Consider a DOM made of thousands of divs. Remember, we are modern web developers, our app is very SPA! We have lots of methods that handle events - clicks, submits, type-ins… A typical jQuery-like event handler looks like this:
- find every node interested on an event
- update it if necessary
Which has two problems:
- It’s hard to manage. Imagine that you have to tweak an event handler. If you lost the context, you have to dive really deep into the code to even know what’s going on. Both time-consuming and bug-risky.
- It’s inefficient. Do we really need to do all this findings manually? Maybe we can be smarter and tell in advance which nodes are to-be-updated?
Virtual DOM
- React uses the Virtual DOM to create an in-memory copy of the browsers DOM
- When changing the state of components, React updates the virtual DOM first
- After that it computes the resulting differences, and updates the browser’s displayed DOM efficiently

- The Virtual DOM: As discussed above, React.js brought in the helpful Virtual DOM - a virtual browser infinite times friendlier than the real browser. You may take it as the middleman sitting between the developer and the real browser.
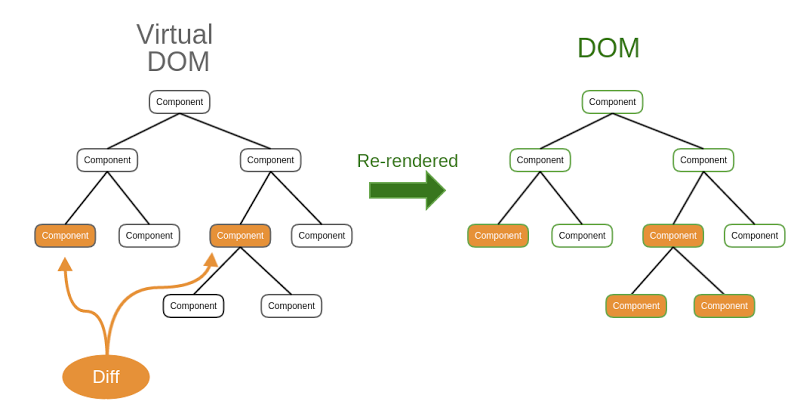
The Virtual DOM assists React by modeling two versions of the DOM: the original and the updated one which reflects the changes made on the view. The framework then notes the differences and updates only the parts of the UI that differ from the original. Hence, easing the previous SSR version where they had to recreate the entire updated view.
------------------越是喧嚣的世界,越需要宁静的思考------------------ 合抱之木,生于毫末;九层之台,起于垒土;千里之行,始于足下。 积土成山,风雨兴焉;积水成渊,蛟龙生焉;积善成德,而神明自得,圣心备焉。故不积跬步,无以至千里;不积小流,无以成江海。骐骥一跃,不能十步;驽马十驾,功在不舍。锲而舍之,朽木不折;锲而不舍,金石可镂。蚓无爪牙之利,筋骨之强,上食埃土,下饮黄泉,用心一也。蟹六跪而二螯,非蛇鳝之穴无可寄托者,用心躁也。





















