一、前言
本篇博客主要是对Java第二阶段作业进行总结。相较于第一阶段作业,第二阶段作业更多是关于Java的三大特性:封装、继承与多态。第四次作业有三道题,包括7-1 水文数据校验处理、7-2日期问题面对对象设计(聚合一)、7-3 图形继承,涉及的知识点有正则表达式、 StringBuilder用法、类的聚合、类的继承、子类重写父类方法等等,题量虽不多但难度较 大。第五次作业有四道题,包括7-5 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二)、7-4 统计Java程序中关键词的出现次数等,涉及的知识点有类的聚合、Java关键字、正则表达式、Map集合、插入排序、选择排序及冒泡排序三种算法等,题量适中难度适中。第六次作业有六道题,包括7-5 图形继承与多态、7-6 实现图形接口及多态性等,题量虽多但难度不大。通过这几次作业,我进一步的学习了解了Java的三大特性,对Java语法也有进一步的了解。
二、设计与分析
7-2 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一) (35 分)
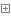
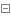
参考题目7-2的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1900,2050] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:

应用程序共测试三个功能:
- 求下n天
- 求前n天
- 求两个日期相差的天数
注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改)
输入格式:
有三种输入方式(以输入的第一个数字划分[1,3]):
- 1 year month day n //测试输入日期的下n天
- 2 year month day n //测试输入日期的前n天
- 3 year1 month1 day1 year2 month2 day2 //测试两个日期之间相差的天数
输出格式:
- 当输入有误时,输出格式如下:
Wrong Format - 当第一个数字为1且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year-month-day- 当第一个数字为2且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year-month-day- 当第一个数字为3且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
天数值我的代码:
1 import java.util.Scanner;
2
3 public class Main {
4 public static void main(String[] args) {
5 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
6 int n = input.nextInt();
7 int year = input.nextInt();
8 int month = input.nextInt();
9 int day = input.nextInt();
10 DateUtil q = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
11 switch (n){
12 case 1:
13 int num = input.nextInt();
14 if (num < 0 || !q.checkInputvalidity()) {
15 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
16 } else {
17 System.out.print(q.getNextNdays(num).showDate());
18 }
19 break;
20 case 2:
21 int num1 = input.nextInt();
22 if (num1 < 0 || !q.checkInputvalidity()) {
23 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
24 } else {
25 System.out.print(q.getPreviousNDays(num1).showDate());
26 }
27 break;
28 case 3:
29 int y = input.nextInt();
30 int m = input.nextInt();
31 int d = input.nextInt();
32 DateUtil p = new DateUtil(y,m,d);
33 if (!q.checkInputvalidity() || !p.checkInputvalidity()) {
34 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
35 } else {
36 System.out.print(q.getDaysofDates(p));
37 }
38 break;
39 default:System.out.print("Wrong Format");break;
40 }
41 }
42
43 }
44
45 class Year{
46 int value;
47 public Year(){
48 }
49 public Year(int value){
50 this.value = value;
51 }
52 public int getValue() {
53 return value;
54 }
55 public void setValue(int value){
56 this.value = value;
57 }
58 public boolean isLeapYear(){
59 if ((value % 4 == 0 && value % 100 != 0) || value % 400 == 0) {
60 return true;
61 } else {
62 return false;
63 }
64 }
65 public boolean validate(){
66 if (value >= 1900 && value <= 2050){
67 return true;
68 }else {
69 return false;
70 }
71 }
72 public void yearIncrement(){
73 value = value + 1;
74 }
75 public void yaerReduction(){
76 value = value - 1;
77 }
78 }
79 class Month{
80 int value;
81 Year year;
82 public Month(){
83 }
84 public Month(int yearValue,int monthValue){
85 this.year = new Year(yearValue);
86 this.value = monthValue;
87 }
88
89 public int getValue() {
90 return value;
91 }
92 public void setValue(int value){
93 this.value = value;
94 }
95 public Year getYear(){
96 return year;
97 }
98 public void setYear(Year year) {
99 this.year = year;
100 }
101 public void resetMin(){
102 value = 1;
103 }
104 public void resetMax(){
105 value = 12;
106 }
107 public boolean validate(){
108 if (value >= 1 && value <=12){
109 return true;
110 }else {
111 return false;
112 }
113 }
114 public void monthIncrement(){
115 value = value + 1;
116 }
117 public void monthReduction(){
118 value = value - 1;
119 }
120 }
121 class Day{
122 int value;
123 Month month;
124 int mon_maxnum[] = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
125 public Day(){
126 }
127 public Day(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue){
128 this.month = new Month(yearValue,monthValue);
129 this.value = dayValue;
130 }
131
132 public int getValue() {
133 return value;
134 }
135 public void setValue(int value){
136 this.value = value;
137 }
138 public Month getMonth(){
139 return month;
140 }
141 public void setMonth(Month value){
142 this.month = value;
143 }
144 public void resetMin(){
145 value = 1;
146 }
147 public void resetMax(){
148 value = mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1];
149 }
150 public boolean validate(){
151 if (this.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()){
152 mon_maxnum[1] = 29;
153 }
154 if (month.getValue() > 12 || month.getValue() < 1){
155 return false;
156 }
157 if (value < 1 || value > mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]){
158 return false;
159 }else {
160 return true;
161 }
162 }
163 public void dayIncrement(){
164 value = value + 1;
165 }
166 public void dayReduction(){
167 value = value - 1;
168 }
169 }
170 class DateUtil{
171 Day day;
172 public DateUtil(){
173 }
174 public DateUtil(int d,int m,int y){
175 this.day = new Day(d,m,y);
176 }
177 public Day getDay(){
178 return day;
179 }
180 public void setDay(Day d){
181 this.day = d;
182 }
183 public boolean checkInputvalidity(){
184 if (day.validate() && day.getMonth().validate() && day.getMonth().getYear().validate()){
185 return true;
186 }else{
187 return false;
188 }
189 }
190 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) {
191 if (date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() < this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
192 return false;
193 } else if (date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() && date.getDay().getMonth().getValue() < this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) {
194 return false;
195 } else if (date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() && date.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() && date.getDay().getValue() < this.getDay().getValue()) {
196 return false;
197 } else {
198 return true;
199 }
200 }
201 public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) {
202 if (date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() && date.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() && date.getDay().getValue() == this.getDay().getValue()) {
203 return true;
204 }else {
205 return false;
206 }
207 }
208
209 public String showDate(){
210 return day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()+"-"+day.getMonth().getValue()+"-"+day.getValue();
211 }
212 public int syts(DateUtil d){
213 int num = 0;
214 int a[] = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
215 int i = 12;
216 while (i > d.getDay().getMonth().getValue()){
217 num = num + a[i-1];
218 i--;
219 }
220 num = num + a[d.getDay().getMonth().getValue()-1]-d.getDay().getValue();
221 if (d.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear() && d.getDay().getMonth().getValue() <= 2){
222 num =num + 1;
223 }
224 return num;
225 }
226 //求下n天
227 public DateUtil getNextNdays(int n){
228 int a[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
229 int y = this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue();
230 int m = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue();
231 int d = this.getDay().getValue();
232 int sum = 0;
233 int num = syts(this);
234 int ynum = 0;
235 int mnum = 0;
236 if (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()){
237 a[2] = 29;
238 }else {
239 a[2]= 28;
240 }
241 if (n > num){//n大于本年剩余天数
242 n = n - num;
243 y ++;
244 if (new Year(y).isLeapYear()){
245 ynum = 366;
246 }else {
247 ynum = 365;
248 }
249 //大于本年剩余天数但小于下一年天数
250 if(n < ynum){
251 int i = 0;
252 for (i = 0 ;i < 12 && sum < n; i++){
253 sum = sum + a[i];
254 }
255 m = i-1;
256 d = n - sum + a[i-1] ;
257 }else if (n > ynum){//大于本年剩余天数且大于下一年天数
258 int j = 0;
259 while (n-ynum > 0){
260 if (new Year(y).isLeapYear()){
261 ynum = 366;
262 }else {
263 ynum = 365;
264 }
265 n=n-ynum;
266 y ++;
267 }
268 for (j = 0; j < 12 && sum < n ; j ++){
269 sum = sum + a[j];
270 }
271 m = j-1;
272 d = n - sum + a[j-1] ;
273 }
274
275 }else { //小于本年剩余天数
276 int k = 0;
277 mnum = a[m]-d;
278 if (n <= mnum){ //小于本月剩余天数
279 d = d + n;
280 }else {
281 n = n - mnum;
282 for (k = m+1;k <= 12 && sum < n ; k ++){
283 sum = sum + a[k];
284 }
285 m = k-1;
286 d = n - sum + a[k-1] ;
287 }
288 }
289 return new DateUtil(y,m,d);
290 }
291 // 求n天前
292 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){
293 int a[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
294 int y = this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue();
295 int m = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue();
296 int d = this.getDay().getValue();
297 int sum = 0;
298 int ynum = 0;
299 int mnum = 0;
300 if (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()){
301 a[2] = 29;
302 }else {
303 a[2]= 28;
304 }
305 if (new Year(y).isLeapYear()){
306 ynum = 366;
307 }else {
308 ynum = 365;
309 }
310 int num = ynum - syts(this);//今年已有多少天
311 //n天前不是本年
312 if (n > num){
313 n = n - num;
314 y --;
315 if (new Year(y).isLeapYear()){
316 ynum = 366;
317 }else {
318 ynum = 365;
319 }
320 if (n > ynum){ //上某一年
321 while (n-ynum >0){
322 if (new Year(y).isLeapYear()){
323 ynum = 366;
324 }else {
325 ynum = 365;
326 }
327 n=n-ynum;
328 y --;
329 }
330 int j = 0;
331 if (new Year(y).isLeapYear()){
332 a[2] = 29;
333 }else {
334 a[2] = 28;
335 }
336 for (j = 12; j > 0 && sum < n ; j --){
337 sum = sum + a[j];
338 }
339 m = j+1;
340 d = sum - n ;
341
342 }else {
343 int j = 0;
344 for (j = 12; j > 0 && sum < n ; j --){
345 sum = sum + a[j];
346 }
347 m = j+1;
348 d = sum - n;
349 }
350 }else { //n天前是本年
351 if (n > d){ //不是本月
352 n = n-d;
353 int k = 0;
354 for (k = m-1; k > 0 && sum < n ; k --){
355 sum = sum + a[k];
356 }
357 m = k + 1;
358 d = sum - n;
359 }else {
360 d = d - n;
361 }
362
363 }
364 return new DateUtil(y,m,d);
365 }
366 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){
367 DateUtil d1 = this;
368 DateUtil d2 = date;
369 int y1 = d1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue();
370 int y2 = d2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue();
371 int anum = 0;
372 int bnum = 0;
373 int ynum = 0;
374 int sum = 0;
375 anum = syts(d1);
376 bnum = syts(d2);
377
378 if (y1 > y2){
379 if (new Year(y1).isLeapYear()){
380 ynum = 366;
381 }else {
382 ynum = 365;
383 }
384 sum = sum + bnum + ynum -anum;
385 y2++;
386 while (y2 <= y1-1){
387 if (new Year(y2).isLeapYear()){
388 ynum = 366;
389 }else {
390 ynum = 365;
391 }
392 sum = sum + ynum;
393 y2++;
394 }
395 }else if (y1 < y2) {
396 if (new Year(y2).isLeapYear()){
397 ynum = 366;
398 }else {
399 ynum = 365;
400 }
401 sum = sum + anum + ynum -bnum;
402 y1++;
403 while (y1 <= y2-1){
404 if (new Year(y1).isLeapYear()){
405 ynum = 366;
406 }else {
407 ynum = 365;
408 }
409 sum = sum + ynum;
410 y1++;
411 }
412 }else {
413 int m1 = d1.getDay().getMonth().getValue();
414 int m2 = d2.getDay().getMonth().getValue();
415
416 if (d1.getDay().getMonth().getValue() < d2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()){
417 sum = d2.getDay().getValue() + d1.getDay().mon_maxnum[d1.getDay().getMonth().getValue()-1] - d1.getDay().getValue();
418 m1++;
419 while(m1 <= m2-1){
420 if (new Year(y1).isLeapYear()){
421 d1.getDay().mon_maxnum[1] = 29;
422 }else {
423 d1.getDay().mon_maxnum[1] = 28;
424 }
425 sum = sum + d1.getDay().mon_maxnum[m1-1];
426 m1++;
427 }
428 }else if (d1.getDay().getMonth().getValue() >d2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()){
429 sum = d1.getDay().getValue() + d2.getDay().mon_maxnum[d2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()-1] - d2.getDay().getValue();
430 m2++;
431 while(m2 <= m1-1){
432 if (new Year(y1).isLeapYear()){
433 d1.getDay().mon_maxnum[1] = 29;
434 }else {
435 d1.getDay().mon_maxnum[1] = 28;
436 }
437 sum = sum + d2.getDay().mon_maxnum[m2-1];
438 m2++;
439 }
440 }else {
441 if (d1.getDay().getValue() > d2.getDay().getValue()){
442 sum = d1.getDay().getValue() - d2.getDay().getValue();
443 }else if (d1.getDay().getValue() < d2.getDay().getValue()){
444 sum = d2.getDay().getValue() - d1.getDay().getValue();
445 }else {
446 sum = 0;
447 }
448 }
449 }
450 return sum;
451 }
452 }View Code
7-5 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二) (40 分)
参考题目7-3的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1820,2020] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:

应用程序共测试三个功能:
- 求下n天
- 求前n天
- 求两个日期相差的天数
注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改)
输入格式:
有三种输入方式(以输入的第一个数字划分[1,3]):
- 1 year month day n //测试输入日期的下n天
- 2 year month day n //测试输入日期的前n天
- 3 year1 month1 day1 year2 month2 day2 //测试两个日期之间相差的天数
输出格式:
- 当输入有误时,输出格式如下:
Wrong Format - 当第一个数字为1且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year1-month1-day1 next n days is:year2-month2-day2- 当第一个数字为2且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year1-month1-day1 previous n days is:year2-month2-day2- 当第一个数字为3且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
The days between year1-month1-day1 and year2-month2-day2 are:值我的代码:


1 import java.util.Scanner;
2
3 public class Main {
4 public static void main(String[] args) {
5 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
6 int n = input.nextInt();
7 int year = input.nextInt();
8 int month = input.nextInt();
9 int day = input.nextInt();
10 DateUtil q = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
11 switch (n){
12 case 1:
13 int num = input.nextInt();
14 if (num < 0 || !q.checkInputvalidity()) {
15 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
16 } else {
17 System.out.print(q.showDate()+" next "+num+" days is:"+ q.getNextNdays(num).showDate());
18 }
19 break;
20 case 2:
21 int num1 = input.nextInt();
22 if (num1 < 0 || !q.checkInputvalidity()) {
23 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
24 } else {
25 System.out.print(q.showDate()+" previous "+num1+" days is:"+ q.getPreviousNDays(num1).showDate());
26 }
27 break;
28 case 3:
29 int y = input.nextInt();
30 int m = input.nextInt();
31 int d = input.nextInt();
32 DateUtil p = new DateUtil(y,m,d);
33 if (!q.checkInputvalidity() || !p.checkInputvalidity()) {
34 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
35 } else {
36 System.out.print("The days between "+q.showDate()+" and "+p.showDate()+" are:"+q.getDaysofDates(p));
37 }
38 break;
39 default:System.out.print("Wrong Format");break;
40 }
41 }
42
43 }
44
45 class Year{
46 int value;
47 public Year(){
48 }
49 public Year(int value){
50 this.value = value;
51 }
52 public int getValue() {
53 return value;
54 }
55 public void setValue(int value){
56 this.value = value;
57 }
58 public boolean isLeapYear(){
59 if ((value % 4 == 0 && value % 100 != 0) || value % 400 == 0) {
60 return true;
61 } else {
62 return false;
63 }
64 }
65 public boolean validate(){
66 if (value >= 1820 && value <= 2020){
67 return true;
68 }else {
69 return false;
70 }
71 }
72 public void yearIncrement(){
73 value = value + 1;
74 }
75 public void yaerReduction(){
76 value = value - 1;
77 }
78 }
79 class Month{
80 int value;
81 public Month(){
82 }
83 public Month(int Value){
84 this.value = Value;
85 }
86
87 public int getValue() {
88 return value;
89 }
90 public void setValue(int value){
91 this.value = value;
92 }
93
94 public void resetMin(){
95 value = 1;
96 }
97 public void resetMax(){
98 value = 12;
99 }
100 public boolean validate(){
101 if (value >= 1 && value <=12){
102 return true;
103 }else {
104 return false;
105 }
106 }
107 public void monthIncrement(){
108 value = value + 1;
109 }
110 public void monthReduction(){
111 value = value - 1;
112 }
113 }
114 class Day{
115 int value;
116 public Day(){
117 }
118 public Day(int Value){
119 this.value = Value;
120 }
121 public int getValue() {
122 return value;
123 }
124 public void setValue(int value){
125 this.value = value;
126 }
127 public void dayIncrement(){
128 value = value + 1;
129 }
130 public void dayReduction(){
131 value = value - 1;
132 }
133 }
134 class DateUtil{
135 Year year;
136 Month month;
137 Day day;
138 int mon_maxnum[] = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
139 public DateUtil(){
140 }
141 public DateUtil(int y,int m,int d){
142 this.year = new Year(y);
143 this.month = new Month(m);
144 this.day = new Day(d);
145 }
146
147 public Year getYear() {
148 return year;
149 }
150 public void setYear(Year year) {
151 this.year = year;
152 }
153 public Month getMonth() {
154 return month;
155 }
156 public void setMonth(Month month) {
157 this.month = month;
158 }
159 public Day getDay(){
160 return day;
161 }
162 public void setDay(Day day){
163 this.day = day;
164 }
165 public void setDayMin(){
166 day.setValue(1);
167 }
168 public void setDayMax(){
169 day.setValue(mon_maxnum[this.month.getValue()]);
170 }
171 public boolean checkInputvalidity(){
172 if (this.getYear().isLeapYear()){
173 mon_maxnum[1] = 29;
174 }
175 if (month.getValue() > 12 || month.getValue() < 1){
176 return false;
177 }
178 if (this.getDay().getValue() > 0 && this.getDay().getValue() <= this.mon_maxnum[this.getMonth().getValue()-1] && this.getMonth().validate() && this.getYear().validate()){
179 return true;
180 }else{
181 return false;
182 }
183 }
184 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) {
185 if (date.getYear().getValue() < this.getYear().getValue()) {
186 return false;
187 } else if (date.getYear().getValue() == this.getYear().getValue() && date.getMonth().getValue() < this.getMonth().getValue()) {
188 return false;
189 } else if (date.getYear().getValue() == this.getYear().getValue() && date.getMonth().getValue() == this.getMonth().getValue() && date.getDay().getValue() < this.getDay().getValue()) {
190 return false;
191 } else {
192 return true;
193 }
194 }
195 public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) {
196 if (date.getYear().getValue() == this.getYear().getValue() && date.getMonth().getValue() == this.getMonth().getValue() && date.getDay().getValue() == this.getDay().getValue()) {
197 return true;
198 }else {
199 return false;
200 }
201 }
202
203 public String showDate(){
204 return this.getYear().getValue()+"-"+this.getMonth().getValue()+"-"+day.getValue();
205 }
206 public int syts(DateUtil d){
207 int num = 0;
208 int a[] = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
209 int i = 12;
210 while (i > d.getMonth().getValue()){
211 num = num + a[i-1];
212 i--;
213 }
214 num = num + a[d.getMonth().getValue()-1]-d.getDay().getValue();
215 if (d.getYear().isLeapYear() && d.getMonth().getValue() <= 2){
216 num =num + 1;
217 }
218 return num;
219 }
220 //求下n天
221 public DateUtil getNextNdays(int n){
222 int a[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
223 int y = this.getYear().getValue();
224 int m = this.getMonth().getValue();
225 int d = this.getDay().getValue();
226 int sum = 0;
227 int num = syts(this);
228 int ynum = 0;
229 int mnum = 0;
230 if (this.getYear().isLeapYear()){
231 a[2] = 29;
232 }else {
233 a[2]= 28;
234 }
235 if (n > num){//n大于本年剩余天数
236 n = n - num;
237 y ++;
238 if (new Year(y).isLeapYear()){
239 ynum = 366;
240 }else {
241 ynum = 365;
242 }
243 //大于本年剩余天数但小于下一年天数
244 if(n < ynum){
245 int i = 0;
246 for (i = 0 ;i <= 12 && sum < n; i++){
247 sum = sum + a[i];
248 }
249 m = i-1;
250 d = n - sum + a[i-1] ;
251 }else {
252 int j = 0;
253 while (n-ynum > 0){
254 if (new Year(y).isLeapYear()){
255 ynum = 366;
256 }else {
257 ynum = 365;
258 }
259 n=n-ynum;
260 y ++;
261 }
262 if (new Year(y).isLeapYear()){
263 a[2] = 29;
264 }else {
265 a[2] = 28;
266 }
267 for (j = 0; j <= 12 && sum < n ; j ++){
268 sum = sum + a[j];
269 }
270 m = j - 1;
271 d = n - sum + a[j-1] ;
272 }
273
274 }else { //小于本年剩余天数
275 int k = 0;
276 mnum = a[m]-d;
277 if (n <= mnum){ //小于本月剩余天数
278 d = d + n;
279 }else {
280 n = n - mnum;
281 if (new Year(y).isLeapYear()){
282 a[2] = 29;
283 }else {
284 a[2] = 28;
285 }
286 for (k = m+1;k <= 12 && sum < n ; k ++){
287 sum = sum + a[k];
288 }
289 m = k-1;
290 d = n - sum + a[k-1] ;
291 }
292 }
293 return new DateUtil(y,m,d);
294 }
295 // 求n天前
296 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){
297 int a[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
298 int y = this.getYear().getValue();
299 int m = this.getMonth().getValue();
300 int d = this.getDay().getValue();
301 int sum = 0;
302 int ynum = 0;
303 int mnum = 0;
304 if (this.getYear().isLeapYear()){
305 a[2] = 29;
306 }else {
307 a[2]= 28;
308 }
309 if (new Year(y).isLeapYear()){
310 ynum = 366;
311 }else {
312 ynum = 365;
313 }
314 int num = ynum - syts(this);//今年已有多少天
315 //n天前不是本年
316 if (n > num){
317 n = n - num;
318 y --;
319 if (new Year(y).isLeapYear()){
320 ynum = 366;
321 }else {
322 ynum = 365;
323 }
324 if (n > ynum){ //上某一年
325 while (n-ynum >0){
326 if (new Year(y).isLeapYear()){
327 ynum = 366;
328 }else {
329 ynum = 365;
330 }
331 n=n-ynum;
332 y --;
333 }
334 int j = 0;
335 if (new Year(y).isLeapYear()){
336 a[2] = 29;
337 }else {
338 a[2] = 28;
339 }
340 for (j = 12; j > 0 && sum < n ; j --){
341 sum = sum + a[j];
342 }
343 m = j+1;
344 d = sum - n ;
345
346 }else {
347 int j = 0;
348 for (j = 12; j > 0 && sum < n ; j --){
349 sum = sum + a[j];
350 }
351 m = j+1;
352 d = sum - n;
353 }
354 }else { //n天前是本年
355 if (n > d){ //不是本月
356 n = n-d;
357 int k = 0;
358 for (k = m-1; k > 0 && sum < n ; k --){
359 sum = sum + a[k];
360 }
361 m = k + 1;
362 d = sum - n;
363 }else {
364 d = d - n;
365 }
366
367 }
368 return new DateUtil(y,m,d);
369 }
370 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){
371 DateUtil d1 = this;
372 DateUtil d2 = date;
373 int y1 = d1.getYear().getValue();
374 int y2 = d2.getYear().getValue();
375 int anum = 0;
376 int bnum = 0;
377 int ynum = 0;
378 int sum = 0;
379 anum = syts(d1);
380 bnum = syts(d2);
381
382 if (y1 > y2){
383 if (new Year(y1).isLeapYear()){
384 ynum = 366;
385 }else {
386 ynum = 365;
387 }
388 sum = sum + bnum + ynum -anum;
389 y2++;
390 while (y2 <= y1-1){
391 if (new Year(y2).isLeapYear()){
392 ynum = 366;
393 }else {
394 ynum = 365;
395 }
396 sum = sum + ynum;
397 y2++;
398 }
399 }else if (y1 < y2) {
400 if (new Year(y2).isLeapYear()){
401 ynum = 366;
402 }else {
403 ynum = 365;
404 }
405 sum = sum + anum + ynum -bnum;
406 y1++;
407 while (y1 <= y2-1){
408 if (new Year(y1).isLeapYear()){
409 ynum = 366;
410 }else {
411 ynum = 365;
412 }
413 sum = sum + ynum;
414 y1++;
415 }
416 }else {
417 int m1 = d1.getMonth().getValue();
418 int m2 = d2.getMonth().getValue();
419
420 if (d1.getMonth().getValue() < d2.getMonth().getValue()){
421 sum = d2.getDay().getValue() + d1.mon_maxnum[d1.getMonth().getValue()-1] - d1.getDay().getValue();
422 m1++;
423 while(m1 <= m2-1){
424 if (new Year(y1).isLeapYear()){
425 d1.mon_maxnum[1] = 29;
426 }else {
427 d1.mon_maxnum[1] = 28;
428 }
429 sum = sum + d1.mon_maxnum[m1-1];
430 m1++;
431 }
432 }else if (d1.getMonth().getValue() >d2.getMonth().getValue()){
433 sum = d1.getDay().getValue() + d2.mon_maxnum[d2.getMonth().getValue()-1] - d2.getDay().getValue();
434 m2++;
435 while(m2 <= m1-1){
436 if (new Year(y1).isLeapYear()){
437 d1.mon_maxnum[1] = 29;
438 }else {
439 d1.mon_maxnum[1] = 28;
440 }
441 sum = sum + d2.mon_maxnum[m2-1];
442 m2++;
443 }
444 }else {
445 if (d1.getDay().getValue() > d2.getDay().getValue()){
446 sum = d1.getDay().getValue() - d2.getDay().getValue();
447 }else if (d1.getDay().getValue() < d2.getDay().getValue()){
448 sum = d2.getDay().getValue() - d1.getDay().getValue();
449 }else {
450 sum = 0;
451 }
452 }
453 }
454 return sum;
455 }
456 }View Code
(1)7-2日期问题面对对象设计(聚合一)和7-5 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二)两种日期类聚合设计的优劣比较:
两道题的圈复杂度:两种日期聚合设计的圈复杂度差不多


两道题的类图:


题目7-2 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)是一层一层聚合,DateUtil与Day聚合,Day与Month聚合,Month与Year聚合。而题目7-5 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二)是DateUtil分别与Day,Month,Year聚合。前者的访问方式是通过day的访问器方法一层一层访问,后者是直接访问DateUtil来调用。7-2的设计类间的关系更加紧密,但如果修改了其中一个类,其他类都会受到影响,修改起来工程更大。而7-5的设计修改起来更加方便,不需要修改所有的类,耦合度低。题目7-5是对题目7-2的改进。
(2)题目集4(7-3)、题目集6(7-5、7-6)三种渐近式图形继承设计的思路与技术运用(封装、继承、多态、接口等)
7-3 图形继承 (15 分)
编写程序,实现图形类的继承,并定义相应类对象并进行测试。
- 类Shape,无属性,有一个返回0.0的求图形面积的公有方法
public double getArea();//求图形面积 - 类Circle,继承自Shape,有一个私有实型的属性radius(半径),重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求圆的面积
- 类Rectangle,继承自Shape,有两个私有实型属性width和length,重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求矩形的面积
- 类Ball,继承自Circle,其属性从父类继承,重写父类求面积方法,求球表面积,此外,定义一求球体积的方法
public double getVolume();//求球体积 - 类Box,继承自Rectangle,除从父类继承的属性外,再定义一个属性height,重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求立方体表面积,此外,定义一求立方体体积的方法
public double getVolume();//求立方体体积 - 注意:
- 每个类均有构造方法,且构造方法内必须输出如下内容:
Constructing 类名 - 每个类属性均为私有,且必须有getter和setter方法(可用Eclipse自动生成)
- 输出的数值均保留两位小数
主方法内,主要实现四个功能(1-4): 从键盘输入1,则定义圆类,从键盘输入圆的半径后,主要输出圆的面积; 从键盘输入2,则定义矩形类,从键盘输入矩形的宽和长后,主要输出矩形的面积; 从键盘输入3,则定义球类,从键盘输入球的半径后,主要输出球的表面积和体积; 从键盘输入4,则定义立方体类,从键盘输入立方体的宽、长和高度后,主要输出立方体的表面积和体积;
假如数据输入非法(包括圆、矩形、球及立方体对象的属性不大于0和输入选择值非1-4),系统输出Wrong Format
输入格式:
共四种合法输入
- 1 圆半径
- 2 矩形宽、长
- 3 球半径
- 4 立方体宽、长、高
输出格式:
按照以上需求提示依次输出
我的代码:


1 import java.util.Scanner;
2
3 public class Main {
4
5 public static void main(String[] args) {
6 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
7 int n = input.nextInt();
8 if (n < 1 || n > 4){
9 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
10 }else {
11 switch (n){
12 case 1:
13 double radius = input.nextDouble();
14 if (Input(radius)){
15 Circle c = new Circle();
16 c.setRadius(radius);
17 System.out.printf("Circle's area:%.2f",c.getArea());
18 }
19 break;
20 case 2:
21 double width = input.nextDouble();
22 double length = input.nextDouble();
23 if (Input(width) && Input(length)){
24 Rectangle r = new Rectangle();
25 r.setLength(length);
26 r.setWidth(width);
27 //System.out.printf("Rectangle's area:%.2f",r.getArea());
28 System.out.print(String.format("Rectangle's area:%.2f",r.getArea()));
29 }
30 break;
31 case 3:
32 double radius1 = input.nextDouble();
33 if (Input(radius1)){
34 Ball b = new Ball();
35 b.setRadius(radius1);
36 System.out.printf("Ball's surface area:%.2f\n",b.getArea());
37 System.out.printf("Ball's volume:%.2f",b.getVolume());
38 }
39 break;
40 case 4:
41 double width1 = input.nextDouble();
42 double length1 = input.nextDouble();
43 double height = input.nextDouble();
44 if (Input(width1) && Input(length1) && Input(height)){
45 Box box = new Box();
46 box.setWidth(width1);
47 box.setLength(length1);
48 box.setHeight(height);
49 System.out.printf("Box's surface area:%.2f\n",box.getArea());
50 System.out.printf("Box's volume:%.2f",box.getVolume());
51 }
52 break;
53 default:break;
54 }
55
56 }
57
58 }
59 public static boolean Input(double n){
60 if (n < 0 ) {
61 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
62 return false;
63 }
64 return true;
65 }
66 }
67
68 class Shape{
69 Shape() {
70 System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
71 }
72 public double getArea(){
73 return 0.0;
74 }
75 }
76 class Circle extends Shape{
77
78 private double radius;
79 Circle(){
80 System.out.println("Constructing Circle");
81 }
82 public double getRadius() {
83 return radius;
84 }
85 public void setRadius(double radius) {
86 this.radius = radius;
87 }
88
89 @Override
90 public double getArea() {
91 return radius * radius * Math.PI;
92 }
93 }
94 class Rectangle extends Shape{
95 private double width;
96 private double length;
97 public Rectangle(){
98 System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle");
99 }
100 public double getWidth() {
101 return width;
102 }
103 public void setWidth(double width) {
104 this.width = width;
105 }
106 public double getLength() {
107 return length;
108 }
109 public void setLength(double length) {
110 this.length = length;
111 }
112 @Override
113 public double getArea() {
114 return width * length;
115 }
116 }
117
118 class Ball extends Circle{
119 public Ball(){
120 System.out.println("Constructing Ball");
121 }
122 @Override
123 public double getArea() {
124 return 4.0 * Math.PI * super.getRadius() * super.getRadius();
125 }
126 public double getVolume(){
127 return 4.0/3.0 * Math.PI * super.getRadius() * super.getRadius() * super.getRadius();
128 }
129 }
130
131 class Box extends Rectangle{
132 public Box(){
133 System.out.println("Constructing Box");
134 }
135 private double height;
136
137 public double getHeight() {
138 return height;
139 }
140 public void setHeight(double height){
141 this.height = height;
142 }
143 @Override
144 public double getArea() {
145 return ((super.getWidth() * super.getLength()) + (height * super.getWidth()) +(height * super.getLength())) * 2;
146 }
147 public double getVolume(){
148 return super.getWidth() * super.getLength() * height;
149 //return super.getArea() * height;
150 }
151 }View Code
7-5 图形继承与多态 (50 分)
掌握类的继承、多态性及其使用方法。具体需求参见作业指导书。
输入格式:
从键盘首先输入三个整型值(例如a b c),分别代表想要创建的Circle、Rectangle及Triangle对象的数量,然后根据图形数量继续输入各对象的属性值(均为实型数),数与数之间可以用一个或多个空格或回车分隔。
输出格式:
- 如果图形数量非法(小于0)或图形属性值非法(数值小于0以及三角形三边关系),则输出
Wrong Format。 - 如果输入合法,则正常输出,输出内容如下(输出格式见输入输出示例):
- 各个图形的面积;
- 所有图形的面积总和;
- 排序后的各个图形面积;
- 再次所有图形的面积总和。
我的代码:


1 import java.util.*;
2 import java.util.ArrayList;
3 public class Main {
4 public static void main(String args[]) {
5 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
6 ArrayList<Double>area = new ArrayList<Double>();
7 int num1 = input.nextInt();
8 int num2 = input.nextInt();
9 int num3 = input.nextInt();
10 if(num1 < 0 || num2 < 0 || num3 < 0 ){
11 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
12 System.exit(0);
13 }
14 Shape []c = new Circle[num1];
15 Shape []r = new Rectangle[num2];
16 Shape []t = new Triangle[num3];
17 for (int i = 0 ; i < num1; i ++ ){
18 double radius = input.nextDouble();
19 c[i] = new Circle(radius);
20 if(!c[i].validate()){
21 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
22 System.exit(0);
23 }
24 area.add(c[i].getArea());
25 }
26 for (int i = 0 ; i < num2; i ++ ){
27 double width = input.nextDouble();
28 double length = input.nextDouble();
29 r[i] = new Rectangle(width,length);
30 if(!r[i].validate()){
31 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
32 System.exit(0);
33 }
34 area.add(r[i].getArea());
35 }
36 for (int i = 0 ; i < num3; i ++ ){
37 double side1 = input.nextDouble();
38 double side2 = input.nextDouble();
39 double side3 = input.nextDouble();
40 t[i] = new Triangle(side1,side2,side3);
41 if(!t[i].validate()){
42 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
43 System.exit(0);
44 }
45 area.add(t[i].getArea());
46 }
47 output(area);
48 }
49
50 public static String output(ArrayList<Double>area){
51 System.out.println("Original area:");
52 OpArea(area);
53 OpSum(area);
54 System.out.println("\nSorted area:");
55 Collections.sort(area);
56 OpArea(area);
57 OpSum(area);
58 return String.valueOf(true);
59 }
60 public static void OpArea(ArrayList<Double>area){
61 for (int i = 0 ; i < area.size() ; i ++){
62 System.out.printf("%.2f ",area.get(i));
63 }
64 }
65 public static void OpSum(ArrayList<Double>area){
66 double sum = 0;
67 for (int i = 0 ; i < area.size() ; i ++){
68 sum = area.get(i)+sum;
69 }
70 System.out.printf("\nSum of area:%.2f",sum);
71 }
72
73 }
74 abstract class Shape{
75 public abstract double getArea();
76 public abstract boolean validate();
77 public String toString(){
78 return String.valueOf(true);
79 }
80 }
81 //圆
82 class Circle extends Shape{
83 double radius;
84 Circle(double radius){
85 this.radius = radius;
86 }
87 public double getRadius() {
88 return radius;
89 }
90 public void setRadius(double radius) {
91 this.radius = radius;
92 }
93 @Override
94 public double getArea() {
95 return this.radius * this.radius *Math.PI;
96 }
97 @Override
98 public boolean validate(){
99 return this.radius > 0;
100 }
101 }
102 //矩形
103 class Rectangle extends Shape{
104 double width;
105 double length;
106 Rectangle(double width , double length){
107 this.width = width;
108 this.length = length;
109 }
110 public double getWidth() {
111 return width;
112 }
113 public void setWidth(double width) {
114 this.width = width;
115 }
116 public double getLength() {
117 return length;
118 }
119 public void setLength(double length) {
120 this.length = length;
121 }
122
123 @Override
124 public double getArea() {
125 return this.width * this.length;
126 }
127
128 @Override
129 public boolean validate() {
130 return this.width > 0 && this.length > 0;
131 }
132 }
133 //三角形
134 class Triangle extends Shape{
135 double side1;
136 double side2;
137 double side3;
138 Triangle(double side1,double side2,double side3){
139 this.side1 = side1;
140 this.side2 = side2;
141 this.side3 = side3;
142 }
143 public double getSide1() {
144 return side1;
145 }
146 public double getSide2() {
147 return side2;
148 }
149 public double getSide3() {
150 return side3;
151 }
152 public void setSide1(double side1) {
153 this.side1 = side1;
154 }
155 public void setSide2(double side2) {
156 this.side2 = side2;
157 }
158 public void setSide3(double side3) {
159 this.side3 = side3;
160 }
161
162 @Override
163 public double getArea() {
164 double p = 0;
165 p = (side1 + side2 + side3) / 2;
166 return Math.sqrt(p * (p - side1) * (p - side2) * (p - side3));
167 }
168
169 @Override
170 public boolean validate() {
171 return (this.side1 > 0) && (this.side2 > 0) &&(this.side3 > 0) && (side1 + side2 > side3) && (side1 + side3 > side2) && (side2 + side3 > side1);
172 }
173 }View Code
7-6 实现图形接口及多态性
编写程序,使用接口及类实现多态性,类图结构如下所示:

其中:
- GetArea为一个接口,无属性,只有一个GetArea(求面积)的抽象方法;
- Circle及Rectangle分别为圆类及矩形类,分别实现GetArea接口
- 要求:在Main类的主方法中分别定义一个圆类对象及矩形类对象(其属性值由键盘输入),使用接口的引用分别调用圆类对象及矩形类对象的求面积的方法,直接输出两个图形的面积值。(要求只保留两位小数)
输入格式:
从键盘分别输入圆的半径值及矩形的宽、长的值,用空格分开。
输出格式:
- 如果输入的圆的半径值及矩形的宽、长的值非法(≤0),则输出
Wrong Format - 如果输入合法,则分别输出圆的面积和矩形的面积值(各占一行),保留两位小数。
我的代码:


1 import java.util.*;
2 public class Main {
3 public static void main(String args[]) {
4 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
5 double radius = input.nextDouble();
6 double width = input.nextDouble();
7 double length = input.nextDouble();
8 if (radius <= 0 || width <=0 || length <= 0){
9 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
10 System.exit(0);
11 }
12 GetArea c = new Circle(radius);
13 GetArea r = new Rectangle(width,length);
14 System.out.printf("%.2f\n",c.getArea());
15 System.out.printf("%.2f",r.getArea());
16 }
17 }
18
19 interface GetArea{
20 public abstract double getArea();
21 }
22 class Circle implements GetArea{
23 double radius;
24 Circle(){
25 }
26 Circle(double radius){
27 this.radius = radius;
28 }
29 public double getRadius() {
30 return radius;
31 }
32 public void setRadius(double radius) {
33 this.radius = radius;
34 }
35 public double getArea(){
36 return this.radius * this.radius * Math.PI;
37 }
38 }
39 class Rectangle implements GetArea {
40 double width;
41 double length;
42 Rectangle() {
43 }
44 Rectangle(double width, double length) {
45 this.width = width;
46 this.length = length;
47 }
48
49 public double getWidth() {
50 return width;
51 }
52 public double getLength() {
53 return length;
54 }
55 public void setWidth(double width) {
56 this.width = width;
57 }
58 public void setLength(double length) {
59 this.length = length;
60 }
61 public double getArea() {
62 return this.width * this.length;
63 }
64 }View Code
三种图形继承设计的报表:



由图可知,题目集4(7-3)的最大全圈复杂度18,平均圈复杂度1.73,题目集6(7-5)最大全圈复杂度10,平均圈复杂度2,题目集6(7-6)最大全圈复杂度4,平均圈复杂度1.23 。7-6的圈复杂度最低,7-3的圈复杂度最高。
三种图形继承设计的类图:
7-3

7-4、7-5


题目集4(7-3)主要用的是类的封装与继承。Shape类中有一个有一个返回0.0的求图形面积的公有方法。Circle类继承Shape类,Rectangle类继承Shape类,Ball类继承Circle类,Box类继承自Rectangle。每个类都有构造方法,属性均为私有。Circle类和Rectangle类通过重写父类中的方法来求图形面积,Ball类和Box类通过重写父类的面积方法来求图形表面积。可以看出使用继承能提高效率,提高了代码的复用性。
题目集6(7-5)相比题目集4(7-3)多了多态的使用。采用的是抽象类定义、实体类构建的方式。Shape 为抽象类,其中包含抽象的求面积的方法,判断数据合理性的方法和将其他数据类型转换为字符串String类型的方法。Circle、Rectangle 及 Triangle 为实体类继承自Shape类,子类通过重写父类的抽象方法求图形面积。这道题运用了类的封装、继承与多态。
题目集6(7-6)中GetArea为一个接口,无属性,只有一个GetArea(求面积)的抽象方法,Circle及Rectangle分别实现GetArea接口,使用了接口中求面积的方法。这题主要体现了接口的使用。
(3)对三次题目集中用到的正则表达式技术的分析总结
题目集4(7-1 水文数据校验及处理)中运用到的正则表达式:
运用“\\|”将数据一个一个切割开来
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("\\|");题目集5(7-4 统计Java程序中关键词的出现次数 )中运用到的正则表达式:
这道题的正则表达式是这三个题目集中最难的也是最多的,要考虑输入源码中单行注释多行注释,字符串等情况。我先用正则表达式判断把输入案例中所有不是代码的剔除再进行关键字的判断。
//去掉字符串和单行注释
str.append(s.replaceAll(".*//.*",""));s = s.replaceAll("\"(.*?)\""," "); //去掉字符串
s = s.replaceAll("/\\*.*?\\*/"," "); //去掉/* */多行注释
s = s.replaceAll("\\p{P}"," "); //去掉所有标点符号
s = s.replaceAll("\\s+"," "); //去掉空白字符题目集6(7-1 正则表达式训练-QQ号校验)中运用到的正则表达式:
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("^[1-9]{1}[\\d]{4,14}$");
Matcher m = p.matcher(str);题目集6(7-3 正则表达式训练-验证码校验)中运用到的正则表达式:
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("^([\\d]|[A-Z[a-z]]){4}$");
Matcher m = p.matcher(str);题目集6(7-4 正则表达式训练-学号校验)中运用到的正则表达式:
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("^(2020){1}(1[1-7]|61|7[1-3]|8[1-2])([0-3][1-9]|40|30|20|10)$");
Matcher m = p.matcher(str);题目集6中涉及的正则表达式较为简单,但在做题时也需考虑全面,不要漏了任何一种情况。
(4)题目集5(7-4)中Java集合框架应用的分析总结
7-4 统计Java程序中关键词的出现次数 (25 分)
编写程序统计一个输入的Java源码中关键字(区分大小写)出现的次数。说明如下:
- Java中共有53个关键字(自行百度)
- 从键盘输入一段源码,统计这段源码中出现的关键字的数量
- 注释中出现的关键字不用统计
- 字符串中出现的关键字不用统计
- 统计出的关键字及数量按照关键字升序进行排序输出
- 未输入源码则认为输入非法
输入格式:
输入Java源码字符串,可以一行或多行,以exit行作为结束标志
输出格式:
- 当未输入源码时,程序输出
Wrong Format - 当没有统计数据时,输出为空
- 当有统计数据时,关键字按照升序排列,每行输出一个关键字及数量,格式为
数量\t关键字
我的代码:


1 import java.util.*;
2 import java.util.regex.Pattern;
3 import java.util.Map;
4 import java.util.TreeMap;
5 public class Main {
6 public static void main(String args[]) {
7 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
8 int count;
9 String[] key = {"abstract","assert","boolean","break","byte","case","catch",
10 "char","class","const","continue","default","do","double","else",
11 "enum","extends","false","final","finally","float",
12 "for","goto","if","implements","import","instanceof",
13 "int","interface","long","native","new","null","package",
14 "private","protected","public","return","short","static",
15 "strictfp","super","switch","synchronized","this","throw",
16 "throws","transient","true","try","void","volatile","while"};
17
18 Map<String,Integer>map = new TreeMap<String,Integer>();
19 Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
20 // Iterator<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> iter = map.entrySet().iterator();
21 String s ;
22 StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
23 while(!(s = input.nextLine().trim()).equals("exit")){
24 // if(s.matches(".*//.*")){
25 // continue;
26 // }; //去掉字符串和单行注释
27 str.append(s.replaceAll(".*//.*",""));
28 str.append(" ");
29 }
30 s = str.toString();
31 if(s.isEmpty()){
32 System.out.println("Wrong Format");
33 System.exit(0);
34 }
35
36 s = s.replaceAll("\"(.*?)\""," ");
37 s = s.replaceAll("/\\*.*?\\*/"," ");
38 s=s.replaceAll("\\p{P}"," ");
39 s = s.replaceAll("\\s+"," ");
40 Pattern p = Pattern.compile(" ");
41 String[] st = p.split(s);
42 for(int i = 0 ;i < st.length ; i ++){
43 for(int j = 0 ; j < key.length ; j ++ ){
44 if(st[i].equals(key[j])){
45 map.put(key[j],0);
46 }
47 }
48 }
49 for(int i = 0 ;i < st.length ; i ++){
50 int j = 0;
51 while(j < key.length){
52 if(st[i].equals(key[j])){
53 count = map.get(key[j]);
54 map.put(key[j],count+1);
55 }
56 j++;
57 }
58 }
59 for (Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry:map.entrySet()) {
60 String s1 = entry.getKey();
61 int n = entry.getValue();
62 System.out.println(n+"\t"+s1);
63 }
64 System.exit(0);
65 }
66
67 }View Code

这里我主要运用的是map集合
Map:存储双列数据的集合,通过键值对存储数据,存储 的数据是无序的,Key值不能重复,value值可以重复。
由于输出关键字按升序排列,所以我选择的是TreeMap,下面是我在网上搜集到的使用方法:
TreeMjiap集合按照键是可排序不重复的键值对集合。(默认升序)
TreeMap集合按照键排序的特点与TreeSet是完全一样的。
TreeMap集合和TreeSet集合都是排序不重复集合
TreeSet集合的底层是基于TreeMap,只是键没有附属值而已。
三、踩坑心得
下面是我在这几次作业中遇到的一些问题及学到的一些知识:
1、在题目集5(7-4 统计Java程序中关键词的出现次数 )中,由于我的正则表达式有问题,去除多行注释的正则表达式考虑的不全面,最后一个测试点一直过不去。
修改前:
s = s.replaceAll("/\\(*.*)?\\*/"," ");修改后:
s = s.replaceAll("/\\*.*?\\*/"," ");2、在题目集6(7-5 图形继承与多态 )中要求将面积排序后输出,我用到了ArrayList 数组,下面是我的笔记:
ArrayList 继承了 AbstractList ,并实现了 List 接口。

ArrayList 类是一个可以动态修改的数组,与普通数组的区别就是它是没有固定大小的限制,我们可以添加或删除元素。
ArrayList常用方法:
add() 将元素插入到指定位置的 arraylist 中
addAll() 添加集合中的所有元素到 arraylist 中
clear() 删除 arraylist 中的所有元素
get() 通过索引值获取 arraylist 中的元素
remove() 删除 arraylist 里的单个元素
size() 返回 arraylist 里元素数量
isEmpty() 判断 arraylist 是否为空
set() 替换 arraylist 中指定索引的元素
sort() 对 arraylist 元素进行排序
toArray() 将 arraylist 转换为数组
toString() 将 arraylist 转换为字符串
forEach() 遍历 arraylist 中每一个元素并执行特定操作
四、改进建议
在题目集4(7-1 水文数据校验及处理 )中由于有些方法我当时没有理解意思,有些方法没有用到,于是做了以下改进:getDealDateResult()方法用来获取结果,computeData()方法用来计算数据。
public void getDealDateResult(){
String[] inValue = this.sb.split("\n");
int i=0;
while(i<inValue.length){
CheckData inputCheck = new CheckData(inValue[i],i+1);
if(inputCheck.validateData()){
hydrologicalInfo[i] = inputCheck.toHydrologicalInfo();
}
i++;
}
this.computeData(hydrologicalInfo);
}
public void computeData(HydrologicalInfo hydrologicalInfo[]){
int i=0;
double maxWaterLevel = hydrologicalInfo[0].getActualWaterLevel();
double totalFlow = 0;
while(hydrologicalInfo[i]!=null){
if(hydrologicalInfo[i].getActualGateOpening()>hydrologicalInfo[i].getObjectGateOpening()){
System.out.println("Row:"+(i+1)+" GateOpening Warning");
}
if(hydrologicalInfo[i].getActualWaterLevel()>maxWaterLevel){
maxWaterLevel = hydrologicalInfo[i].getActualWaterLevel();
}
totalFlow += 2*60*60*hydrologicalInfo[i].getWaterFlow();
i++;
}
System.out.printf("Max Actual Water Level:%.2f\n",maxWaterLevel);
System.out.printf("Total Water Flow:%.2f\n",totalFlow);
}2、在题目集4(7-2 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一))中,我的求下一天方法较为复杂,且dayIncrement()、resetMin()、monthIncrement()等方法未用到,于是在同学的提示下做了以下改进:
改进前:
public DateUtil getNextNdays(int n){
int a[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int y = this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue();
int m = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue();
int d = this.getDay().getValue();
int sum = 0;
int num = syts(this);
int ynum = 0;
int mnum = 0;
if (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()){
a[2] = 29;
}else {
a[2]= 28;
}
if (n > num){//n大于本年剩余天数
n = n - num;
y ++;
if (new Year(y).isLeapYear()){
ynum = 366;
}else {
ynum = 365;
}
//大于本年剩余天数但小于下一年天数
if(n < ynum){
int i = 0;
for (i = 0 ;i < 12 && sum < n; i++){
sum = sum + a[i];
}
m = i-1;
d = n - sum + a[i-1] ;
}else if (n > ynum){//大于本年剩余天数且大于下一年天数
int j = 0;
while (n-ynum > 0){
if (new Year(y).isLeapYear()){
ynum = 366;
}else {
ynum = 365;
}
n=n-ynum;
y ++;
}
for (j = 0; j < 12 && sum < n ; j ++){
sum = sum + a[j];
}
m = j-1;
d = n - sum + a[j-1] ;
}
}else { //小于本年剩余天数
int k = 0;
mnum = a[m]-d;
if (n <= mnum){ //小于本月剩余天数
d = d + n;
}else {
n = n - mnum;
for (k = m+1;k <= 12 && sum < n ; k ++){
sum = sum + a[k];
}
m = k-1;
d = n - sum + a[k-1] ;
}
}
return new DateUtil(y,m,d);
}改进后:
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) {
int countDays = 0;
while (countDays < n) {
this.day.dayIncrement();
countDays++;
if (this.day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) {
this.day.mon_maxnum[1] = 29;
}else {
this.day.mon_maxnum[1] = 28;
}
if (this.day.getValue() > this.day.mon_maxnum[this.day.getMonth().getValue() - 1]) {
this.day.getMonth().monthIncrement();//月份加1
if (this.day.getMonth().getValue() > 12) {//月份累加大于12
this.day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement();//年份加1
this.day.getMonth().resetMin();//月份归1
}
this.day.resetMin();//天数归1
}
}
return this;
}
五、总结
通过这几次作业,我对Java三大特性:封装、继承和多态有了更深入的理解,正则表达式的运用也更加熟练。
封装只能通过规定的方法访问数据,将事物拥有的属性和动作隐藏起来,只保留特定的方法与外界联系。当内部的逻辑发生变化时,外部调用不用因此而修改,它们只调用开放的接口,而不用去关心内部的实现,方便修改和实现。
继承是面向对象的最显著的一个特征。子类拥有父类非private的属性和方法,子类可以添加自己的方法和属性,即对父类进行扩展,子类可以重新定义父类的方法,即方法的覆盖/重写。父类的构造函数不能被继承,子类可以通过super()显示调用父类的构造函数。创建子类时,编译器会自动调用父类的无参构造函数。super关键字可以从子类访问父类中的内容。
多态有三个条件:1、继承:在多态中必须存在有继承关系的子类和父类;2、重写:子类对父类中某些方法进行重新定义,在调用这些方法时就会调用子类的方法;3、向上转型:在多态中需要将子类的引用赋给父类对象,只有这样该引用才既能可以调用父类的方法,又能调用子类的方法。
还了解到抽象类的使用,抽象方法没有方法体,抽象方法必须存在于抽象类中,子类重写父类时,必须重写父类所有的抽象方法。





















