实在不知道说什么好了,这个东西以前也没做过,这两天公司有这方面的需求,就实现一下,然后把功能跟大家分享一下,以后有需要直接拿去用就好。
效果图:
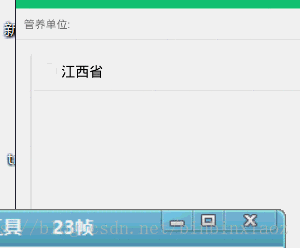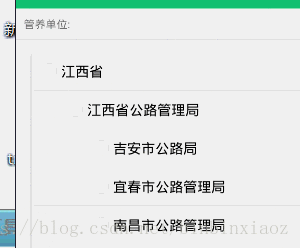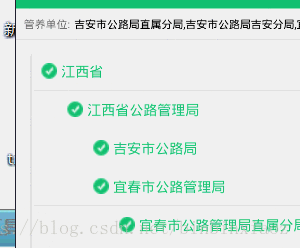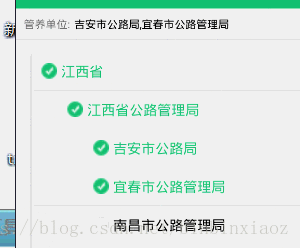
分析一波:
·1.层级父节点与子节点的关联
·2.布局的复用
·3.层级展开与关闭,显示与隐藏问题
·4.checkbox的标记勾选
功能的初步准备
具体的代码mean,项目注释都有··
一、数据的实体类
```
public class Node<T, B> {
/**
* 数据源的字段
*/
private String title;
private String bmid;
private String content;
private String code;
private String childBmid;
/**
* ****************** 分级树状等字段
*/
//传入的实体对象
public B bean;
//父级id子级pid
private T id;
//根节点pId为0
private T pId;
//节点名称
private String name;
//当前的级别
private int level;
//是否展开
private boolean isExpand = false;
//子节点数据 ,套用当前node
private List<Node> children = new ArrayList<>();
//父节点
private Node parent;
//是否被checked选中
private boolean isChecked;
public Node() {
}
public Node(T id, T pId, String name) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.pId = pId;
this.name = name;
}
public Node(T id, T pId, String name, B bean) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.pId = pId;
this.name = name;
this.bean = bean;
}
public boolean isChecked() {
return isChecked;
}
public void setChecked(boolean isChecked) {
this.isChecked = isChecked;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getBmid() {
return bmid;
}
public void setBmid(String bmid) {
this.bmid = bmid;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getChildBmid() {
return childBmid;
}
public void setChildBmid(String childBmid) {
this.childBmid = childBmid;
}
public T getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(T id) {
this.id = id;
}
public T getpId() {
return pId;
}
public void setpId(T pId) {
this.pId = pId;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setLevel(int level) {
this.level = level;
}
public boolean isExpand() {
return isExpand;
}
public List<Node> getChildren() {
return children;
}
public void setChildren(List<Node> children) {
this.children = children;
}
public Node getParent() {
return parent;
}
public void setParent(Node parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
/**
* 是否为跟节点
*/
public boolean isRoot() {
return parent == null;
}
/**
* 判断父节点是否展开
*/
public boolean isParentExpand() {
if (parent == null)
return false;
return parent.isExpand();
}
/**
* 是否是叶子界点
*/
public boolean isLeaf() {
return children.size() == 0;
}
/**
* 获取当前所在层级,
* 设置层级间隔
*/
public int getLevel() {
return parent == null ? 0 : parent.getLevel() + 1;
}
/**
* 设置展开
*/
public void setExpand(boolean isExpand) {
this.isExpand = isExpand;
if (!isExpand) {
for (Node node : children) {
node.setExpand(isExpand);
}
}
}
}
```二、设置节点关系
```
public class TreeHelper {
/**
* 传入node 返回排序后的Node
*/
public static List<Node> getSortedNodes(List<Node> datas,
int defaultExpandLevel) {
List<Node> result = new ArrayList<Node>();
// 设置Node间父子关系
List<Node> nodes = convetData2Node(datas);
// 拿到根节点
List<Node> rootNodes = getRootNodes(nodes);
// 排序以及设置Node间关系
for (Node node : rootNodes) {
addNode(result, node, defaultExpandLevel, 1);
}
return result;
}
/**
* 过滤出所有可见的Node
*/
public static List<Node> filterVisibleNode(List<Node> nodes) {
List<Node> result = new ArrayList<Node>();
for (Node node : nodes) {
// 如果为跟节点,或者上层目录为展开状态
if (node.isRoot() || node.isParentExpand()) {
result.add(node);
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 设置Node间,父子关系;让每两个节点都比较一次,即可设置其中的关系
*/
private static List<Node> convetData2Node(List<Node> nodes) {
for (int i = 0; i < nodes.size(); i++) {
Node n = nodes.get(i);
for (int j = i + 1; j < nodes.size(); j++) {
Node m = nodes.get(j);
if (m.getpId() instanceof String) {
if (m.getpId().equals(n.getId())) {
n.getChildren().add(m);
m.setParent(n);
} else if (m.getId().equals(n.getpId())) {
m.getChildren().add(n);
n.setParent(m);
}
} else {
if (m.getpId() == n.getId()) {
n.getChildren().add(m);
m.setParent(n);
} else if (m.getId() == n.getpId()) {
m.getChildren().add(n);
n.setParent(m);
}
}
}
}
return nodes;
}
// 拿到根节点
private static List<Node> getRootNodes(List<Node> nodes) {
List<Node> root = new ArrayList<Node>();
for (Node node : nodes) {
if (node.isRoot())
root.add(node);
}
return root;
}
/**
* 把一个节点上的所有的内容都挂上去
*/
private static <T, B> void addNode(List<Node> nodes, Node<T, B> node,
int defaultExpandLeval, int currentLevel) {
nodes.add(node);
if (defaultExpandLeval >= currentLevel) {
node.setExpand(true);
}
if (node.isLeaf())
return;
for (int i = 0; i < node.getChildren().size(); i++) {
addNode(nodes, node.getChildren().get(i), defaultExpandLeval,
currentLevel + 1);
}
}
}
```三、Adapter的封装
```
public abstract class TreeListViewAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
protected Context mContext;
/**
* 存储所有可见的Node
*/
protected List<Node> mNodes = new ArrayList<>();
protected LayoutInflater mInflater;
/**
* 存储所有的Node
*/
protected List<Node> mAllNodes = new ArrayList<>();
public TreeListViewAdapter(ListView mTree, Context context, List<Node> datas,
int defaultExpandLevel) {
mContext = context;
/**
* 对所有的Node进行排序
*/
mAllNodes = TreeHelper.getSortedNodes(datas, defaultExpandLevel);
/**
* 过滤出可见的Node
*/
mNodes = TreeHelper.filterVisibleNode(mAllNodes);
mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
/**
* 设置节点点击时,可以展开以及关闭;并且将ItemClick事件继续往外公布
*/
mTree.setOnItemClickListener(new AdapterView.OnItemClickListener() {
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view,
int position, long id) {
expandOrCollapse(position);
}
});
}
/**
* 相应ListView的点击事件 展开或关闭某节点
*/
public void expandOrCollapse(int position) {
Node n = mNodes.get(position);
if (n != null) {// 排除传入参数错误异常
if (!n.isLeaf()) {
n.setExpand(!n.isExpand());
mNodes = TreeHelper.filterVisibleNode(mAllNodes);
notifyDataSetChanged();// 刷新视图
}
}
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return mNodes.size();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return mNodes.get(position);
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
Node node = mNodes.get(position);
convertView = getConvertView(node, position, convertView, parent);
// 设置内边距
convertView.setPadding(node.getLevel() * 50, 3, 3, 3);
return convertView;
}
/**
* 设置多选
*/
protected void setChecked(final Node node, boolean checked) {
node.setChecked(checked);
setChildChecked(node, checked);
if (node.getParent() != null)
setNodeParentChecked(node.getParent(), checked);
notifyDataSetChanged();
}
/**
* 设置是否选中
*/
public <T, B> void setChildChecked(Node<T, B> node, boolean checked) {
if (!node.isLeaf()) {
node.setChecked(checked);
for (Node childrenNode : node.getChildren()) {
setChildChecked(childrenNode, checked);
}
} else {
node.setChecked(checked);
}
}
private void setNodeParentChecked(Node node, boolean checked) {
if (checked) {
node.setChecked(checked);
if (node.getParent() != null)
setNodeParentChecked(node.getParent(), checked);
} else {
List<Node> childrens = node.getChildren();
boolean isChecked = false;
for (Node children : childrens) {
if (children.isChecked()) {
isChecked = true;
}
}
//如果所有自节点都没有被选中 父节点也不选中
if (!isChecked) {
node.setChecked(checked);
}
if (node.getParent() != null)
setNodeParentChecked(node.getParent(), checked);
}
}
public abstract View getConvertView(Node node, int position,
View convertView, ViewGroup parent);
}
```Adapter实现类
一、布局代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:descendantFocusability="blocksDescendants"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/check_box"
android:layout_width="20dp"
android:layout_height="20dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:background="@drawable/screen_check_box_style"//selector图片
android:button="@null" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:paddingBottom="10dp"
android:paddingTop="10dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dp"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:text="项目"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="18sp" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout> 二、Adapter
```
public class SimpleTreeAdapter extends TreeListViewAdapter {
private onNodeDataListener onNodeDataListener;
public SimpleTreeAdapter(ListView mTree, Context context, List<Node> datas, int defaultExpandLevel) {
super(mTree, context, datas, defaultExpandLevel);
}
@Override
public View getConvertView(final Node node, int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
final ViewHolder holder;
if (convertView == null) {
convertView = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.item_tree_title, parent, false);
holder = new ViewHolder();
holder.tvName = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_name);
holder.cb = (CheckBox) convertView.findViewById(R.id.check_box);
convertView.setTag(holder);
} else {
holder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
}
holder.cb.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
setChecked(node, holder.cb.isChecked());
onNodeDataListener.onNodeDataListener(node);
}
});
if (node.isChecked()) {
holder.cb.setChecked(true);
holder.tvName.setTextColor(Color.parseColor("#1FCC7C"));
} else {
holder.cb.setChecked(false);
holder.tvName.setTextColor(Color.parseColor("#000000"));
}
holder.tvName.setText(node.getName());
return convertView;
}
class ViewHolder {
TextView tvName;
CheckBox cb;
}
public void setNodeDataListener(onNodeDataListener setNodeDataListener) {
this.onNodeDataListener = setNodeDataListener;
}
public interface onNodeDataListener {
void onNodeDataListener(Node node);
}
}```
数据源的填充
声明
private List<Node> mDatas = new ArrayList<>();//装载的总数据
private List<Node> mResultDatas = new ArrayList<>();//check勾选的数据
private SimpleTreeAdapter mAdapter;
root节点:
//rootList不用关注,我用的greendao查询的表数据
List<DepartMentForm> rootList = daoSession.getDepartMentFormDao().queryBuilder().where(DepartMentFormDao.Properties.Id.eq(unit)).list();
Node root = new Node();
String rootId = rootList.get(0).getId();
root.setId(rootId);
root.setpId(0);
root.setName(rootList.get(0).getName());
mDatas.add(root); 数据源我直接用的我们公司的,这里我就介绍一下数据源的节点关联。
pid作为根的节点值。
rootId为当前节点的id值,为下级节点的父节点值
name就是当前节点的名称
二层下级节点:
Node secondNode = new Node();
String secondId = secondData.get(i).getId();
secondNode.setId(secondId);
secondNode.setpId(rootId);
secondNode.setName(secondData.get(i).getName());
mDatas.add(secondNode); pid为父节点的id值
id为下级节点的父节点值
三层下级节点:
Node threeNode = new Node();
String threeId = three.get(j).getId();
threeNode.setId(threeId);
threeNode.setpId(secondId);
threeNode.setName(three.get(j).getName());
mDatas.add(threeNode);
checkbox的监听
//给 ListView 设置 Adapter
//10为默认展示层级数,自己看需求 调整
mAdapter = new SimpleTreeAdapter(mListview, mContext, mDatas, 10);
mListview.setAdapter(mAdapter);
mAdapter.setNodeDataListener(new SimpleTreeAdapter.onNodeDataListener() {
@Override
public void onNodeDataListener(Node node) {
这块文字没注释,没注释看的清楚 0.0
node返回的是当前的节点数据的值
因为所有的节点数据都已经挂在node上了,
所有在node中可以看到当前节点的parent值,以及子节点值,为null代表没有
结构我说清楚了,具体的这个check怎么处理,看你们需求,我就不多说了。
}
});over,基本就这些





















