一、ab命令
1.ab的简介
ab是apachebench命令的缩写。
ab是apache自带的压力测试工具。ab非常实用,它不仅可以对apache服务器进行网站访问压力测试,也可以对或其它类型的服务器进行压力测试。比如nginx、tomcat、IIS等
2.ab的原理
ab的原理:ab命令会创建多个并发访问线程,模拟多个访问者同时对某一URL地址进行访问。它的测试目标是基于URL的,因此,它既可以用来测试apache的负载压力,也可以测试nginx、lighthttp、tomcat、IIS等其它Web服务器的压力。
ab命令对发出负载的计算机要求很低,它既不会占用很高CPU,也不会占用很多内存。但却会给目标服务器造成巨大的负载,其原理类似CC攻击。自己测试使用也需要注意,否则一次上太多的负载。可能造成目标服务器资源耗完,严重时甚至导致死机。
3.ab的安装
yum -y install httpd-tools检测是否安装成功
[root@localhost orange]# ab -V
This is ApacheBench, Version 2.3 <$Revision: 1430300 $>
Copyright 1996 Adam Twiss, Zeus Technology Ltd, http://www.zeustech.net/
Licensed to The Apache Software Foundation, http://www.apache.org/4.ab的参数说明
[root@localhost orange]# ab --help
ab: wrong number of arguments
Usage: ab [options] [http[s]://]hostname[:port]/path
Options are:
-n requests Number of requests to perform
-c concurrency Number of multiple requests to make at a time
-t timelimit Seconds to max. to spend on benchmarking
This implies -n 50000
-s timeout Seconds to max. wait for each response
Default is 30 seconds
-b windowsize Size of TCP send/receive buffer, in bytes
-B address Address to bind to when making outgoing connections
-p postfile File containing data to POST. Remember also to set -T
-u putfile File containing data to PUT. Remember also to set -T
-T content-type Content-type header to use for POST/PUT data, eg.
'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
Default is 'text/plain'
-v verbosity How much troubleshooting info to print
-w Print out results in HTML tables
-i Use HEAD instead of GET
-x attributes String to insert as table attributes
-y attributes String to insert as tr attributes
-z attributes String to insert as td or th attributes
-C attribute Add cookie, eg. 'Apache=1234'. (repeatable)
-H attribute Add Arbitrary header line, eg. 'Accept-Encoding: gzip'
Inserted after all normal header lines. (repeatable)
-A attribute Add Basic WWW Authentication, the attributes
are a colon separated username and password.
-P attribute Add Basic Proxy Authentication, the attributes
are a colon separated username and password.
-X proxy:port Proxyserver and port number to use
-V Print version number and exit
-k Use HTTP KeepAlive feature
-d Do not show percentiles served table.
-S Do not show confidence estimators and warnings.
-q Do not show progress when doing more than 150 requests
-g filename Output collected data to gnuplot format file.
-e filename Output CSV file with percentages served
-r Don't exit on socket receive errors.
-h Display usage information (this message)
-Z ciphersuite Specify SSL/TLS cipher suite (See openssl ciphers)
-f protocol Specify SSL/TLS protocol
(SSL3, TLS1, TLS1.1, TLS1.2 or ALL)详情说明:
-n在测试会话中所执行的请求个数。默认时,仅执行一个请求。请求的总数量
-c一次产生的请求个数。默认是一次一个。请求的用户量
-t测试所进行的最大秒数。其内部隐含值是-n 50000,它可以使对服务器的测试限制在一个固定的总时间以内。默认时,没有时间限制。
-V显示版本号并退出。
5.性能指标
5.1吞吐量(Requests per second)
服务器并发处理能力的量化描述,单位是reqs/s,指的是在某个并发用户数下单位时间内处理的请求数。某个并发用户数下单位时间内能处理的最大请求数,称之为最大吞吐率。
记住:吞吐率是基于并发用户数的。这句话代表了两个含义:
a、吞吐率和并发用户数相关
b、不同的并发用户数下,吞吐率一般是不同的
计算公式:总请求数/处理完成这些请求数所花费的时间,即
Request per second=Complete requests/Time taken for tests
必须要说明的是,这个数值表示当前机器的整体性能,值越大越好。
5.2 并发连接数(The number of concurrent connections)
并发连接数指的是某个时刻服务器所接受的请求数目,简单的讲,就是一个会话。
5.3 并发用户数(Concurrency Level)
要注意区分这个概念和并发连接数之间的区别,一个用户可能同时会产生多个会话,也即连接数。在HTTP/1.1下,IE7支持两个并发连接,IE8支持6个并发连接,FireFox3支持4个并发连接,所以相应的,我们的并发用户数就得除以这个基数。
5.4 用户平均请求等待时间(Time per request)
计算公式:处理完成所有请求数所花费的时间/(总请求数/并发用户数),即: Time per request=Time taken for tests/(Complete requests/Concurrency Level)
5.5 服务器平均请求等待时间(Time per request:across all concurrent requests)
计算公式:处理完成所有请求数所花费的时间/总请求数,即: Time taken for/testsComplete requests 可以看到,它是吞吐率的倒数。 同时,它也等于用户平均请求等待时间/并发用户数,即 Time per request/Concurrency Level
6.ab的应用
ab的命令参数比较多,我们经常使用的是-c和-n参数。
ab -c 10 -n 100 http://www.myvick.cn/index.php :同时处理100个请求并运行10次index.php
-c10表示并发用户数为10
-n100表示请求总数为100以下是返回信息
Benchmarking www.myvick.cn (be patient).....done
Server Software: Apache/2.4.7
Server Hostname: www.myvick.cn
Server Port: 80
Document Path: /index.php
Document Length: 0 bytes
Concurrency Level: 10
Time taken for tests: 21.512 seconds
Complete requests: 100
Failed requests: 0
Write errors: 0
Non-2xx responses: 100
Total transferred: 19400 bytes
HTML transferred: 0 bytes
Requests per second: 4.65 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 2151.185 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 215.118 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 0.88 [Kbytes/sec] received
Connection Times (ms)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 229 269 196.9 229 1230
Processing: 338 1399 997.4 1372 7118
Waiting: 338 1350 948.2 1372 6303
Total: 568 1668 1018.2 1602 7347
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
50% 1602
66% 1625
75% 1725
80% 2014
90% 2650
95% 3677
98% 4576
99% 7347
100% 7347 (longest request)7 nginx和apache对比
nginx性能确实比apache性能高。nginx的吞吐量大于apache的,吞吐量越大越好
———————————————————————————————————
我觉得这个原因和nginx是异步非阻塞,而apache是同步阻塞是有关系得
二、tcp copy
本部分转载自简书https://www.jianshu.com/p/8df317dbf653
1.tcpcopy工具介绍
tcpcopy 是一个分布式在线压力测试工具,可以将线上流量拷贝到测试机器,实时的模拟线上环境,达到在程序不上线的情况下实时承担线上流量的效果,尽早发现 bug,增加上线信心。
tcpcopy 的优势在于其实时性及真实性,除了少量的丢包,完全拷贝线上流量到测试机器,真实的模拟线上流量的变化规律。
2.tcpcopy原理
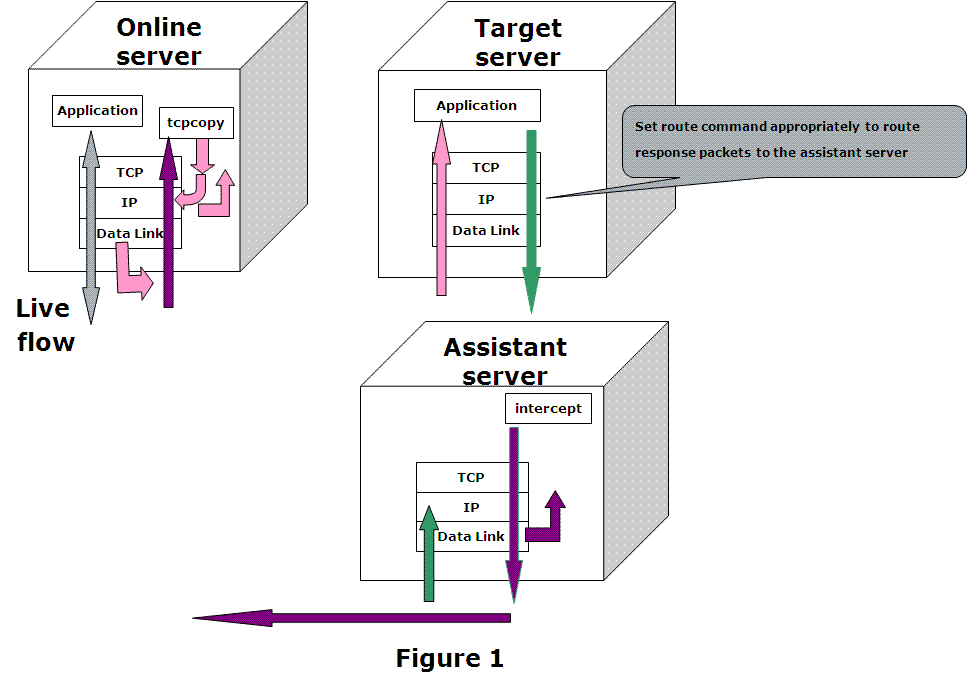
tcpcopy包含三部分:online server、assistant server、target server
1. tcpcopy :运行在线上机器,捕获线上请求
2. intercept: 运行在辅助机器,负责向tcpcopy发送响应信息。
3. 目标机器:被测机器
tcpcopy默认捕获网络层的包(也可以配置为捕获数据链路层的包),然后做一些必要的处理,将包发送给被测机器
tcpcopy拷贝一次流量访问的步骤如下:
① 一个客户请求到达线上机器;
② 拷贝IP层(或者数据链路层)的包到tcpcopy进程;
③ tcpcopy修改包的目的及源地址,发给目标测试机;
④ 拷贝的包到达目标测试机;
⑤ 目标测试机的应用处理访问,并返回结果给辅助机;
⑥ 返回结果在辅助机的数据链路层被截获,drop响应的body,copy返回的ip header;
⑦ 辅助机将响应header发送给线上机器的tcpcopy进程。























