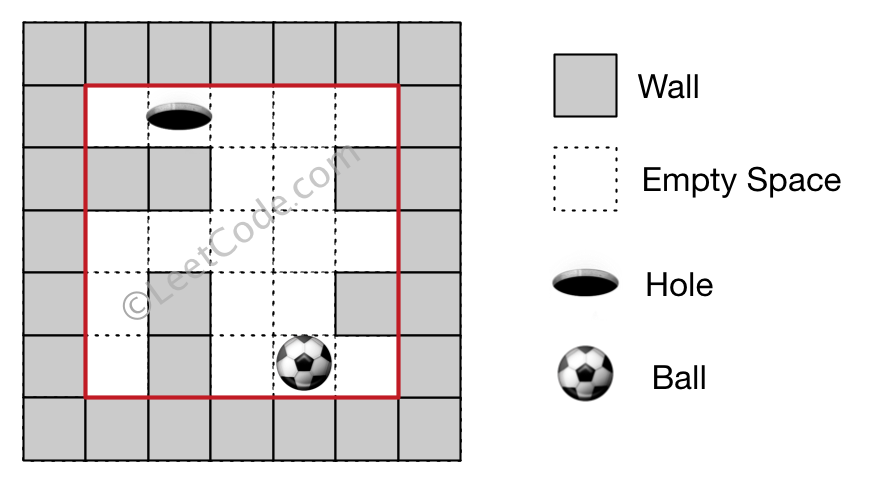
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolling up (u), down (d), left (l) or right (r), but it won't stop rolling until hitting a wall. When the ball stops, it could choose the next direction. There is also a hole in this maze. The ball will drop into the hole if it rolls on to the hole.
Given the ball position, the hole position and the maze, find out how the ball could drop into the hole by moving the shortest distance. The distance is defined by the number of empty spaces traveled by the ball from the start position (excluded) to the hole (included). Output the moving directions by using 'u', 'd', 'l' and 'r'. Since there could be several different shortest ways, you should output the lexicographically smallest way. If the ball cannot reach the hole, output "impossible".
The maze is represented by a binary 2D array. 1 means the wall and 0 means the empty space. You may assume that the borders of the maze are all walls. The ball and the hole coordinates are represented by row and column indexes.
Example 1:
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array
0 0 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 1
0 1 0 0 0
Input 2: ball coordinate (rowBall, colBall) = (4, 3)
Input 3: hole coordinate (rowHole, colHole) = (0, 1)
Output: "lul"
Explanation: There are two shortest ways for the ball to drop into the hole.
The first way is left -> up -> left, represented by "lul".
The second way is up -> left, represented by 'ul'.
Both ways have shortest distance 6, but the first way is lexicographically smaller because 'l' < 'u'. So the output is "lul".

Example 2:
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array
0 0 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 1
0 1 0 0 0
Input 2: ball coordinate (rowBall, colBall) = (4, 3)
Input 3: hole coordinate (rowHole, colHole) = (3, 0)
Output: "impossible"
Explanation: The ball cannot reach the hole.

https://leetcode.com/problems/the-maze-iii/discuss/97797/Similar-to-The-Maze-II.-Easy-understanding-Java-bfs-solution
// NPE
class Solution {
class Point implements Comparable<Point>{ // implements ? Comparable<Point>
int x;
int y;
int l; // level , how far it is from the the source
String s; // the path string to the current point
public Point(int x, int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
l = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
s = "";
}
public Point(int x, int y, int l, String s){ // why do we need two constructors for point
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.l = l;
this.s = s;
}
public int compareTo(Point p){
return l == p.l ? s.compareTo(p.s) : l - p.l;
}
}
private static final int[][] dirs = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
private static final String[] strs = {"r", "l", "d", "u"};
public String findShortestWay(int[][] maze, int[] ball, int[] hole) {
int m = maze.length;
int n = maze[0].length;
Point[][] points = new Point[m][n];
// fill in the coordinates
for(int i = 0; i < m * n ; i++){
points[i / n][i % n] = new Point(i / n , i % n);
// why use a bq
PriorityQueue<Point> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.offer(new Point(ball[0], ball[1], 0, ""));
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
Point p = pq.poll();
if(points[p.x][p.y].compareTo(p) <= 0) continue;
points[p.x][p.y] = p;
for(int index = 0; index < 4; index++){
int row = p.x;
int col = p.y;
int level = p.l;
while(row >= 0 && row < m && col >= 0 && col < n && maze[row][col] == 0 && (row != hole[0] && col != hole[1])){
row += dirs[index][0];
col += dirs[index][1];
level++;
}
if(row != hole[0] || col != hole[1]){
row -= dirs[index][0];
col -= dirs[index][1];
level--;
}
pq.offer(new Point(row, col, level, p.s + strs[index]));
}
}
}
return points[hole[0]][hole[1]].l == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "impossible" : points[hole[0]][hole[1]].s;
}
}
// accepted , other’s code
class Solution {
class Point implements Comparable<Point> {
int x,y,l;
String s;
public Point(int _x, int _y) {x=_x;y=_y;l=Integer.MAX_VALUE;s="";}
public Point(int _x, int _y, int _l,String _s) {x=_x;y=_y;l=_l;s=_s;}
public int compareTo(Point p) {return l==p.l?s.compareTo(p.s):l-p.l;}
}
public String findShortestWay(int[][] maze, int[] ball, int[] hole) {
int m=maze.length, n=maze[0].length;
Point[][] points=new Point[m][n];
for (int i=0;i<m*n;i++) points[i/n][i%n]=new Point(i/n, i%n);
int[][] dir=new int[][] {{-1,0},{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1}};
String[] ds=new String[] {"u","r","d","l"};
PriorityQueue<Point> list=new PriorityQueue<>(); // using priority queue
list.offer(new Point(ball[0], ball[1], 0, ""));
while (!list.isEmpty()) {
Point p=list.poll();
if (points[p.x][p.y].compareTo(p)<=0) continue; // if we have already found a route shorter
points[p.x][p.y]=p;
for (int i=0;i<4;i++) {
int xx=p.x, yy=p.y, l=p.l;
while (xx>=0 && xx<m && yy>=0 && yy<n && maze[xx][yy]==0 && (xx!=hole[0] || yy!=hole[1])) {
xx+=dir[i][0];
yy+=dir[i][1];
l++;
}
if (xx!=hole[0] || yy!=hole[1]) { // check the hole
xx-=dir[i][0];
yy-=dir[i][1];
l--;
}
list.offer(new Point(xx, yy, l, p.s+ds[i]));
}
}
return points[hole[0]][hole[1]].l==Integer.MAX_VALUE?"impossible":points[hole[0]][hole[1]].s;
}
}