如果说要按类型来划分的话,自定义View的实现方式大概可以分为三种,自绘控件、组合控件、以及继承控件。那么下面我们就来依次学习一下,每种方式分别是如何自定义View的。
自绘控件
自绘控件的意思就是,这个View上所展现的内容全部都是我们自己绘制出来的。绘制的代码是写在onDraw()方法中的。
我们来写一个经常会看到的音量调节View的例子,就是下面这种效果

1.自定义View的属性
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="CustomVolumControlBar">
<attr name="firstColor" format="color" />
<attr name="secondColor" format="color" />
<attr name="circleWidth" format="dimension" />
<attr name="dotCount" format="integer" />
<attr name="splitSize" format="integer" />
<attr name="bg" format="reference" />
</declare-styleable>
</resources>布局文件:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
xmlns:custom="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.hx.test"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<com.hx.test.CustomVolumControlBar
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
custom:firstColor="#8f8f8f"
custom:secondColor="#4169E1"
custom:circleWidth="30sp"
custom:dotCount="30"
custom:splitSize="2"
custom:bg="@drawable/volume" />
</RelativeLayout>2.View的构造方法中,获得我们的自定义的属性
//第一圈的颜色
private int mFirstColor;
//第二圈的颜色
private int mSecondColor;
//圈的宽度
private int mCircleWidth;
//当前进度
private int mCurrentCount = 3;
//中间的图片
private Bitmap mImage;
//每个块块间的间隙
private int mSplitSize;
//个数
private int mCount;
private Paint mPaint;
private Rect mRect;
public CustomVolumControlBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public CustomVolumControlBar(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public CustomVolumControlBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
TypedArray a = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CustomVolumControlBar, defStyle, 0);
int n = a.getIndexCount();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int attr = a.getIndex(i);
switch (attr)
{
case R.styleable.CustomVolumControlBar_firstColor:
mFirstColor = a.getColor(attr, Color.GREEN);
break;
case R.styleable.CustomVolumControlBar_secondColor:
mSecondColor = a.getColor(attr, Color.CYAN);
break;
case R.styleable.CustomVolumControlBar_bg:
mImage = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), a.getResourceId(attr, 0));
break;
case R.styleable.CustomVolumControlBar_circleWidth:
mCircleWidth = a.getDimensionPixelSize(attr, (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(
TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_PX, 20, getResources().getDisplayMetrics()));
break;
case R.styleable.CustomVolumControlBar_dotCount:
mCount = a.getInt(attr, 20);// 默认20
break;
case R.styleable.CustomVolumControlBar_splitSize:
mSplitSize = a.getInt(attr, 20);
break;
}
}
a.recycle();
mPaint = new Paint();
mRect = new Rect();
}3.重写onDraw
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
canvas.drawColor(0xaa000000); //背景颜色
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true); // 消除锯齿
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(mCircleWidth); // 设置圆环的宽度
// mPaint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND); // 定义线段断电形状为圆头
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); // 设置空心
int centre = getWidth() / 2; // 获取圆心的x坐标
int radius = centre - mCircleWidth / 2;// 半径
/**
* 画出每个小块
*/
drawOval(canvas, centre, radius);
/**
* 计算内切正方形的位置
*/
int relRadius = radius - mCircleWidth / 2;// 获得内圆的半径
/**
* 内切正方形的距离左边 = centre - relRadius - √2 / 2
*/
mRect.left = (int) (centre - Math.sqrt(2) * 1.0f / 2 * relRadius);
mRect.top = (int) (centre - Math.sqrt(2) * 1.0f / 2 * relRadius);
/**
* 内切正方形的距离右边 = centre + relRadius - √2 / 2
*/
mRect.right = (int) (centre + Math.sqrt(2) * 1.0f / 2 * relRadius);
mRect.bottom = (int) (centre + Math.sqrt(2) * 1.0f / 2 * relRadius);
/**
* 如果图片比较小,那么根据图片的尺寸放置到正中心
*/
if (mImage.getWidth() < Math.sqrt(2) * relRadius) {
mRect.left = (int) (centre - mImage.getWidth() * 1.0f / 2);
mRect.top = (int) (centre - mImage.getWidth() * 1.0f / 2);
mRect.right = (int) (mRect.left + mImage.getWidth());
mRect.bottom = (int) (mRect.top + mImage.getHeight());
}
// 绘图
canvas.drawBitmap(mImage, null, mRect, mPaint);
}
/**
* 根据参数画出每个小块
*
* @param canvas
* @param centre
* @param radius
*/
private void drawOval(Canvas canvas, int centre, int radius) {
/**
* 根据需要画的个数以及间隙计算每个块块所占的比例*360
*/
float itemSize = (360 * 1.0f - mCount * mSplitSize) / mCount;
RectF oval = new RectF(centre - radius, centre - radius, centre + radius, centre + radius); // 用于定义的圆弧的形状和大小的界限
mPaint.setColor(mFirstColor); // 设置圆环的颜色
for (int i = 0; i < mCount; i++) {
canvas.drawArc(oval, i * (itemSize + mSplitSize), itemSize, false, mPaint); // 根据进度画圆弧
}
mPaint.setColor(mSecondColor); // 设置圆环的颜色
for (int i = 0; i < mCurrentCount; i++) {
canvas.drawArc(oval, i * (itemSize + mSplitSize), itemSize, false, mPaint); // 根据进度画圆弧
}
}我们再给它添加Touch事件来调节音量:
private int xDown, xUp;
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
xDown = (int) event.getY();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
xUp = (int) event.getY();
if (xUp > xDown) {
mCurrentCount--;
} else {
mCurrentCount++;
}
postInvalidate();
break;
}
return true;
}运行效果图如下,是不是很简单呢?
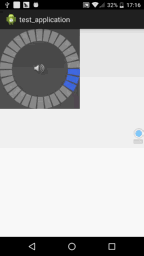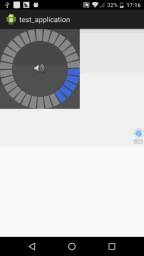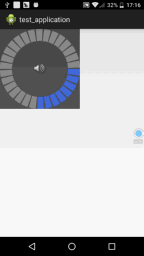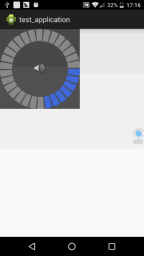
组合控件
组合控件的意思就是,我们并不需要自己去绘制视图上显示的内容,而只是用系统原生的控件就好了,但我们可以将几个系统原生的控件组合到一起,这样创建出的控件就被称为组合控件。
标题栏就是个很常见的组合控件,很多界面的头部都会放置一个标题栏,标题栏上会有个返回按钮,点击按钮后就可以返回到上一个界面。那么下面我们就来尝试去实现这样一个标题栏控件。
组合布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:background="#CFCFCF" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button_left"
android:layout_width="40dp"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dp"
android:background="@drawable/back" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/title_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="This is Title"
android:textColor="#EE2C2C"
android:textSize="20sp" />
</RelativeLayout>接下来创建一个TitleBar继承自FrameLayout,代码如下:
public class TitleBar extends FrameLayout {
private Button leftButton;
private TextView titleText;
public TitleBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.title_layout, this);
titleText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.title_text);
leftButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button_left);
leftButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
((Activity) getContext()).finish();
}
});
}
public void setTitleText(String text) {
titleText.setText(text);
}
public void setLeftButtonListener(OnClickListener l) {
leftButton.setOnClickListener(l);
}
}由于我们这里没有自定义属性(当然也可以添加),所以直接跳过第1,2步,组合控件的测量和绘图是按照原生控件来的,也就没必要重写onMesure和onDraw了。这里是通过调用LayoutInflater的inflate()方法来加载刚刚定义的布局文件。
另外,为了让TitleBar有更强地扩展性,我们还提供了setTitleText()、setLeftButtonListener()等方法,分别用于设置标题栏上的文字以及返回按钮的点击事件。
使用组合View:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
xmlns:custom="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.hx.test"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<com.hx.test.TitleBar
android:id="@+id/title"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<com.hx.test.CustomVolumControlBar
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_below="@+id/title"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
custom:firstColor="#8f8f8f"
custom:secondColor="#4169E1"
custom:circleWidth="30sp"
custom:dotCount="30"
custom:splitSize="2"
custom:bg="@drawable/volume" />
</RelativeLayout>这样就成功将一个标题栏控件引入到布局文件中了,运行一下程序,效果如下:
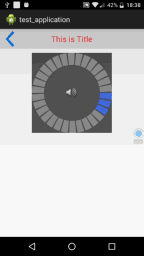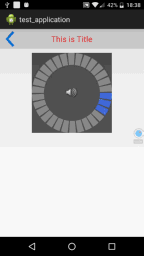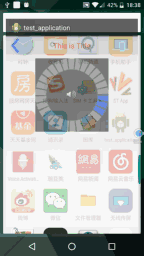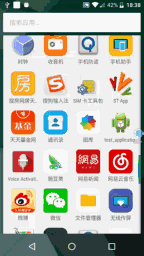
可以看到点击一下back按钮,就可以关闭当前的Activity了。如果你想要修改标题栏上显示的内容,或者返回按钮的默认事件,只需要在Activity中通过findViewById()方法得到TitleBar的实例,然后调用setTitleText()和setLeftButtonListener()方法进行设置就OK了。
继承控件
继承控件的意思就是,我们并不需要自己从头去实现一个控件,只需要去继承一个现有的控件,然后在这个控件上增加一些新的功能,就可以形成一个自定义的控件了。这种自定义控件的特点就是不仅能够按照我们的需求加入相应的功能,还可以保留原生控件的所有功能。





















