核心思想:
同时产生多个随机数让差值=goal的概率提高
例子: 在1--1000中随机查找一个数字等于345, p=1/1000
查找两个数字的差是345的概率则是 :
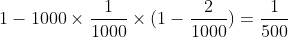
于是通过这种方法也能查找N的因子,通过随机函数和随机数种子来产生一系列的随机数。
随机函数为
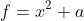
的形式
最开始的随机数通常用2,即
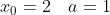
;
比如查找8051的因子:
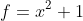
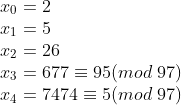
(97是8051的因子)

然而出现了f环,这样会无限循环下去。floyd发现了一种方法解决了它。假设两个人A,B沿着同样的路线向前走,后者的速度是前的两倍,当B追上A时,我们知道B已经走了一圈了。
算法实现:
生成两个数字a和b,计算p=(a-b,n),直到1<p<n, 或者a, b出现循环。如果p=n,那么n是一个质数,否则是n的一个约数,分解递归。
这里的a和b就是用函数f=x^2+1生成的,b=a^2+1.
实现代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N=6e5;
LL fac[N],num[N];
int cnt;
LL gcd(LL a,LL b){
return b==0?a:gcd(b,a%b);
}
LL multi(LL a,LL b,LL m){
LL ans=0;
while(b){
if(b&1) ans=(ans+a)%m;
a=(a+a)%m;
b>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
LL quick_mod(LL a,LL p,LL m){
LL ans=1;
while(p){
if(p&1) ans=multi(ans,a,m);
a=multi(a,a,m);
p>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
LL Pollard_rho(LL n,LL c){
LL x,y,k=2,i=1;
x=rand()%(n-1)+1;
y=x;
while(1>0){
i++;
x=(multi(x,x,n)+c)%n;
LL d=gcd((y-x+n)%n,n);
if(1<d&&d<n) return d;
if(y==x) return n; // 出现循环
if(i==k) {
y=x;
k<<=1; //x 比y多跑一圈
}
}
}
bool Miller_rabin(LL p){
if(p==2) return 1;
if(p<2 || (p&1)==0) return 0;
LL m=p-1;
int sum=0;
while((m&1)==0){
m>>=1;
sum++;
}
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
LL a=rand()%(p-1)+1;
LL x=quick_mod(a,m,p);
LL g=0;
for(int j=0;j<sum;j++){
g=multi(x,x,p);
if(g==1&&x!=1&&x!=p-1) return 0;
x=g;
}
if(g!=1) return 0;
}
return 1;
}
void find(LL n,LL c){
if(n==1) return ;
if(Miller_rabin(n)){
fac[cnt++]=n;
return ;
}
LL p=n;
while(p>=n) p=Pollard_rho(p,c--); //循环避免没找到
find(p,c);
find(n/p,c);
}
int main()
{
//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);
LL x;
while(cin>>x){
cnt=0;
find(x,120);
sort(fac,fac+cnt);
memset(num,0,sizeof(num));
int k=0;
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++){
if(i==0){
num[k]++;
continue;
}
if(fac[i]==fac[i-1]){
num[k]++;
}
else {
k++;
fac[k]=fac[i];
num[k]++;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
printf("%lld^%lld*",fac[i],num[i]);
}
printf("%lld^%lld\n",fac[k],num[k]);
}
return 0;
}
/*
自制数据,经mathematica验证,OK。
In[14]:= FactorInteger[232290989000]
Out[14]= {{2, 3}, {5, 3}, {7, 1}, {61, 1}, {544007, 1}}
In[15]:= FactorInteger[23432590000448]
Out[15]= {{2, 6}, {466201, 1}, {785357, 1}}
In[16]:= FactorInteger[43253245288004]
Out[16]= {{2, 2}, {1493, 1}, {7242673357, 1}}
In[17]:= FactorInteger[200998882133322200]
Out[17]= {{2, 3}, {5, 2}, {29, 1}, {967, 1}, {35837621177, 1}}
In[18]:= FactorInteger[8900446284609340]
Out[18]= {{2, 2}, {5, 1}, {139, 1}, {881, 1}, {3634051513, 1}}
In[19]:= FactorInteger[900046234690488422]
Out[19]= {{2, 1}, {14081, 1}, {31959599271731, 1}}
In[20]:= FactorInteger[4460806408]
Out[20]= {{2, 3}, {3041, 1}, {183361, 1}}
input:
232290989000
23432590000448
43253245288004
200998882133322200
8900446284609340
900046234690488422
4460806408
output:
2^3*5^3*7^1*61^1*544007^1
2^6*466201^1*785357^1
2^2*1493^1*7242673357^1
2^3*5^2*29^1*967^1*35837621177^1
2^2*5^1*139^1*881^1*3634051513^1
2^1*14081^1*31959599271731^1
2^3*3041^1*183361^1
Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.305 s
Press any key to continue.
*/
POJ 1811 Prime Test
http://poj.org/problem?id=1811
大意:判断一个数字是否是素数,如果不是输出最小的素因子。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL min_fac;
LL gcd(LL a,LL b){
return b==0?a:gcd(b,a%b);
}
LL multi(LL a,LL p,LL m){
LL ans=0;
while(p){
if(p&1) ans=(ans+a)%m;
a=(a+a)%m;
p>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
LL quick_mod(LL a,LL p,LL m){
LL ans=1;
while(p){
if(p&1) ans=multi(ans,a,m);
a=multi(a,a,m);
p>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
bool Miller_Rabin(LL p){
if(p==2) return 1;
if(p<2 || (p&1)==0) return 0;
int sum=0;
LL m=p-1;
while((m&1)==0){
m>>=1;
sum++;
}
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
LL a=rand()%(p-1)+1;
LL x=quick_mod(a,m,p);
LL g=0;
for(int j=0;j<sum;j++){
g=multi(x,x,p);
if(g==1&&x!=1&&x!=p-1) return 0;
x=g;
}
if(g!=1) return 0;
}
return 1;
}
LL Pollard_rho(LL n,LL c){
LL i=1,k=2;
LL x=rand()%(n-1)+1;
LL y=x;
while(1>0){
i++;
x=(multi(x,x,n)+c)%n;
LL d=gcd((y-x+n)%n,n);
if(d<n&&d>1) return d;
if(x==y) return n;
if(i==k){
y=x;
k<<=1;
}
}
}
void find(LL x,LL c){
if(x==1) return ;
if(Miller_Rabin(x)){
min_fac=min_fac<x?min_fac:x;
return ;
}
LL p=x;
while(p>=x) p=Pollard_rho(p,c--);
find(p,c);
find(x/p,c);
}
int main()
{
//freopen("cin.txt","r",stdin);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
LL x;
scanf("%lld",&x);
min_fac=x;
if(Miller_Rabin(x)) {
puts("Prime");
continue;
}
find(x,120);
printf("%lld\n",min_fac);
}
return 0;
}
POJ 2429 GCD & LCM Inverse
http://poj.org/problem?id=2429
大意: 给出最大公倍数和最小公约数
求出原来的两个数字,升序输出,有多个的话输出和最小的一个。
分析: gcd(a,b)=G, lcm(a,b)=L 那么L/G=a/G * b/G
a/G + b/G也是最小的。a/G * b/G和a/G + b/G有什么联系?在答案一定的情况下,当a/Gb/G的差越小,a/G + b/G越大。(周长一定的情况下,圆是面积最大的二维图形)
所以,我们对r=L/G因子分解。找到因子积最大值(<=sqrt(r)) --》 ans
找到这样一个值也需要注意,不是直接排个序,相乘比较就行。比如:
假设一个值分解成:2 3 4 5 --> 120
LL limit=(LL) sqrt(120)=10
ans=2*3吗? 显然不是,2*5才是答案
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N=5e5+10;
LL fac[N],ff[N],cnt;
LL gcd(LL a,LL b){
return b==0?a:gcd(b,a%b);
}
LL multi(LL a,LL p,LL m){
LL ans=0;
while(p){
if(p&1) ans=(ans+a)%m;
a=(a+a)%m;
p>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
LL quick_mod(LL a,LL p,LL m){
LL ans=1;
while(p){
if(p&1) ans=multi(ans,a,m);
a=multi(a,a,m);
p>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
bool Miller_Rabin(LL p){
if(p==2) return 1;
if(p<2 || (p&1)==0) return 0;
int sum=0;
LL m=p-1;
while((m&1)==0){
m>>=1;
sum++;
}
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
LL a=rand()%(p-1)+1;
LL x=quick_mod(a,m,p);
LL g=0;
for(int j=0;j<sum;j++){
g=multi(x,x,p);
if(g==1&&x!=1&&x!=p-1) return 0;
x=g;
}
if(g!=1) return 0;
}
return 1;
}
LL Pollard_rho(LL n,LL c){
LL i=1,k=2;
LL x=rand()%(n-1)+1;
LL y=x;
while(1>0){
i++;
x=(multi(x,x,n)+c)%n;
LL d=gcd((y-x+n)%n,n);
if(d<n&&d>1) return d;
if(x==y) return n;
if(i==k){
y=x;
k<<=1;
}
}
}
void find(LL x,LL c){
if(x==1) return ;
if(Miller_Rabin(x)){
fac[cnt++]=x;
return ;
}
LL p=x;
while(p>=x) p=Pollard_rho(p,c--);
find(p,c);
find(x/p,c);
}
int main()
{
LL G,L;
while(cin>>G>>L){
if(G==L){
printf("%lld %lld\n",G,L);
continue;
}
LL r=L/G;
cnt=0;
find(r,120);
sort(fac,fac+cnt);
int top=0;
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++){
if(i==0){
ff[top]=fac[i];
continue;
}
if(fac[i]==fac[i-1]){
ff[top]=ff[top]*fac[i];
}
else {
top++;
ff[top]=fac[i];
}
}
top++;
LL ans=1,temp=1;
LL limit=(LL)sqrt(r*1.0);
for(int i=1;i<(1<<top);i++){
temp=1;
for(int j=0;j<top;j++){
if(i&(1<<j)) temp*=ff[j];
}
if(temp<=limit) {
ans=ans>temp?ans:temp;
}
}
printf("%lld %lld\n",ans*G,r/ans*G);
}
return 0;
}





















