1. linux脚本编程 3h
2. 补ML代码 3h
3. 项目 3h
# linux ## 文件系统管理   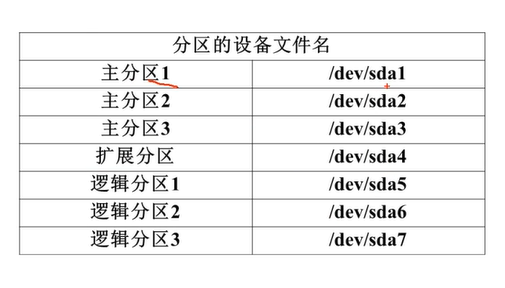  1,2,3,4只能给主分区,逻辑分区从5开始 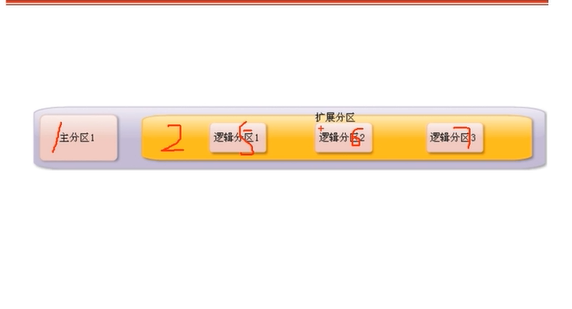
格式化:为了写入文件系统

shell编程


#!bin/bash 标识, 说明这是一个shell脚本, 不能省略

cat -A 查看文件完整格式,window中的换行符和linux不一样, 导致windows中写的脚本不能在linux中运行
格式转换 dos2unix


别名alias vi='vim'【临时】 删除unalias

echo $PATH 查看path变量


重定向, 输入由屏幕转到文件,文件输入替代键盘







set 查看变量; unset 删除变量

环境变量:全局; bash, dash等shell嵌套--查看pstree


路径添加 PATH="$PATH":/home/hichens/sh

自定义操作目录



read -s -t 10 -p "input age: " age

这个代码之所以写了这么久, 我觉得自己主要是对树形结构不了解,递归抓住三点:1.递归的入口;2.递归的方式;3.递归的出口
'''
Implement the decision_tree to adjust more than 1 dimension
'''
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
class DecisionTreeRegression():
def __init__(self, depth = 5, min_leaf_size = 5):
self.depth = depth
self.min_leaf_size = min_leaf_size
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.prediction = None
self.j = None
self.s = None
def mean_squared_error(self, labels, prediction):
if labels.ndim != 1:
print("Error: Input labels must be one dimensional")
return np.mean((labels - prediction) ** 2)
def train(self, X, y):
if X.ndim == 1:
X = X.reshape(-1, 1)
if y.ndim != 1:
print("Error: Data set labels must be one dimensional")
return
#控制最小叶子
if len(X) < 2 * self.min_leaf_size:
self.prediction = np.mean(y)
return
#深度为一
if self.depth == 1:
self.prediction = np.mean(y)
return
j, s, best_split, _ = self.split(X, y)
if s != None:
left_X = X[:best_split]
left_y = y[:best_split]
right_X = X[best_split:]
right_y = y[best_split:]
self.s = s
self.j = j
self.left = DecisionTreeRegression(depth = self.depth - 1, min_leaf_size = self.min_leaf_size)
self.right = DecisionTreeRegression(depth = self.depth - 1, min_leaf_size = self.min_leaf_size)
#左右递归
self.left.train(left_X, left_y)
self.right.train(right_X, right_y)
else:
self.prediction = np.mean(y)
# 出口
return
def squaErr(self, X, y, j, s):
mask_left = X[:, j] < s
mask_right = X[:, j] >= s
X_left = X[mask_left, j]
X_right = X[mask_right, j]
c_left = np.mean(y[mask_left])
c_right = np.mean((y[mask_right]))
error_left = np.sum((X_left - c_left) ** 2)
error_right = np.sum((X_right - c_right) ** 2)
return error_left + error_right
def split(self, X, y):
min_j = 0
min_error = np.inf
for j in range(len(X[0])):
X_sorted = np.sort(X[:, min_j]) # 不改变X
slice_value = (X_sorted[1:] + X_sorted[:-1]) / 2
min_s = X[0, min_j] + X[-1, min_j]
min_s_index = slice_value[0]
for s_index in range(len(slice_value)):
error = self.squaErr(X, y, j, slice_value[s_index])
if error < min_error:
min_error = error
min_j = j
min_s = slice_value[s_index]
min_s_index = s_index
return min_j, min_s, s_index, min_error
def predict(self, x):
# to avoid a number
if x.ndim == 0:
x = np.array([x])
if self.prediction is not None:
return self.prediction
elif self.left or self.right is not None:
if x[self.j] >= self.s:
return self.right.predict(x)
else:
return self.left.predict(x)
else:
print("Error: Decision tree not yet trained")
return None
def main():
X = np.array([[1, 1], [2, 2], [3, 3], [4, 4], [5, 5], [6, 6], [7, 7], [8, 8], [9, 9], [10, 10]])
y = np.array([5.56, 5.70, 5.91, 6.40, 6.80, 7.05, 8.90, 8.70, 9.00, 9.05])
tree = DecisionTreeRegression(depth = 4, min_leaf_size = 2)
tree.train(X,y)
test_cases = np.array([np.arange(0.0, 10.0, 0.01), np.arange(0.0, 10.0, 0.01)]).T
predictions = np.array([tree.predict(x) for x in test_cases])
#绘图
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection="3d")
ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], y, s=20, edgecolor="black",
c="darkorange", label="data")
ax.plot(test_cases[:, 0], test_cases[:, 1], predictions, c='r')
# plt.scatter(X[:, 0], y, s=20, edgecolor="black", c="darkorange", label="data")
# plt.plot(test_cases[:, 1], predictions, c="r")
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
代码终于跑出来了。。。这是最小二乘树回归算法, 没想到从一维到多维这么麻烦。





















