在很多时候,我们会非常关注网站的访问量,比如网站的日PV是多少、网站某个功能上线之后点击量是多少,像这些东西都是需要从web容器中的访问日志统计出来的,下面我们看一下如何在nginx中统计网站的访问信息
1、设置Nginx访问日志记录格式
在默认情况下,nginx只是记录相关get信息,像post页面是不记录的,所以下面需要修改nginx.conf,让其访问日志记录post等请求信息,在nginx.conf中server段中加入如下信息
log_format access '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request"' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer"' '"$http_user_agent" $http_x_forwarded_for';
access_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log access;
2、设置日志定期截取
设置日志定期截取一是为了方便查阅,二是为了I/O拥塞(截止到目前笔者维护过的服务器中单台服务器日访问日志大小就达到1.6G,如果不定期截取,由于文件内容较大,后期对文件进程查询、移动时将会严重影响系统性能)。nginx日志格式不像apache、resin那么人性化,nginx访问日志无法在nginx的配置文件中设置成按日期格式存储,目前常见的设置方法主要靠第三方工具或者脚本来实现,下面我们就通过一个最简单的脚本进行实现
#vi /etc/nginx_access_log.sh
#!/bin/bash
mv /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log /opt/nginx_access_`date +%Y%m%d`.log
killall -s USR1 nginx
脚本说明:这个脚本主要实现两个功能,一是将nginx访问日志按照日期移动到目的地,而是移动完毕后让nginx重新生成日志文件
#chmod +x /etc/nginx_access_log.sh
使用cron服务定期执行该脚本,下面设置成的是每晚23点59执行,这样nginx访问日志正好记录的是全天的访问记录
#crontab -e
59 23 * * * /etc/nginx_access_log.sh
3、日志查询
下面做一个最简单的统计,统计http://blog.luwenju.com页面的日点击量是多少
#grep -c 'http://blog.luwenju.com/' /opt/nginx_access_20110815.log
396
总结:像本篇文章所介绍的统计方法只适合访问量较小、应用相对简单的网站,像复杂应用、访问量较大的网站还需要借助第三方工具来统计,目前应用最广泛的是awstats,《Nginx日志分析(下)》将介绍如何使用awstats来分析nginx日志
第一步,日志的处理。
最好每天分割一下日志,一开始没注意这个工作,结果不久日志文件就上G了,很痛苦。分割日志很简单,首先把日志文件复制到别的地方,然后再通知nginx重新生成日志就可以了。shell脚本如下:
#
!/bin/bash
logs_path
=
"
/nginx/logs/
"
mv ${logs_path}access
.
log
${logs_path}access_$(date
-
d
"
yesterday
"
+
"
%Y%m%d
"
)
.
log
kill
-
USR1 `cat
/
nginx
/
logs
/
nginx
.
pid`
代码中的/nginx/logs指的是nginx的log日志文件所在目录,生成了以昨天日期命名的日志文件。
为了达到每天自动分割的目的,在crontab中加入以下部分:
1
0
*
*
*
sh
/
home
/
zyf
/
sh
/
cut_nginx_log
.
sh
这样就每天的0点1分把nginx日志重命名为日期格式,并重新生成今天的新日志文件。
第二步,Awstats的配置。
日志文件分割好了,接下来就是分析了,也就是Awstats的使用了。
Awstats的配置文件默认会存储在/etc/awstats/目录下,包括你安装时设置的域名如:awstats.www.xxxxke.com.conf。在这个配置文件中修改这个地方:
LogFile = " /nginx/logs/access_%YYYY-0%MM-0%DD-24.log "
这个意思是要去读取nginx昨天的日志文件,关于后边%YYYY-0%MM-0%DD-24的设置,规则如下:

#
You can also use tags in this filename if you need a dynamic file name
# depending on date or time (Replacement is made by AWStats at the beginning
# of its execution). This is available tags :
# %YYYY-n is replaced with 4 digits year we were n hours ago
# %YY-n is replaced with 2 digits year we were n hours ago
# %MM-n is replaced with 2 digits month we were n hours ago
# %MO-n is replaced with 3 letters month we were n hours ago
# %DD-n is replaced with day we were n hours ago
# %HH-n is replaced with hour we were n hours ago
# %NS-n is replaced with number of seconds at 00:00 since 1970
# %WM-n is replaced with the week number in month (1-5)
# %Wm-n is replaced with the week number in month (0-4)
# %WY-n is replaced with the week number in year (01-52)
# %Wy-n is replaced with the week number in year (00-51)
# %DW-n is replaced with the day number in week (1-7, 1=sunday)
# use n=24 if you need (1-7, 1=monday)
# %Dw-n is replaced with the day number in week (0-6, 0=sunday)
# use n=24 if you need (0-6, 0=monday)
# Use 0 for n if you need current year, month, day, hour

第三步,开始分析、生成结果。
最后,可以执行分析了。使用这个命令:
/
usr
/
local
/
awstats
/
wwwroot
/
cgi
-
bin
/
awstats
.
pl
-
update
-
config
=
www
.
xxxxke
.
com
这个命令会把结果生成到/var/lib/awstats 目录下 awstatsXXXX.www.XXXX.com.txt文件。
当然啦,这样看起来不太方便哦,呵呵,可以再用下面的命令来生成html页面,相当漂亮:
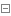
perl /usr/local/awstats/tools/awstats_buildstaticpages.pl -update \
-config=www.xxxxoke.com -lang=cn \
-dir=/html/awstats \
-awstatsprog=/usr/local/awstats/wwwroot/cgi-bin/awstats.pl
这样就会在/html/awstats目录下生成很漂漂的分析结果页,很暴力很强大。
第四步,自动化。
要是每天都去服务器上运行几条命令肯定是件令人烦燥的事情,所以呢,linux的世界里有crontab这样的好东东,很简单,下面是我的crontab
1
0
*
*
*
sh
/
home
/
zyf
/
sh
/
cut_nginx_log
.
sh
0
1
*
*
*
/
usr
/
local
/
awstats
/
wwwroot
/
cgi
-
bin
/
awstats
.
pl
-
update
-
config
=
www
.
xxxxke
.
com
0
2
*
*
*
perl
/
usr
/
local
/
awstats
/
tools
/
awstats_buildstaticpages
.
pl
-
update
-
config
=
www
.
xxxxke
.
com
-
lang
=
cn
-
dir
=/
html
/
awstats
-
awstatsprog
=/
usr
/
local
/
awstats
/
wwwroot
/
cgi
-
bin
/
awstats
.
pl
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
大功告成,打完收功……





















