LeetCode: 126. Word Ladder II
最近工作和毕设压力比较大, 刷 LeetCode 有点不在状态,代码可能有点难看。不过,整体的思路应该是没有问题的。
题目描述
Given two words (beginWord and endWord), and a dictionary’s word list, find all shortest transformation sequence(s) from beginWord to endWord, such that:
Only one letter can be changed at a time
Each transformed word must exist in the word list. Note that beginWord is not a transformed word.
For example,
Given:
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
Return
[
["hit","hot","dot","dog","cog"],
["hit","hot","lot","log","cog"]
]
Note:
Return an empty list if there is no such transformation sequence.
All words have the same length.
All words contain only lowercase alphabetic characters.
You may assume no duplicates in the word list.
You may assume beginWord and endWord are non-empty and are not the same.
题目大意: 根据给定的开始结束单词以及字母表,找到所有从开始单词到结束单词的最短路径。要求路径上的每个单词之间只有一个字母之差。
解题思路 —— 广度搜索
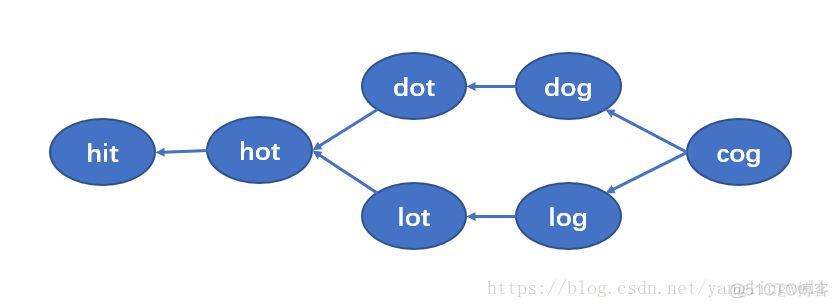
广度搜索可以直接求到最短路径。我们可以在计算最短路径的过程中,记录下当前到达节点的最短路径的前驱,然后推出所有的路径。如下图:
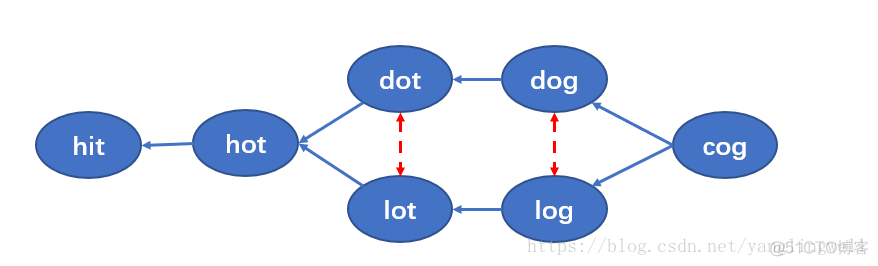
虽然 dot <--> lot, dog <--> log 等路径也存在,但其不是到达相应节点的最短路径,因此可以忽略掉。如下图:
AC 代码
class Solution {
private:
// 记录广度搜索状态的结构
struct LadderState
{
vector<string> frontState; // 记录当前状态是由哪些状态转换而来
int level; // 记录当前状态的层数
};
private:
// 判断两个单词是否只相差一个字母
bool isNear(string lhv, string rhv)
{
if(lhv.size() != rhv.size()) return false;
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < lhv.size() && cnt < 2; ++i)
{
if(lhv[i] != rhv[i])
{
++cnt;
}
}
return (cnt == 1);
}
// 返回到达 endWord 的所有最短路径
set<vector<string>> recoverPaths(string beginWord, string endWord, map<string, LadderState>& wordStates)
{
if(beginWord == endWord) return {{beginWord}};
set<vector<string>> paths;
for(size_t i = 0; i < wordStates[endWord].frontState.size(); ++i)
{
set<vector<string>> curPaths = recoverPaths(beginWord, wordStates[endWord].frontState[i], wordStates);
for(auto path : curPaths)
{
path.push_back(endWord);
paths.insert(path);
}
}
return paths;
}
public:
vector<vector<string>> findLadders(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {
multimap<string, string> wordDir; //wordDir[i] = j 表示 i 到 j 只有一个字母不同
// 计算距离,将相邻的节点存入 wordDir 中
for(int i = 0; i < wordList.size(); ++i)
{
for(int j = i+1; j < wordList.size(); ++j)
{
if(isNear(wordList[i], wordList[j]))
{
wordDir.insert({wordList[i], wordList[j]});
wordDir.insert({wordList[j], wordList[i]});
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < wordList.size(); ++i)
{
if(isNear(wordList[i], beginWord))
{
wordDir.insert({wordList[i], beginWord});
wordDir.insert({beginWord, wordList[i]});
}
}
// 初始化各个节点的状态
map<string, LadderState> wordStates;
for(size_t i = 0; i < wordList.size(); ++i)
{
wordStates[wordList[i]] = { {}, 0};
}
wordStates[beginWord] = { {}, 0 };
// 计算最短路径
queue<string> que;
unordered_set<string> flags;
que.push(beginWord);
que.push("#");
flags.insert(beginWord);
int stepNum = 0;
while(!que.empty())
{
string curWord = que.front();
que.pop();
if(curWord == "#")
{
++stepNum;
if(!que.empty()) que.push("#");
continue;
}
if(curWord == endWord)
{
continue;
}
for(auto iter = wordDir.find(curWord); iter != wordDir.end() && iter->first == curWord; ++iter)
{
if(flags.find(iter->second) == flags.end())
{
flags.insert(iter->second);
que.push(iter->second);
wordStates[iter->second].level = wordStates[curWord].level + 1;
}
if(wordStates[iter->second].level == wordStates[curWord].level + 1)
{
wordStates[iter->second].frontState.push_back(curWord);
}
}
}
// 根据 wordStates 恢复各个路径
set<vector<string>> paths = recoverPaths(beginWord, endWord, wordStates);
vector<vector<string>> ans(paths.begin(), paths.end());
return ans;
}
};























