经常接触Linux的同学应该有这样的体验,当遇到一个不会使用的命令时通常敲一下xCmd -h或者xCmd --help来获取命令提示,例如tcpdump命令或者iptables命令,像这样的选项仅仅是获取提示帮助的,实现起来不会很难,但如果考虑到一些复杂的选项,比如说下面这条命令:
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -m limit --limit 25/minute --limit-burst 100 -j ACCEPT这个命令包含多个选项,且选项或许还带有参数,如果完全由自己进行实现的话,可以是可以的,但是难免要花费一些功夫,尤其是在已有现成的实现情况下,函数getopt和getopt_long就是专门用来解析命令行参数的,一个是用来处理短选项(-开头)一个长选项(--开头)功能强大易用,简单方便,妈妈再也不担心我写错代码了^_^。
先看下getopt函数定义和声明:
#include <unistd.h>
int getopt(int argc, char * const argv[],
const char *optstring);
extern char *optarg;
extern int optind, opterr, optopt;
给定了命令参数的数量 (argc)、指向这些参数的数组 (argv) 和选项字符串 (optstring) 后,getopt() 将返回第一个选项,并设置一些全局变量。使用相同的参数再次调用该函数时,它将返回下一个选项,并设置相应的全局变量。如果不再有识别到的选项,将返回 -1,此任务就完成了。
getopt() 所设置的全局变量包括:
optarg——指向当前选项参数(如果有)的指针。
optind——再次调用 getopt() 时的下一个 argv 指针的索引。
optopt——最后一个已知选项。
对于每个选项,选项字符串 (optstring) 中都包含一个对应的字符。具有参数的选项(如示例中的 -l 和 -o 选项)后面跟有一个 : 字符。可以重复调用 getopt(),直到其返回 -1 为止;示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
/* 处理abch四个选项,其中bc含有参数 */
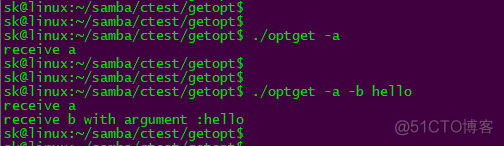
static const char *optString = "ab:c:h";
void main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int opt;
opt = getopt( argc, argv, optString );
while( opt != -1 ) {
switch( opt ) {
case 'a':
printf("receive a \n");
break;
case 'b':
printf("receive b with argument :%s \n", optarg);
break;
case 'h':
printf("Usage : help \n");
break;
default:
printf("*** can't recognize input char!!! \n");
break;
}
opt = getopt( argc, argv, optString );
}
return ;
}
getopt只能处理带一个 ‘-’的选项,如果是含有两个‘--’则可以使用getopt_long了,
int getopt_long(int argc, char * const argv[],
const char *optstring,
const struct option *longopts, int *longindex);
struct option {
char *name;
int has_arg;
int *flag;
int val;
};
name 成员是指向长选项名称(带两个短横线)的指针。has_arg 成员设置为 no_argument、optional_argument, 或 required_argument(均在 getopt.h 中定义)之一,
以指示选项是否具有参数。如果 flag 成员未设置为 NULL,在处理期间遇到此选项时,
会使用 val 成员的值填充它所指向的 int 值。如果 flag 成员为 NULL,在 getopt_long()
遇到此选项时,将返回 val 中的值。用例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <unistd.h>
static const char *optString = "h";
static int do_init = 0;
/* 收到init参数会将1的值赋值给do_init,
* 收到name或者age返回字符,这里可以返回数字
*/
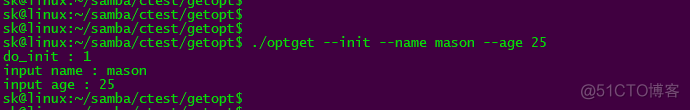
static const struct option longOpts[] = {
{ "init", no_argument, &do_init, 1 },
{ "name", required_argument, NULL, 'n' },
{ "age", required_argument, NULL, 'a' },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 }
};
void main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int longIndex, opt;
opt = getopt_long( argc, argv, optString, longOpts, &longIndex );
while( opt != -1 ) {
switch( opt ) {
case 0 :
printf("do_init : %d\n", do_init);
break;
case 'h':
printf("Usage : --init --name xx \n");
break;
case 'n':
printf("input name : %s\n", optarg);
break;
case 'a':
printf("input age : %s\n", optarg);
break;
default:
printf("*** fail, unrecognized option ***\n");
break;
}
opt = getopt_long( argc, argv, optString, longOpts, &longIndex );
}
return ;
}
参考资料:
1. https://linux.die.net/man/3/getopt
2. https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/aix/library/au-unix-getopt.html























