isLeafTask()) {
//调用新父区域的 onLeafTaskMoved 方法来通知新父区域叶子Task已经移动。
newParent.onLeafTaskMoved(this, onTop);
}
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "Task=" + this + " can't reparent to " + newParent);
}
}其中reparent(newParent, onTop ? POSITION_TOP : POSITION_BOTTOM);实际执行reparent的操作。这里根据 onTop 的值来决定任务应该被放置在新父区域的顶部还是底部。我们再看看这方法的具体实现。
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowContainer.java
void reparent(WindowContainer newParent, int position) {
if (newParent == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("reparent: can't reparent to null " + this);
}
if (newParent == this) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can not reparent to itself " + this);
}
final WindowContainer oldParent = mParent;
if (mParent == newParent) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("WC=" + this + " already child of " + mParent);
}
// Collect before removing child from old parent, because the old parent may be removed if
// this is the last child in it.
//记录reparent的容器(this)相关信息,这里的this指的是移动的Task,newParent是新的TaskDisplayArea
mTransitionController.collectReparentChange(this, newParent);
// The display object before reparenting as that might lead to old parent getting removed
// from the display if it no longer has any child.
//获取之前的DisplayContent和新的DisplayContent
final DisplayContent prevDc = oldParent.getDisplayContent();
final DisplayContent dc = newParent.getDisplayContent();
//设置 mReparenting 为 true,表示正在执行reparent操作。
//然后从旧父容器中移除当前容器,并将其添加到新父容器的指定位置。
//最后,将 mReparenting 设置为 false,表示reparent操作完成。
mReparenting = true;
oldParent.removeChild(this);
newParent.addChild(this, position);
mReparenting = false;
// Relayout display(s)
//标记新父容器对应的显示内容为需要布局。
//如果新父容器和旧父容器的显示内容不同,
//则触发显示内容改变的通知,并标记旧显示内容也需要布局。
//最后,调用layoutAndAssignWindowLayersIfNeeded方法确保显示内容按需进行布局和窗口层级的分配。
dc.setLayoutNeeded();
if (prevDc != dc) {
onDisplayChanged(dc);
prevDc.setLayoutNeeded();
}
getDisplayContent().layoutAndAssignWindowLayersIfNeeded();
// Send onParentChanged notification here is we disabled sending it in setParent for
// reparenting case.
//处理窗口容器在父容器变更时的各种逻辑
onParentChanged(newParent, oldParent);
//处理窗口容器在不同父容器之间同步迁移的逻辑
onSyncReparent(oldParent, newParent);
}rootTask.resumeNextFocusAfterReparent();代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/Task.java
void resumeNextFocusAfterReparent() {
//调整焦点
adjustFocusToNextFocusableTask("reparent", true /* allowFocusSelf */,
true /* moveDisplayToTop */);
//恢复当前焦点任务的顶部活动
mRootWindowContainer.resumeFocusedTasksTopActivities();
// Update visibility of activities before notifying WM. This way it won't try to resize
// windows that are no longer visible.
//更新activities的可见性
mRootWindowContainer.ensureActivitiesVisible(null /* starting */, 0 /* configChanges */,
!PRESERVE_WINDOWS);
}更新activity可见性和配置
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/RootWindowContainer.java
/**
* Make sure that all activities that need to be visible in the system actually are and update
* their configuration.
*/
void ensureActivitiesVisible(ActivityRecord starting, int configChanges,
boolean preserveWindows) {
ensureActivitiesVisible(starting, configChanges, preserveWindows, true /* notifyClients */);
}
/**
* @see #ensureActivitiesVisible(ActivityRecord, int, boolean)
*/
void ensureActivitiesVisible(ActivityRecord starting, int configChanges,
boolean preserveWindows, boolean notifyClients) {
//检查mTaskSupervisor是否正在进行活动可见性更新或是否延迟了根可见性更新
if (mTaskSupervisor.inActivityVisibilityUpdate()
|| mTaskSupervisor.isRootVisibilityUpdateDeferred()) {
// Don't do recursive work.
return;
}
try {
//开始更新
mTaskSupervisor.beginActivityVisibilityUpdate();
// First the front root tasks. In case any are not fullscreen and are in front of home.
//遍历每个DisplayContent对象
for (int displayNdx = getChildCount() - 1; displayNdx >= 0; --displayNdx) {
final DisplayContent display = getChildAt(displayNdx);
//对于每个DisplayContent对象,调用其ensureActivitiesVisible方法来确保该显示内容上的活动可见并更新其配置。
display.ensureActivitiesVisible(starting, configChanges, preserveWindows,
notifyClients);
}
} finally {
//结束更新
mTaskSupervisor.endActivityVisibilityUpdate();
}
}starting指的是Task 中最顶端的activity,保证的正是这个activity在启动或者resume时的可见性。configChanges评估是否被冻结的activity改变部分配置。preserveWindows一个标志位,更新时是否保留窗口。notifyClients一个标志位,把配置和可见性的变化通知客户端,当前固定值为true。
这个方法的主要作用是确保所有需要显示的活动确实在系统中可见,并更新它们的配置。
这里的display.ensureActivitiesVisible(starting, configChanges, preserveWindows,notifyClients);是更新的核心方法,其最终会调用到EnsureActivitiesVisibleHelper中的process方法。
获取WindowedMagnification层级
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/DisplayContent.java
/**
* The direct child layer of the display to put all non-overlay windows. This is also used for
* screen rotation animation so that there is a parent layer to put the animation leash.
*/
private SurfaceControl mWindowingLayer;
SurfaceControl getWindowingLayer() {
return mWindowingLayer;
}mWindowingLayer在DisplayContent的configureSurfaces方法中有进行赋值。
/**
* Configures the surfaces hierarchy for DisplayContent
* This method always recreates the main surface control but reparents the children
* if they are already created.
*
* @param transaction as part of which to perform the configuration
*/
private void configureSurfaces(Transaction transaction) {
final SurfaceControl.Builder b = mWmService.makeSurfaceBuilder(mSession)
.setOpaque(true)
.setContainerLayer()
.setCallsite("DisplayContent");
mSurfaceControl = b.setName(getName()).setContainerLayer().build();
......
final List<DisplayArea<? extends WindowContainer>> areas =
mDisplayAreaPolicy.getDisplayAreas(FEATURE_WINDOWED_MAGNIFICATION);
final DisplayArea<?> area = areas.size() == 1 ? areas.get(0) : null;
if (area != null && area.getParent() == this) {
// The windowed magnification area should contain all non-overlay windows, so just use
// it as the windowing layer.
mWindowingLayer = area.mSurfaceControl;
transaction.reparent(mWindowingLayer, mSurfaceControl);
} else {
......
}
......
}从代码中我们可以看出mWindowingLayer = area.mSurfaceControl,实际上就是FEATURE_WINDOWED_MAGNIFICATION对应的图层,即WindowedMagnification:0:31。
镜像图层
代码路径:frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/SurfaceControl.java
/**
* Creates a mirrored hierarchy for the mirrorOf {@link SurfaceControl}
*
* Real Hierarchy Mirror
* SC (value that's returned)
* |
* A A'
* | |
* B B'
*
* @param mirrorOf The root of the hierarchy that should be mirrored.
* @return A SurfaceControl that's the parent of the root of the mirrored hierarchy.
*
* @hide
*/
public static SurfaceControl mirrorSurface(SurfaceControl mirrorOf) {
long nativeObj = nativeMirrorSurface(mirrorOf.mNativeObject);
SurfaceControl sc = new SurfaceControl();
sc.assignNativeObject(nativeObj, "mirrorSurface");
return sc;
}把复制一个一模一样的图层,作为镜像图层,并且该图层会随着原图层的变化而变化。这个复制会把该图层下的所有子节点一起复制,其图层的根节点一般叫做MirrorRoot。
例如 :SurfaceControl.mirrorSurface(rootTask.getSurfaceControl()); 复制rootTask的图层以及其以后得节点作为镜像。
如图所示:

注意:真实图层(被复制的图层mirrorOf)的变化(坐标、缩放等)会导致镜像图层跟着变化(坐标、缩放等)。
保证底部的activity显示
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowContainer.java
/**
* True if this an AppWindowToken and the activity which created this was launched with
* ActivityOptions.setLaunchTaskBehind.
* <p>
* TODO(b/142617871): We run a special animation when the activity was launched with that
* flag, but it's not necessary anymore. Keep the window invisible until the task is explicitly
* selected to suppress an animation, and remove this flag.
*/
boolean mLaunchTaskBehind;mLaunchTaskBehind为true则表示当前允许activity显示在最下方。例如,桌面就是一直显示最下方的activity。
调用方式:ActivityRecord对象.mLaunchTaskBehind = true; 在双屏拖拽时可能会出现另一屏桌面或者其他顶层Activity界面黑屏的现象,因此需要通过该配置使其保持显示。
ValueAnimator的使用
ValueAnimator anim = ValueAnimator.ofInt(0, 200);
anim.setDuration(3000);
anim.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
int currentValue = (int) animation.getAnimatedValue();
Slog.i("TAG", "onAnimationUpdate current value is " + currentValue);
}
});
valueAnimator.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
super.onAnimationEnd(animation);
Slog.i("TAG", "onAnimationEnd");
});
anim.start();onAnimationUpdate是动画在更新时的监听,从上面的例子上可以看出,是在3秒内平滑打印0~200之间的整数。onAnimationEnd是动画播放结束后的监听,在结束时的操作一般放在这里面。
全局触摸接口
功能接口
代码路径:frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/WindowManagerPolicyConstants.java
interface PointerEventListener {
/**
* 1. onPointerEvent will be called on the service.UiThread.
* 2. motionEvent will be recycled after onPointerEvent returns so if it is needed later a
* copy() must be made and the copy must be recycled.
**/
void onPointerEvent(MotionEvent motionEvent);
}我们触摸相关的操作调用此接口,然后实现。
监听接口
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/policy/WindowManagerPolicy.java
public interface WindowManagerFuncs {
/** Register a system listener for touch events */
void registerPointerEventListener(PointerEventListener listener, int displayId);
/** Unregister a system listener for touch events */
void unregisterPointerEventListener(PointerEventListener listener, int displayId);
}监听接口AOSP内部有实现,我们根据需要调用对应的监听方式接口。
- WindowManagerService中重写监听方法
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
@Override
public void registerPointerEventListener(PointerEventListener listener, int displayId) {
synchronized (mGlobalLock) {
final DisplayContent displayContent = mRoot.getDisplayContent(displayId);
if (displayContent != null) {
displayContent.registerPointerEventListener(listener);
}
}
}
@Override
public void unregisterPointerEventListener(PointerEventListener listener, int displayId) {
synchronized (mGlobalLock) {
final DisplayContent displayContent = mRoot.getDisplayContent(displayId);
if (displayContent != null) {
displayContent.unregisterPointerEventListener(listener);
}
}
}WindowManagerService中对多屏多显状态的屏幕做了处理,除了传递PointerEventListener对象以外,还需要传递需要监听的DisplayContent。最终调用的是DisplayContent中的监听方法。
- DisplayContent中的监听方法
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/DisplayContent.java
void registerPointerEventListener(@NonNull PointerEventListener listener) {
mPointerEventDispatcher.registerInputEventListener(listener);
}
void unregisterPointerEventListener(@NonNull PointerEventListener listener) {
mPointerEventDispatcher.unregisterInputEventListener(listener);
}在DisplayContent中调用registerPointerEventListener监听,仅传递PointerEventListener对象即可。其本质的实现在PointerEventDispatcher中。
- PointerEventDispatcher中实现监听方法
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/PointerEventDispatcher.java
/**
* Add the specified listener to the list.
* @param listener The listener to add.
*/
public void registerInputEventListener(PointerEventListener listener) {
synchronized (mListeners) {
if (mListeners.contains(listener)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("registerInputEventListener: trying to register" +
listener + " twice.");
}
mListeners.add(listener);
mListenersArray = null;
}
}
/**
* Remove the specified listener from the list.
* @param listener The listener to remove.
*/
public void unregisterInputEventListener(PointerEventListener listener) {
synchronized (mListeners) {
if (!mListeners.contains(listener)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("registerInputEventListener: " + listener +
" not registered.");
}
mListeners.remove(listener);
mListenersArray = null;
}
}





















