什么是事件监听
在使用Redis的过程中,我们对Redis做的每一个操作,下发的每一个命令, 都可以认为是事件的存在。所谓事件监听,就是Redis Server会对客户端下发命令进行一个监控, 一但有人对Redis Server做操作, Redis Server都能知道,并通过某种方式将监听到的事件转发到对应的订阅者。
应用场景
需求一:
一个电商商家后台,商家可以设置多个商品的价格并指定价格的生效时间。后台服务需要生效时间到时对所有已经上架的商品进行价格修改。并在价格修改成功后通知所有关注该商品的买家客户。
注意: 假设该平台拥有1w商家,平均每个商家设置了100个商品,也就是你要保证200w件商品价格修改的实时通知性。
解决方案一: 每个商品都有一份表去记录所有的新价格和生效时间,由定时任务job去轮询表中的数据,如果符合当前时间则取出并执行接下来的业务逻辑。

解决方案二: 每个商品都有一份表去记录所有的新价格和生效时间,由多个分布式job去轮询表中的数据,为了减轻job服务实例的压力,设置每2秒执行一次(定时任务不建议设置每秒)。在这基础上其实还有优化的空间,可以在设置分布式job分片处理逻辑。对于每一个job实例,还可以在其内部开启异步线程并行处理。

从上述的描述中我们可以发现,用户量还是比较大,其实实时性要求比较高,所以如果我们把数据落库,然后每次定时的时候从数据库里面去取然后做逻辑的判断,这样肯定是无法达到实时性的要求的,所以有一种方案是采用redis来管理这批数据。但是也有两个个问题
- 当这批数据过期的时候,要提醒用户
- 从redis删除后,要修改数据库的状态。
要解决这个功能就需要使用到redis的一个高级的功能:redis 键空间通知(供Keyspace Notifications功能)其允许客户Publish / Subscribe ,以便以某种方式接收影响Redis数据集的事件。
需求二:
同样是电商平台,商家可以设置商品的预售时间, 当预售时间到达时,修改商品状态,并上架商品。该需求和需求一类似,都是以时间或者秒作为计算依据,每个商品都是独立的,它们的时间属性都不会一样,所以是没有规律性的。
需求三:
订单超时30分钟自动关闭。(不管多少订单,都是固定的时间间隔30分钟,有规律) 这个问题解决的方案就有多种了,我们可以通过MQ来进行,现在大多的MQ都带有死信队列的机制,我们可以通过这个机制来完成,其次也可以通过quartz的轮询方式的完成,选择合适解决方案应对当前的需求即可。当然本次主要是解决第一个需求,所以只谈如何使用redis来解决。
需求四:
- 监控key的操作(set、del、expire……)
- 监听key的过期,自动触发事件
如何使用Keyspace Notifications
由于Keyspace Notifications是在Redis 2.8.0之后的版本才提供的功能,所以我们的Redis版本需要再2.8.0之上,否则无法使用Redis时间监听,在笔者写这篇文章之时,Redis的最新正式版本已经为5.0了
修改Redis配置,开启Keyspace Notifications的两种方式:
- 命令修改
CONFIG set notify-keyspace-events AKEx- 配置文件修改 修改配置文件redis.conf,
notify-keyspace-events AKEx,重新启动Redis
参数说明
1)notify-keyspace-events选项的参数为空字符串时,表示功能关闭,当参数不是空字符串时,表示功能开启
2)notify-keyspace-events默功能是关闭的
3)如果要使用此功能,必须字符串包含 K 或者 E,否则收不到任何事件消息
4)如果参数为“AKE”,意味着接收所有事件消息
notify-keyspace-events 的参数可以是以下字符的任意组合, 它指定了服务器该发送哪些类型的通知:
- K 键空间事件,以__keyspace@__前缀发布。
- E 键事件事件,以__keyevent@__前缀发布。
- g 通用命令(非类型特定),如DEL,EXPIRE,RENAME等等
- $ 字符串命令
- l 列表命令
- s 集合命令
- h 哈希命令
- z 有序集合命令
- x 过期事件(每次键到期时生成的事件)
- e 被驱逐的事件(当一个键由于达到最大内存而被驱逐时产生的事件)
- A g$lshzxe的别名,因此字符串AKE表示所有的事件。
字符串中应当至少存在K或者E,否则将不会传递事件,不管字符串中其余部分是什么。
实例演示
同时监听 set、get、del 、 expire 操作
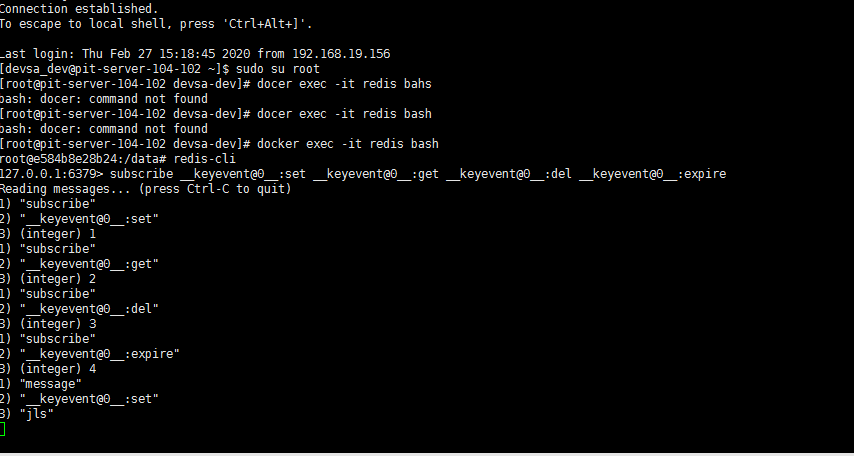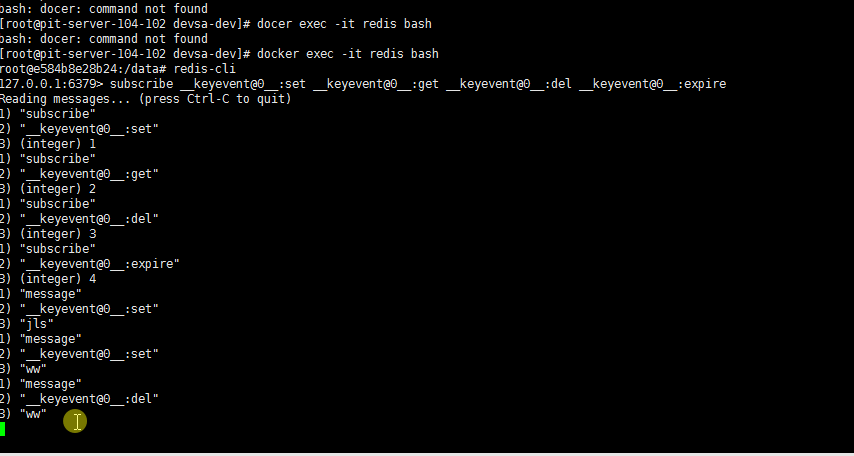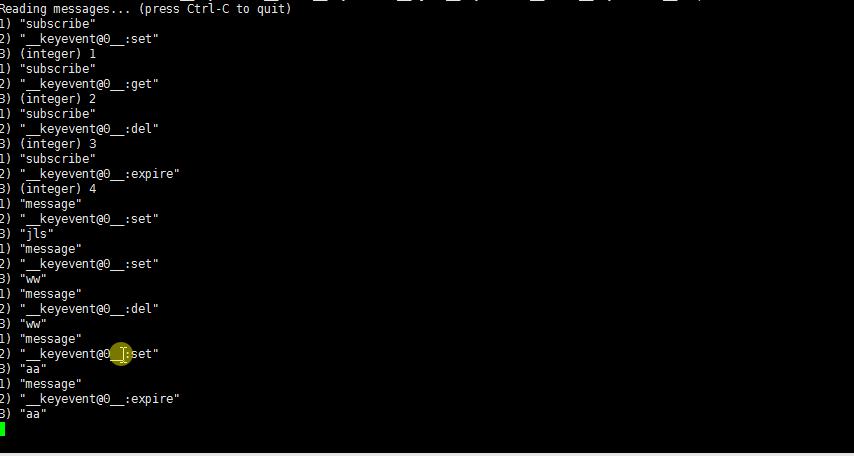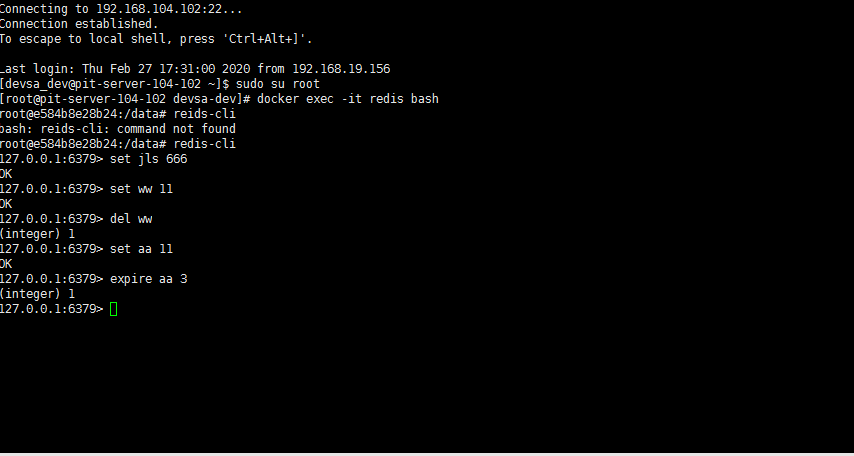
注意:get 操作监听不到消息,set,del ,expire 如果操作成功可以监听到消息,如果操作失败也监听不到消息.
更多命令参考
# 以keyevent订阅库0上的set、get、del、expire多个事件
subscribe __keyevent@0__:set __keyevent@0__:get __keyevent@0__:del __keyevent@0__:expire
# 以keyspace订阅库0上关于key为mykey的所有事件
subscribe __keyspace@0__:mykey模式匹配则使用psubscribe
# 以keyspace订阅库0上关于key为mykey:*的所有事件
psubscribe __keyspace@0__:mykey:*
# 以keyevent、keyspace订阅所有库上的所有事件
psubscribe __key*@*__:*程序实战
使用技术Spring Boot + RedisTemplate
- Redis监听类 RedisExpiredListener
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.Message;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.MessageListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class RedisExpiredListener implements MessageListener {
public final static String LISTENER_PATTERN = "__key*@*__:*";
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message, byte[] bytes) {
// 建议使用: valueSerializer
String body = new String(message.getBody());
String channel = new String(message.getChannel());
System.out.println("onMessage >> " + String.format("channel: %s, body: %s, bytes: %s"
, channel, body, new String(bytes)));
if (body.startsWith("product:")) {
final String productId = body.replace("product:", "");
System.out.println("得到产品id:" + productId);
}
}
}- 启动类 RedisExpiredApplication
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.listener.PatternTopic;
import org.springframework.data.redis.listener.RedisMessageListenerContainer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.listener.Topic;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@SpringBootApplication
public class RedisExpiredApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RedisExpiredApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
@Primary
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate() {
RedisSerializer<String> stringSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(stringSerializer);
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(stringSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(stringSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(stringSerializer);
return redisTemplate;
}
@Bean
public RedisMessageListenerContainer listenerContainer(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnection, Executor executor) {
RedisMessageListenerContainer container = new RedisMessageListenerContainer();
// 设置Redis的连接工厂
container.setConnectionFactory(redisConnection);
// 设置监听使用的线程池
container.setTaskExecutor(executor);
// 设置监听的Topic: PatternTopic/ChannelTopic
Topic topic = new PatternTopic(RedisExpiredListener.LISTENER_PATTERN);
// 设置监听器
container.addMessageListener(new RedisExpiredListener(), topic);
return container;
}
@Bean
public Executor executor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(10);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(20);
executor.setQueueCapacity(100);
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("V-Thread");
// rejection-policy:当pool已经达到max size的时候,如何处理新任务
// CALLER_RUNS:不在新线程中执行任务,而是由调用者所在的线程来执行
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
@Override
public void run(String... strings) throws Exception {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("orderId:123", "过期了是取不到的", 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("初始化设置 key 过期时间 5s");
System.out.println("main 线程休眠10秒");
Thread.sleep(10 * 1000);
System.out.println("main 线程休眠结束:获取key orderId结果为:" + redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("orderId:123"));
}- 配置文件:application.properties
spring.redis.database=0
spring.redis.host=192.168.104.102
spring.redis.port=6378
spring.redis.pool.max-idle=8
spring.redis.pool.min-idle=0
spring.redis.pool.max-active=8
spring.redis.pool.max-wait=-1效果展示:
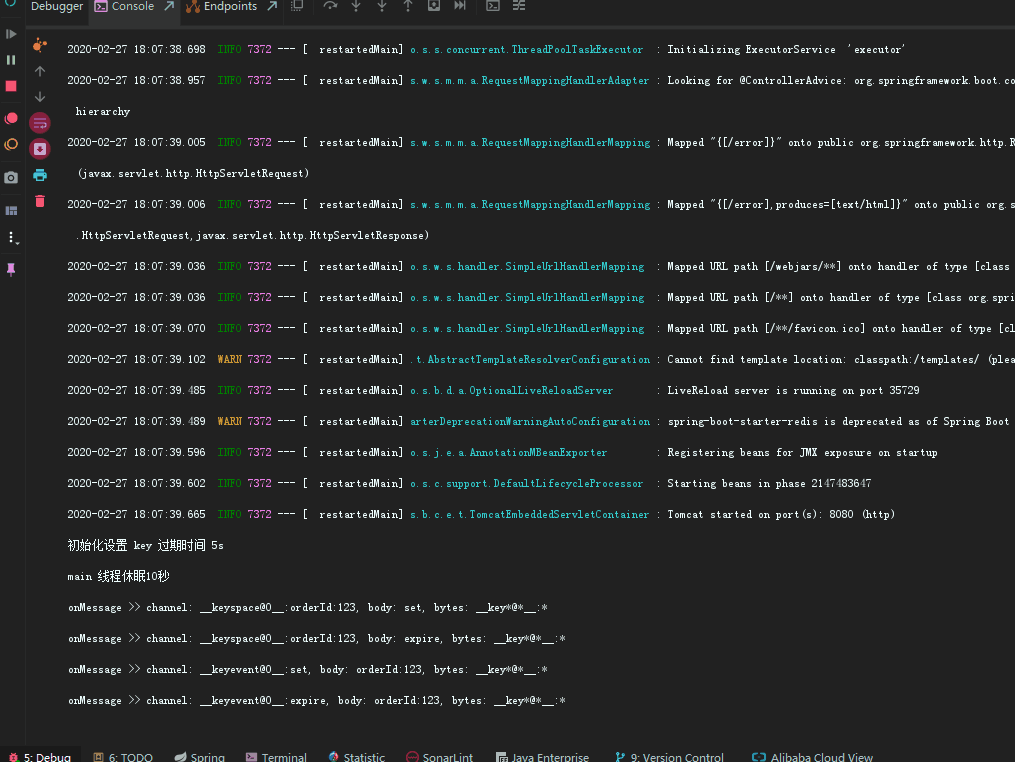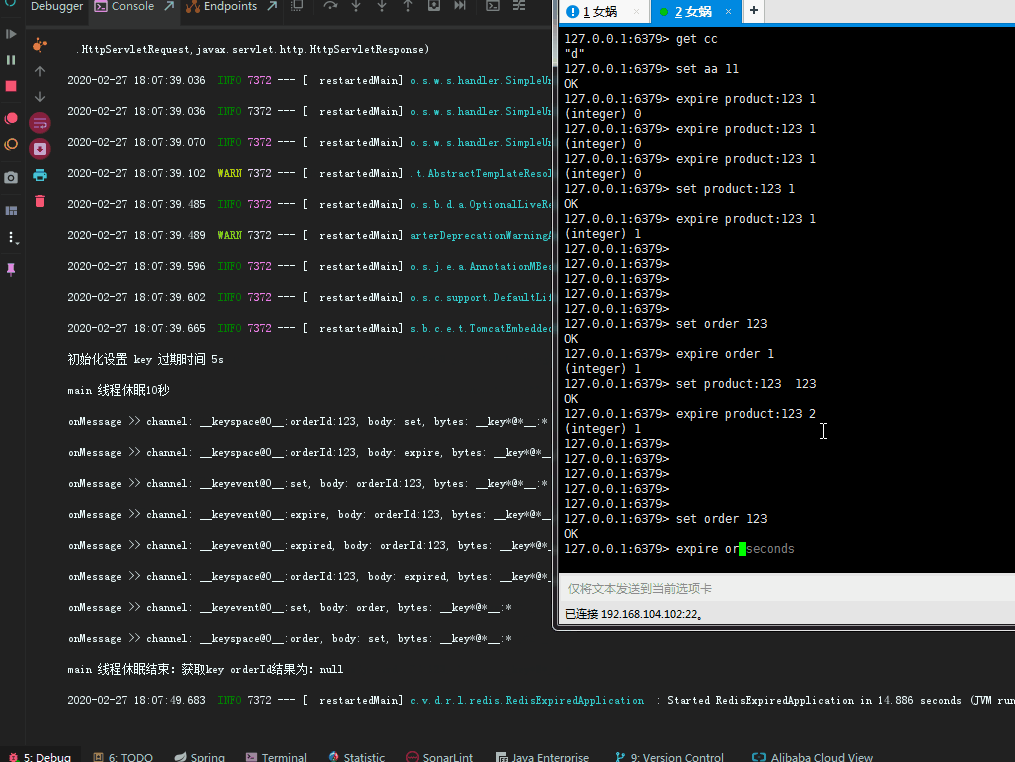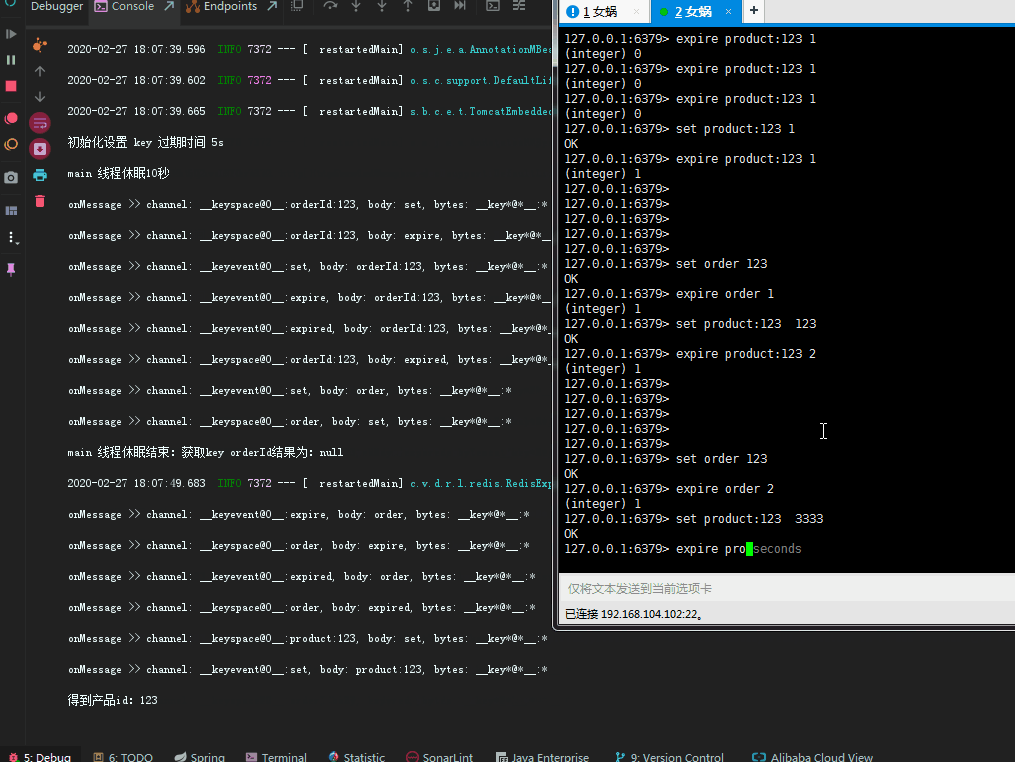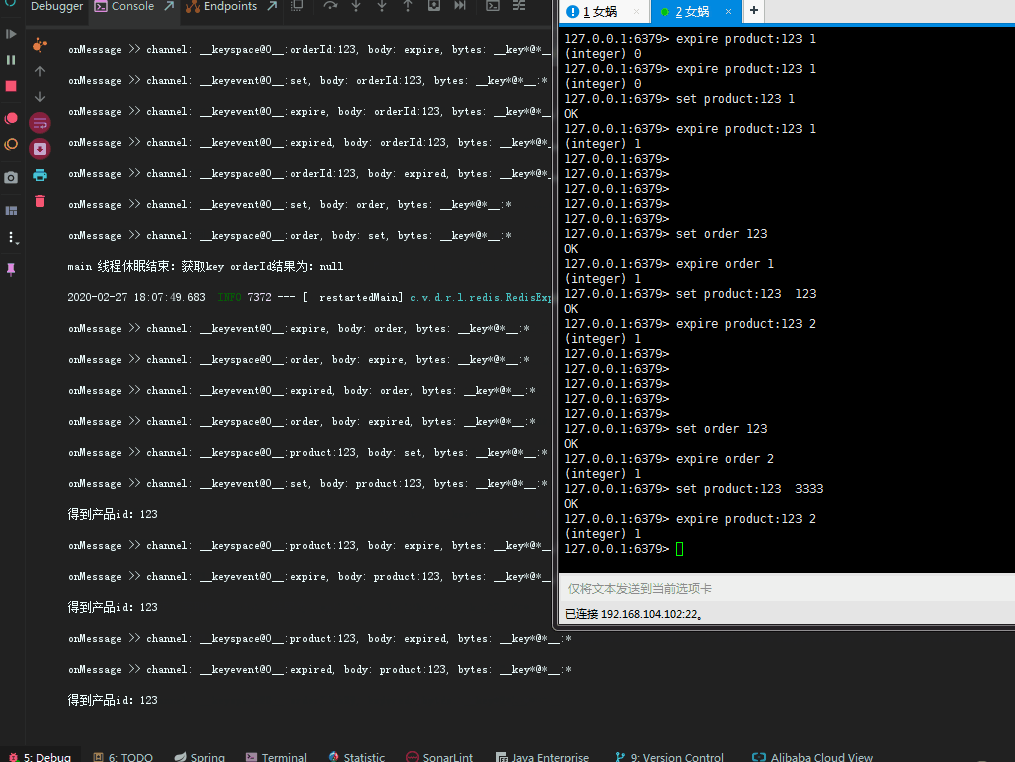
因为redis key 过期之后,其中的value是无法获取到的, 所以在设计key的时候就包含了业务主键id在其中,以此来解决value消失无法处理业务逻辑的情况。到这里,就可以根据具体到期时间执行具体逻辑了。
Redis过期命令设置
# Redis Expire 命令用于设置 key 的过期时间。key 过期后将不再可用。
Expire KEY_NAME TIME_IN_SECONDS
# Redis Expireat 命令用于以 UNIX 时间戳(unix timestamp)格式设置 key 的过期时间。key 过期后将不再可用。
Expireat KEY_NAME TIME_IN_UNIX_TIMESTAMP
# Redis PEXPIREAT 命令用于设置 key 的过期时间,已毫秒计。key 过期后将不再可用。
PEXPIREAT KEY_NAME TIME_IN_MILLISECONDS_IN_UNIX_TIMESTAMP注意事项
因为 Redis 目前的订阅与发布功能采取的是 发送即忘(fire and forget) 策略, 所以如果你的程序需要可靠事件通知(reliable notification of events), 那么目前的键空间通知可能并不适合你:当订阅事件的客户端(服务实例)断线时, 它会丢失所有在断线期间分发给它的事件。并不能确保消息送达。未来有计划允许更可靠的事件传递,但可能这将在更基础的层面上解决,或者为Pub / Sub本身带来可靠性,或者允许Lua脚本拦截Pub / Sub消息来执行诸如推送将事件列入清单。




















