Largest Rectangle in a Histogram
Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
Total Submissions: 19645 | Accepted: 6348 |
Description
A histogram is a polygon composed of a sequence of rectangles aligned at a common base line. The rectangles have equal widths but may have different heights. For example, the figure on the left shows the histogram that consists of rectangles with the heights 2, 1, 4, 5, 1, 3, 3, measured in units where 1 is the width of the rectangles:
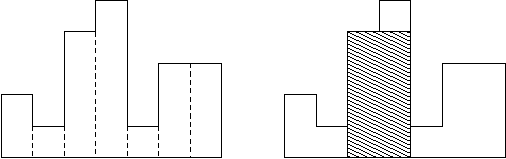
Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.
Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case describes a histogram and starts with an integer n, denoting the number of rectangles it is composed of. You may assume that 1<=n<=100000. Then follow n integers h1,...,hn, where 0<=hi<=1000000000. These numbers denote the heights of the rectangles of the histogram in left-to-right order. The width of each rectangle is 1. A zero follows the input for the last test case.
Output
For each test case output on a single line the area of the largest rectangle in the specified histogram. Remember that this rectangle must be aligned at the common base line.
Sample Input
7 2 1 4 5 1 3 3
4 1000 1000 1000 1000
0
Sample Output
8
4000
Hint
Huge input, scanf is recommended.
【题解
给出一个柱形统计图(histogram), 它的每个项目的宽度是1, 高度和具体问题有关。 现在编程求出在这个柱形图中的最大面积的长方形。
例如:
7 2 1 4 5 1 3 3
7表示柱形图有7个数据,分别是 2 1 4 5 1 3 3, 对应的柱形图如下,最后求出来的面积最大的图如右图所示。

分析:
如果采用枚举的方式,如果当前我们枚举项是 i = 0, 即 height = 2,
我们用另外两个变量 j 和k 向左和向右两个方向搜素,找到第一个 小于 height的下标,这样我们就找到了用 i 项作为高度长方形了。
我们假设 -1位置,和最右高度都是无穷小。
例如:
i = 0, j = -1, k = 1, 最后的面积是 (k - j - 1) * height = 2
i = 1, j = -1, k = 7, 最后面积是( k - j - 1) * height = 7;
...
i = 3, j = 2, k = 5 面积是 ( k - j - 1) * height = 8
枚举出所有的长方形的同时,然后得到最后的面积。
不过这样的程序的时间复杂度是 O(n^2)
我们如何能仅仅做一次,就求出这个面积呢?
观察:
当我们扫扫描到第一个高度 H1 = 2的时候,我可以标记它的起始位置1, 因为我们还不知道它将向右扩展到什么地方,所以继续扫面。
当遇到第二项 H2 = 1, 因为这项比之前的小,我们知道,用H1做高度的长方形结束了,算出它的面积。
同时这个时候,我们多了一个高度H2,用它做长方形高度的长方形起始位置应该是在哪里呢? 因为H1的高度比H2要高,所以这个起始位置自然是H1所在的位置。
为了模拟上面的过程,我们引入单调栈~
我们先定义我们我们要保存的每一项数据
struct Node
{
int height;
int startPosition;
};
用来描述某一个高度,和这个高度的起始位置。
然后我们按照高度来组织成单调栈。我们来看一下它是如何工作的。
为了不用考虑堆栈为空的情况,我们用插入栈底 一个高度(0, 0)的项。
数据:
2 1 4 5 1 3 3
这样初始化
(0 , 0)
I = 1
当扫描到(2, 1)时候,因为高度2 大于栈顶,插入
(0, 0), (2, 1)
I = 2:
当扫描到1的时候,因为1小于栈顶高度2, 我们认为栈顶的那个高度应不能再向右扩展了,所以我们将它弹出
这个时候扫描到 i = 2;
高度是 (i - 1(H1.startIndex)) * H1.height = 2;
我们得到一个面积是2的长方形。
同时我们发现高度是1的当前高度,可以扩展到 H1所在的下标,所以我们插入( 1, 1) 堆栈变成
(0, 0), (1, 1) 因为(2, 1)已经不能向右伸展了,已经被弹出了
i = 3
(0, 0), (1, 1), ( 4 3)
i = 4
(0, 0), (1, 1), (4, 3), (5, 4)
i = 5
这个时候当前高度小于栈顶高度,我们认为栈顶已经不能向右扩展,所以弹出,并且获得面积 ( i - H5.startindex) * H5.height = (5 - 4 ) * 5 = 5
弹出这个元素后,其实(4, 3)的高度也要比 1 大,所以把这个也弹出来,同样方式获得面积 8.
最后我们的堆栈是
(0, 0) , (1, 1)
i = 6
(0, 0), (1, 1), ( 3, 6)
i = 7
(0, 0), (1, 1), (3, 6)
i = 8
最后一步是有点特殊的,因为我们必须要把所有的元素都弹出来,因为栈里面的高度,都坚持到了最后,我们要把这些高度组成的长方形拿出来检测。
我们可以假设扫面到8的时候,高度是0,(最小值)
弹出(3,6)获得面积 (8 - 6 ) * 3 = 6
弹出(1, 1)获得面积(8 - 1) * 1 = 7
最后的面积是8.
【代码君】
//
//Created by just_sort 2016/9/29 20:00
//Copyright (c) 2016 just_sort.All Rights Reserved
//
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
struct node{
LL height,startpos;
};
stack<node>stk;
LL n,a;
int main()
{
while(scanf("%I64d",&n)!=EOF&&n)
{
LL ans = 0;
while(!stk.empty()) stk.pop();
node now;
now.height = 0, now.startpos = 0;
stk.push(now);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
scanf("%I64d",&a);
now.startpos = i;
while(a < stk.top().height){
now = stk.top();
stk.pop();
LL temp = now.height*(i - now.startpos);
if(ans < temp) ans = temp;
}
now.height = a;
stk.push(now);
}
while(!stk.empty())
{
LL temp = stk.top().height*(n - stk.top().startpos);
if(ans < temp) ans = temp;
stk.pop();
}
printf("%I64d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}























