CSS3 positon定位详解(通俗易懂)
原创
©著作权归作者所有:来自51CTO博客作者坚毅的小解同志的原创作品,请联系作者获取转载授权,否则将追究法律责任
CSS3 positon定位详解(通俗易懂),文章内包涵很多个人理解(错误请指出)
positon定位一共有四种,分别是static静态(默认),relative相对,fixed固定,absolute绝对定位,以及sticky粘性定位。
static静态定位
默认的定位方式,不可以使用left,top,right,buttom等属性,Z—index也不能更改,完全遵循文档标准流,
正常定位(static)的效果
<style>
div{
width: 500px;
}
div:nth-child(-n+2){
display: inline;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div style="background-color: red;">123</div>
<div style="background-color: bisque;">132</div>
<div style="background-color: blue;">123</div>
</body>

设置left 等也不会起效
<style>
div{
width: 500px;
}
div:nth-child(-n+2){
display: inline;
left: 1000px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div style="background-color: red;">123</div>
<div style="background-color: bisque;">132</div>
<div style="background-color: blue;">123</div>
</body>
效果跟上图一样。
relative相对定位
相对定位可以使用top等位移属性,相对定位是相对于自己的位置进行移动。
<style>
body{
border: 1px solid;
height: 1000px;
}
div{
width: 500px;
}
div:nth-child(-n+2){
position: relative;
top: 200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div style="background-color: red;" class="div1">123</div>
<div style="background-color: bisque;" class="div2">132</div>
<div style="background-color: blue;" class="div3">123</div>
</body>

div1和div2向下进行了移动,移动的距离指的是自己的位置加了200px后的长度,可以看到div3上面空出了一些空间,空出的空间就是移动前的div1和div2,relative定位的元素进行移动后还会在原来的标准流中占有位置,所以div3不会上移。
absolute绝对定位
俗话说子绝父相,绝对定位是相对于自己的父级定位进行移动的,最常和相对定位一起搭配,如果父级没有定位那么就会对body进行参照,绝对定位是脱离标准流的。
绝对定位脱离标准流
<style>
div {
width: 500px;
}
.div1 {
display: inline;
position: absolute;
}
.div3 {
display: inline;
position: absolute;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div1" style="background-color:blue">123</div>
<div class="div2" style="background-color: yellow">456</div>
<div class="div3" style="background-color: red">789</div>
<div class="div4" style="background-color:brown">987</div>
</body>

div1和div3脱离标准流div2和div4移了上去,然后被div1和div2遮住了于是有了这样的效果。
子绝父相
<style>
body {
border: 1px solid;
}
div {
width: 500px;
}
.div0 {
top: 100px;
position: relative;
height: 300px;
}
.div1 {
top: 200px;
display: inline;
position: absolute;
}
.div3 {
top: 200px;
display: inline;
position: absolute;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div0" style="background-color: green">
<div class="div1" style="background-color:blue">123</div>
</div>
<div class="div2" style="background-color: yellow">456</div>
<div class="div3" style="background-color: red">789</div>
<div class="div4" style="background-color:brown">987</div>
</body>

div1在div0里面,div1的top就是相对于div0的顶部距离,div3的top是到body边框的距离
fixed固定定位
固定定位同样会脱离标准流,同时是相对于window窗口的定位,
固定定位演示
<style>
body {
border: 1px solid;
}
div {
width: 500px;
}
.div0 {
top: 100px;
position: relative;
height: 300px;
}
.div1 {
position: fixed;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
.div3 {
top: 200px;
display: inline;
position: absolute;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div0" style="background-color: green">
<div class="div1" style="background-color:blue">123</div>
</div>
<div class="div2" style="background-color: yellow">456</div>
<div class="div3" style="background-color: red">789</div>
<div class="div4" style="background-color:brown">987</div>
</body>

div1固定定位 是根据window窗口进行居中位移的。
sticky粘性定位
具有两种状态,一种类似固定地位,一种类似于相对定位,兼容性有些问题,
<style>
body {
border: 1px solid;
height: 900px;
}
div {
width: 500px;
}
.div0 {
top: 150px;
position: relative;
height: 300px;
}
.div1 {
position: sticky;
top: 150px;
}
.div3 {
top: 100px;
position: absolute;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- <div class="div0" style="background-color: green">
<div class="div1" style="background-color:blue">123</div>
</div> -->
<div class="div1" style="background-color:blue">123</div>
<div class="div2" style="background-color: yellow">456</div>
<div class="div3" style="background-color: red">789</div>
<div class="div4" style="background-color:brown">987</div>
</body>

顶部元素到边框的 距离大于等于150px时,变成固定定位跟随移动,当距离小于150px时变成相对定位固定、
<style>
body {
border: 1px solid;
height: 900px;
}
div {
width: 500px;
}
.div0 {
top: 150px;
position: relative;
height: 300px;
}
.div1 {
position: sticky;
top: 200px;
}
.div3 {
top: 100px;
position: absolute;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div0" style="background-color: green">
<div class="div1" style="background-color:blue">123</div>
</div>
<div class="div2" style="background-color: yellow">456</div>
<div class="div3" style="background-color: red">789</div>
<div class="div4" style="background-color:brown">987</div>
</body>
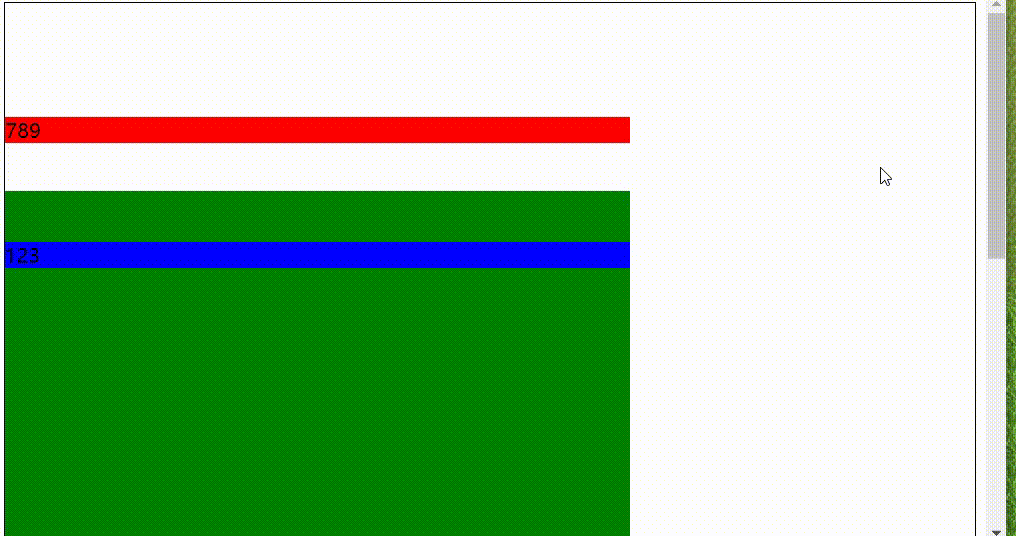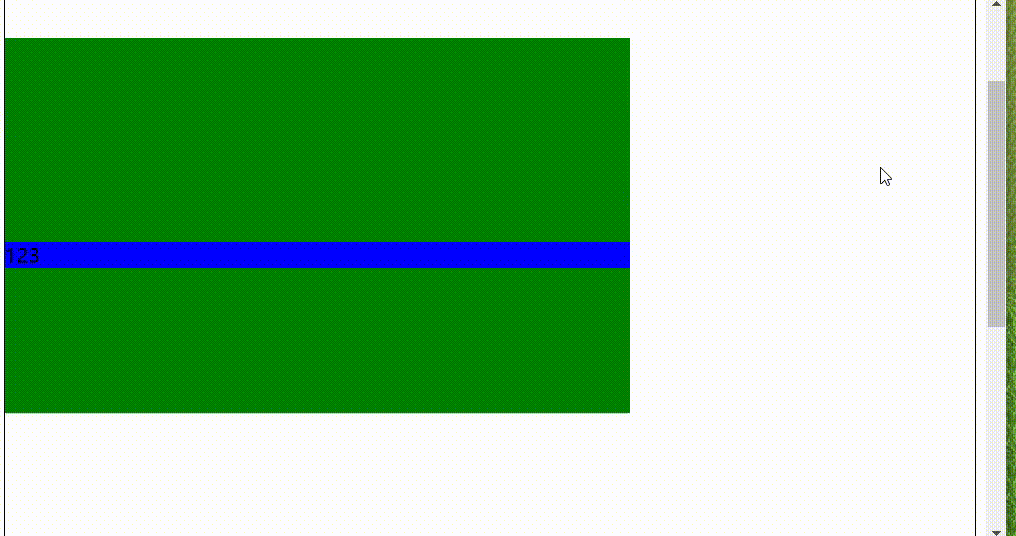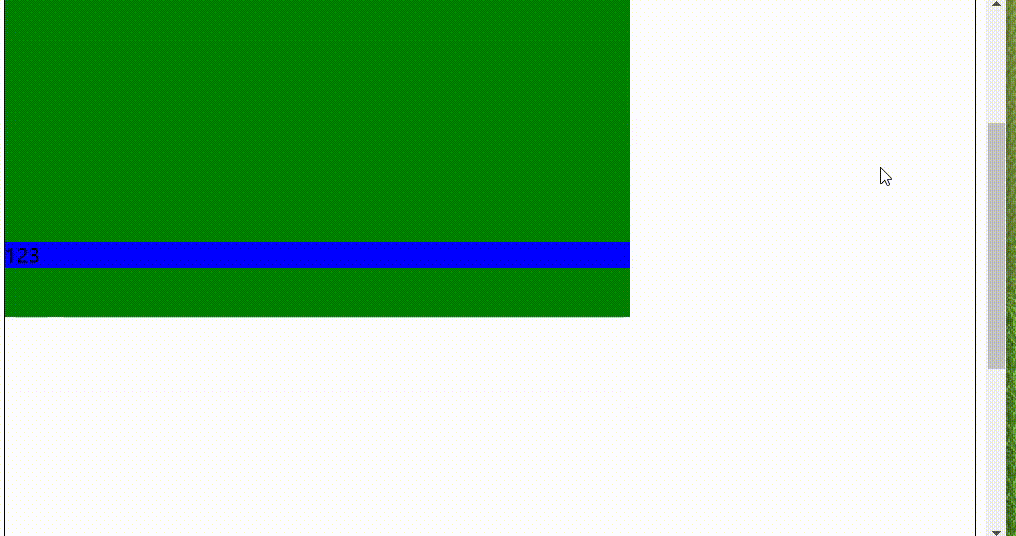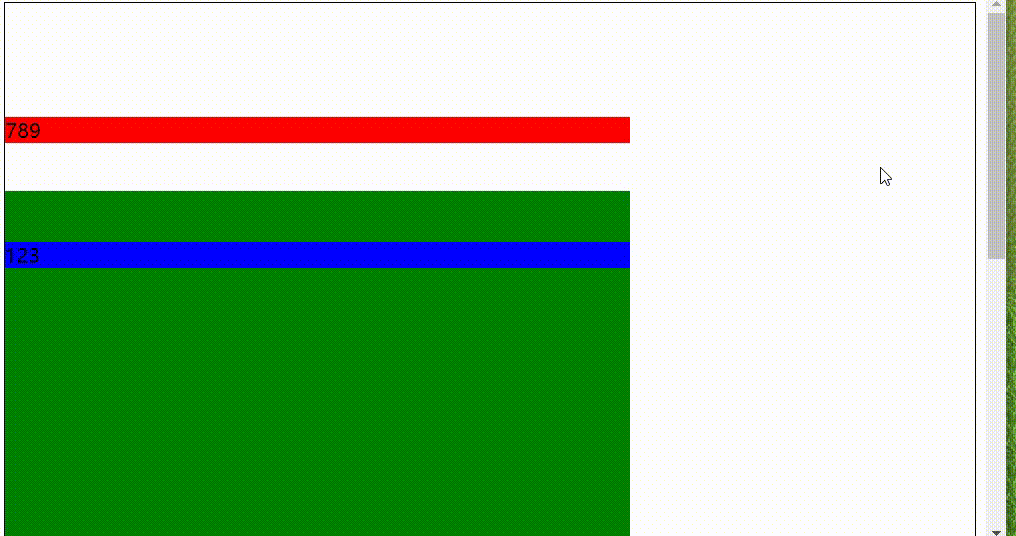
注:当有父级元素时仍然是以body为参考,但是不会超出父元素。




























