Pytorch构造稀疏Tensor
torch.sparse_coo_tensor(indices, values,
size=None, *,
dtype=None,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)Constructs a sparse tensor in COO(rdinate) format with specified values at the given indices.
This function returns an uncoalesced tensor.
1. COO Style Matrix
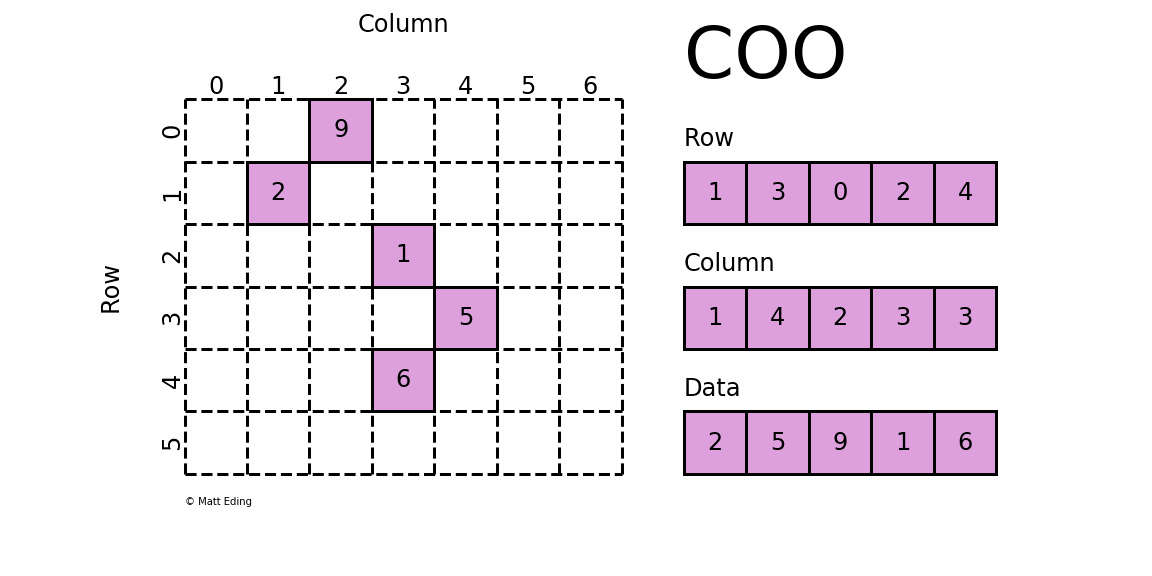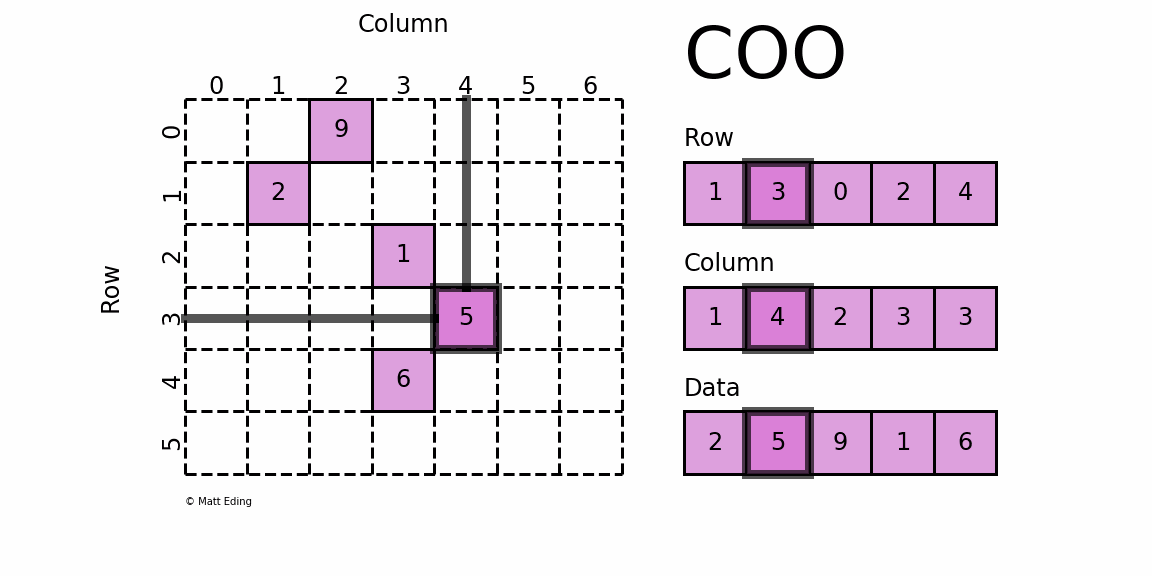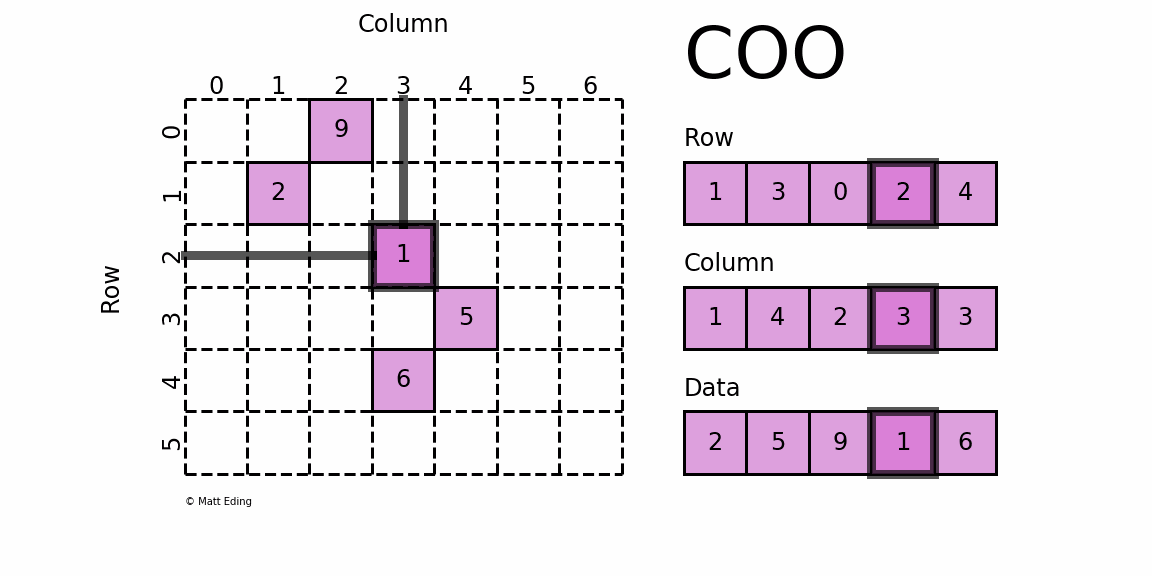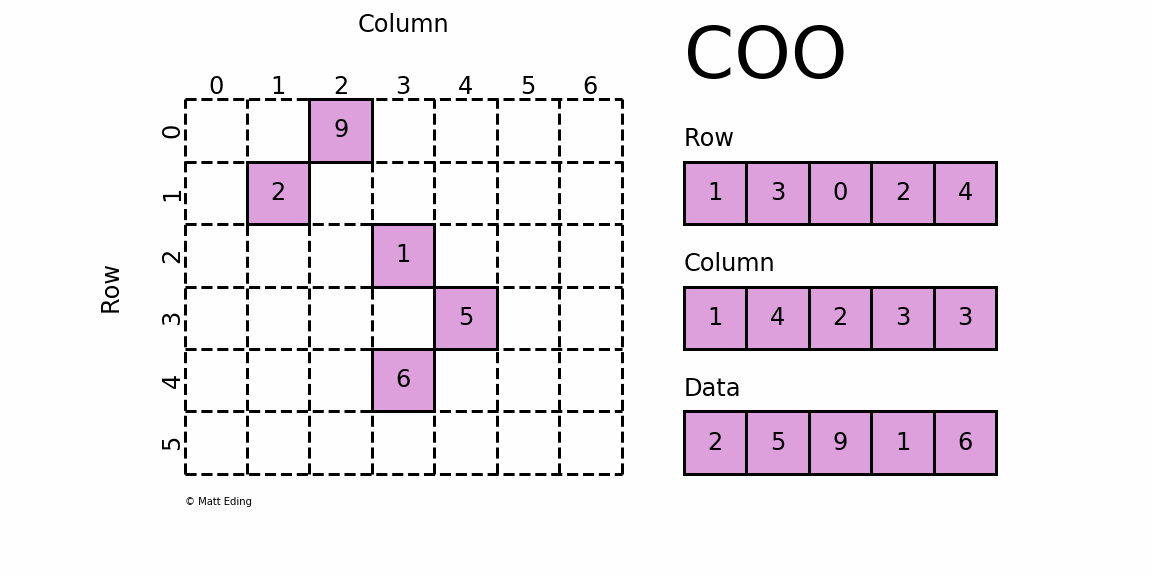
COO 格式的矩阵可以通过一个三元组表示,如上图右侧所示,从上到下依次为:
- ① 矩阵非零元素所在的行;
- ② 矩阵非零元素所在的列(与行位置匹配);
- ③ 矩阵非零元素对应的值。
有了该基础接下来再看 sparse_coo_tensor()
2. sparse_coo_tensor()示例
接下来看一下参数说明,知道了COO格式,下面可以先略过。
Parameters
- indices (array_like) – Initial data for the tensor. Can be a list, tuple, NumPy ndarray, scalar, and other types. Will be cast to a torch.LongTensor internally. The indices are the coordinates of the non-zero values in the matrix, and thus should be two-dimensional where the first dimension is the number of tensor dimensions and the second dimension is the number of non-zero values.
- values (array_like) – Initial values for the tensor. Can be a list, tuple, NumPy ndarray, scalar, and other types.
- size (list, tuple, or torch.Size, optional) – Size of the sparse tensor. If not provided the size will be inferred as the minimum size big enough to hold all non-zero elements.
Keyword Arguments
- dtype (torch.dtype, optional) – the desired data type of returned tensor. Default: if None, infers data type from values.
- device (torch.device, optional) – the desired device of returned tensor. Default: if None, uses the current device for the default tensor type (see torch.set_default_tensor_type()). device will be the CPU for CPU tensor types and the current CUDA device for CUDA tensor types.
- requires_grad (bool, optional) – If autograd should record operations on the returned tensor. Default:
False.
# setting valid pixel location
indice = torch.tensor([[0, 1, 1],
[2, 0, 2]])
# setting match values
values = torch.tensor([3, 4, 5], dtype=torch.float32)
print('COO tensor: \n{}'.format(torch.sparse_coo_tensor(indice, values, [2, 4])))
print('COO tensor: \n{}'.format(torch.sparse_coo_tensor(indice, values))) # inferred as the minimum size
print('COO tensor: \n{}'.format(torch.sparse_coo_tensor(indice, values, [2, 4], dtype=torch.float64)))
# Create a empty sparse tensor.
print('COO tensor: \n{}'.format(torch.sparse_coo_tensor(torch.empty([1, 0]), [], [1])))
print('COO tensor: \n{}'.format(torch.sparse_coo_tensor(torch.empty([1, 0]), torch.empty([0, 2]), [1, 2])))测试结果:
COO tensor:
tensor(indices=tensor([[0, 1, 1],
[2, 0, 2]]),
values=tensor([3., 4., 5.]),
size=(2, 4), nnz=3, dtype=torch.float32, layout=torch.sparse_coo)
COO tensor:
tensor(indices=tensor([[0, 1, 1],
[2, 0, 2]]),
values=tensor([3., 4., 5.]),
size=(2, 3), nnz=3, dtype=torch.float32, layout=torch.sparse_coo)
COO tensor:
tensor(indices=tensor([[0, 1, 1],
[2, 0, 2]]),
values=tensor([3., 4., 5.]),
size=(2, 4), nnz=3, layout=torch.sparse_coo)
COO tensor:
tensor(indices=tensor([], size=(1, 0)),
values=tensor([], size=(0,)),
size=(1,), nnz=0, layout=torch.sparse_coo)
COO tensor:
tensor(indices=tensor([], size=(1, 0)),
values=tensor([], size=(0, 2)),
size=(1, 2), nnz=0, layout=torch.sparse_coo)





















