1、PopupWindow的相关函数
(1)、构造函数:
//方法一:
public PopupWindow (Context context)
//方法二:
public PopupWindow(View contentView)
//方法三:
public PopupWindow(View contentView, int width, int height)
//方法四:
public PopupWindow(View contentView, int width, int height, boolean focusable)
首要注意:看这里有四个构造函数,但要生成一个PopupWindow最基本的三个条件是一定要设置的:View contentView,int width, int height ;少任意一个就不可能弹出来PopupWindow!!!!
所以,如果使用方法一来构造PopupWindow,那完整的构造代码应该是这样的:
View contentView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.popuplayout, null);
PopupWindwo popWnd = PopupWindow (context);
popWnd.setContentView(contentView);
popWnd.setWidth(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
popWnd.setHeight(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);这里的WRAP_CONTENT可以换成match_parent也可以是具体的数值,它是指PopupWindow的大小,也就是contentview的大小,注意popupwindow根据这个大小显示你的View,如果你的View本身是从xml得到的,那么xml的第一层view的大小属性将被忽略。相当于popupWindow的width和height属性直接和第一层View相对应。
设想下面一种场景:
popupWindow 设置为WRAP_CONTENT ,我想得到的是一个宽150dip 高80dip的popupwindow,需要额外加一层LinearLayout,这个LinearLayout 的layout_width和layout_height为任意值。而我们真正想显示的View 放在第二层,并且 android:layout_width="150.0dip" android:layout_height="80.0dip"
如:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<LinearLayout
android:background="@drawable/shape_ret_loading_bg"
android:layout_width="150.0dip"
android:layout_height="80.0dip"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center">
<TextView
android:textSize="14dip"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="10.0dip"
android:text="加载中..."
/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
(2)显示函数
//相对某个控件的位置(正左下方),无偏移
showAsDropDown(View anchor):
//相对某个控件的位置,有偏移;xoff表示x轴的偏移,正值表示向左,负值表示向右;yoff表示相对y轴的偏移,正值是向下,负值是向上;
showAsDropDown(View anchor, int xoff, int yoff):
//相对于父控件的位置(例如正中央Gravity.CENTER,下方Gravity.BOTTOM等),可以设置偏移或无偏移
showAtLocation(View parent, int gravity, int x, int y):这里有两种显示方式:
1、显示在某个指定控件的下方
showAsDropDown(View anchor):
showAsDropDown(View anchor, int xoff, int yoff);
2、指定父视图,显示在父控件的某个位置(Gravity.TOP,Gravity.RIGHT等)
showAtLocation(View parent, int gravity, int x, int y);
(3)、其它函数
public void dismiss()
//另外几个函数,这里不讲其意义,下篇细讲
public void setFocusable(boolean focusable)
public void setTouchable(boolean touchable)
public void setOutsideTouchable(boolean touchable)
public void setBackgroundDrawable(Drawable background)
dismiss(),用于不需要的时候,将窗体隐藏掉。
setFocusable(true);
,
PopupWindow弹出后,所有的触屏和物理按键都有PopupWindows处理。其他任何事件的响应都必须发生在PopupWindow消失之后, (home 等系统层面的事件除外)。比如这样一个PopupWindow出现的时候,按back键首先是让PopupWindow消失,第二次按才是退出activity,准确的说是想退出activity你得首先让PopupWindow消失 。
如果PopupWindow中有Editor的话,focusable要为true。
而setFocusable(false);
则PopUpWindow只是一个浮现在当前界面上的view而已,不影响当前界面的任何操作。
是一个“没有存在感”的东西。
一般情况下
setFocusable(true);
(4)、 为PopupWindow添加动画
为PopupWindow添加动画并不难,只需要使用一个函数即可:
mPopWindow.setAnimationStyle(R.style.contextMenuAnim);
push_bottom_in.xml):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-- 上下滑入式 -->
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<translate
android:duration="200"
android:fromYDelta="100%p"
android:toYDelta="0"/>
<alpha
android:duration="200"
android:fromAlpha="0.0"
android:toAlpha="1.0"
/>
</set>
出场动画(push_bottom_ou.xml):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-- 上下滑入式 -->
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<translate
android:duration="200"
android:fromYDelta="0"
android:toYDelta="50%p"/>
<alpha
android:duration="200"
android:fromAlpha="1.0"
android:toAlpha="0.0"/>
</set>
最后产生一个对应的style -- contextMenuAnim
<style name="PopupAnimation" parent="android:Animation">
<item name="android:windowEnterAnimation">@anim/push_bottom_in</item> //进场动画
<item name="android:windowExitAnimation">@anim/push_bottom_out</item> //出场动画
</style>源码解析:
首先PopupWindow就是一个绘制在屏幕上面的弹框,那么使用到的就是WindowManager,让其绘制在屏幕上,同时它有类似一些View绘制,那它也需要去读取配置文件中的内容,比如我们设置的背景,看源码:
public PopupWindow(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
mContext = context;
mWindowManager = (WindowManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
final TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(
attrs, R.styleable.PopupWindow, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
final Drawable bg = a.getDrawable(R.styleable.PopupWindow_popupBackground);
mElevation = a.getDimension(R.styleable.PopupWindow_popupElevation, 0);
mOverlapAnchor = a.getBoolean(R.styleable.PopupWindow_overlapAnchor, false);
// Preserve default behavior from Gingerbread. If the animation is
// undefined or explicitly specifies the Gingerbread animation style,
// use a sentinel value.
if (a.hasValueOrEmpty(R.styleable.PopupWindow_popupAnimationStyle)) {
final int animStyle = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.PopupWindow_popupAnimationStyle, 0);
if (animStyle == R.style.Animation_PopupWindow) {
mAnimationStyle = ANIMATION_STYLE_DEFAULT;
} else {
mAnimationStyle = animStyle;
}
} else {
mAnimationStyle = ANIMATION_STYLE_DEFAULT;
}
final Transition enterTransition = getTransition(a.getResourceId(
R.styleable.PopupWindow_popupEnterTransition, 0));
final Transition exitTransition;
if (a.hasValueOrEmpty(R.styleable.PopupWindow_popupExitTransition)) {
exitTransition = getTransition(a.getResourceId(
R.styleable.PopupWindow_popupExitTransition, 0));
} else {
exitTransition = enterTransition == null ? null : enterTransition.clone();
}
a.recycle();
setEnterTransition(enterTransition);
setExitTransition(exitTransition);
setBackgroundDrawable(bg);
}
很熟悉这样的代码,因为在自定义View中需要用到的,这里就不详细介绍。
接下来就看看它的构造函数,看一个具体的构造函数
public PopupWindow(View contentView, int width, int height, boolean focusable) {
if (contentView != null) {
mContext = contentView.getContext();
mWindowManager = (WindowManager) mContext.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE); //获取WindowManager
}
setContentView(contentView);//设置内容,因为popupWindow需要我们去设置其中的View,
setWidth(width);//设置宽
setHeight(height);//设置高
setFocusable(focusable);//设置它是否获取焦点
}
这个也和我们使用到View类似。当我们使用一个抽象的View的时候,我们也需要在其中添加View,并且也需要个整个View设置宽和高,为什么不直接从View的配置文件中得到呢,看这个链接的最后一点, 给出了很好的解释。
showAtLocation()函数来分析,先上源码:
public void showAtLocation(IBinder token, int gravity, int x, int y) {
if (isShowing() || mContentView == null) {
return;
}
TransitionManager.endTransitions(mDecorView);//结束View的动画
unregisterForScrollChanged();//并注销掉滚动改变监听事件
mIsShowing = true;
mIsDropdown = false;
//准备LayoutParams,这个就是WindowManager需要用到的,这个就是用来在屏幕显示用到的
final WindowManager.LayoutParams p = createPopupLayoutParams(token);
//准备弹框
preparePopup(p);
// Only override the default if some gravity was specified.
if (gravity != Gravity.NO_GRAVITY) {
p.gravity = gravity;
}
p.x = x;
p.y = y;
//弹框
invokePopup(p);
}
preparePopup()和 invokePopup();从他们字面上看出他们一个是准备弹框,和执行弹框动作。
这里先来看看 createPopupLayoutParams(token)这个方法,这个方法就是来创建WindowManager. LayoutParams,并最后调用windowManager.addView(view, lyoutParams)显示在屏幕上。
private WindowManager.LayoutParams createPopupLayoutParams(IBinder token) {
final WindowManager.LayoutParams p = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
// These gravity settings put the view at the top left corner of the
// screen. The view is then positioned to the appropriate location by
// setting the x and y offsets to match the anchor's bottom-left
// corner.
p.gravity = Gravity.START | Gravity.TOP; //设置弹框的位置
p.flags = computeFlags(p.flags); //设置弹框Flag,其中就有是否让其聚焦和是否可触摸
p.type = mWindowLayoutType; //设置为WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_APPLICATION_PANEL,设置其层级关系
p.token = token; //设置它所依赖的View
p.softInputMode = mSoftInputMode;
p.windowAnimations = computeAnimationResource();
if (mBackground != null) {
p.format = mBackground.getOpacity();
} else {
p.format = PixelFormat.TRANSLUCENT;
}
if (mHeightMode < 0) {
p.height = mLastHeight = mHeightMode;
} else {
p.height = mLastHeight = mHeight;
}
if (mWidthMode < 0) {
p.width = mLastWidth = mWidthMode;
} else {
p.width = mLastWidth = mWidth;
}
// Used for debugging.
p.setTitle("PopupWindow:" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode()));
return p;
}
上面有相关注释,如果有不懂的,请看WindowManager的文章。
接下来,来看看准备弹框做了哪些事情,上源码:
private void preparePopup(WindowManager.LayoutParams p) {
if (mContentView == null || mContext == null || mWindowManager == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("You must specify a valid content view by "
+ "calling setContentView() before attempting to show the popup.");
}
// The old decor view may be transitioning out. Make sure it finishes
// and cleans up before we try to create another one.
if (mDecorView != null) { //取消动画
mDecorView.cancelTransitions();
}
// When a background is available, we embed the content view within
// another view that owns the background drawable.
//设置背景,这个通过查看createBackgroundView()源码,我们可以看到,它其实就重新封装了一层FrameLayout,他会重新调用PopupBackgroundView这个内部类,下面会介绍
//当有背景的时候,就封装一层,没有,就直接将设置View复制给mBackgroundView
if (mBackground != null) {
mBackgroundView = createBackgroundView(mContentView);
mBackgroundView.setBackground(mBackground);
} else {
mBackgroundView = mContentView;
}
//这个就是再次封装一个FrameLayout,并且该FrameLayout做了事件的拦截和分发。
mDecorView = createDecorView(mBackgroundView);
// The background owner should be elevated so that it casts a shadow.
mBackgroundView.setElevation(mElevation);
// We may wrap that in another view, so we'll need to manually specify
// the surface insets.
final int surfaceInset = (int) Math.ceil(mBackgroundView.getZ() * 2);
p.surfaceInsets.set(surfaceInset, surfaceInset, surfaceInset, surfaceInset);
p.hasManualSurfaceInsets = true;
mPopupViewInitialLayoutDirectionInherited =
(mContentView.getRawLayoutDirection() == View.LAYOUT_DIRECTION_INHERIT);
mPopupWidth = p.width;
mPopupHeight = p.height;
}
上面的代码中有一点需要注意的,就是写上注释的地方,就是判断是否有背景的时候,如果有背景,封装一层FrameLayout,最后再封装一层FrameLayout,这次的FrameLayout,有事件的拦截等操作。其他的代码就是对其属性的一些复制,这里我们可以不需要过多的关注。
先来看执行弹框,上源码:
private void invokePopup(WindowManager.LayoutParams p) {
if (mContext != null) {
p.packageName = mContext.getPackageName();
}
final PopupDecorView decorView = mDecorView;
decorView.setFitsSystemWindows(mLayoutInsetDecor);
setLayoutDirectionFromAnchor();
//windowManager添加View,让其显示在屏幕上
mWindowManager.addView(decorView, p);
if (mEnterTransition != null) {
decorView.requestEnterTransition(mEnterTransition);//设置进场动画
}
}
那么他的执行过程就是和WindowManager如何添加一个窗口一样,只是其中多了很多其它细节。
createBackgroundView(),它是如何去给mContentView添加一层FragmentLayout
private PopupBackgroundView createBackgroundView(View contentView) {
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = mContentView.getLayoutParams(); //创建LayoutParams,获取contentView中的高
final int height;
if (layoutParams != null && layoutParams.height == ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
height = ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
} else {
height = ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT;
}
final PopupBackgroundView backgroundView = new PopupBackgroundView(mContext); //创建PopupBackgroundView,内部类,继承了FrameLayout
final PopupBackgroundView.LayoutParams listParams = new PopupBackgroundView.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, height);
backgroundView.addView(contentView, listParams); //给contentView封装了一成FrameLayout
return backgroundView;
}private class PopupBackgroundView extends FrameLayout {
public PopupBackgroundView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
@Override
protected int[] onCreateDrawableState(int extraSpace) {
if (mAboveAnchor) {
final int[] drawableState = super.onCreateDrawableState(extraSpace + 1);
View.mergeDrawableStates(drawableState, ABOVE_ANCHOR_STATE_SET);
return drawableState;
} else {
return super.onCreateDrawableState(extraSpace);
}
}
}
其中里面做一个件事,就是复写了
onCreateDrawableState(),该方法的作用
View生成状态集传递给drawable对象,参数不为0表示有自定义状态,
不能直接给Drawable指定状态,要通过onCreateDrawableState(0)返回的int[],Drawable对象从中可以解析出一个index来找到对应图片,
也就是说Drawable的状态是和View相关联,状态值是View传递给它,而View的状态值是由一系列不同的操作,例如点击,
选中产生。简单的来讲就是对
Drawable的操作。
接下来是createDecorView()方法,这个方法就是对其在进行一次封装,而这次封装就是不管是否有无背景封装过,都在进行一次封装,并且这次在添加一层,这层会对事件的监听分发进行拦截。
private PopupDecorView createDecorView(View contentView) {
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = mContentView.getLayoutParams();
final int height;
if (layoutParams != null && layoutParams.height == ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
height = ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
} else {
height = ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT;
}
final PopupDecorView decorView = new PopupDecorView(mContext);
decorView.addView(contentView, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, height);
decorView.setClipChildren(false);
decorView.setClipToPadding(false);
return decorView;
}
createBackgroundView()一样,那么我们看看PopupDecorView,这个根View做了哪些事情。其中的内容很长,我们一点一点来讲,这里建议大家可以打开PopupWindown的源码来看。
PopupDecorView中对事件的做了处理。
@Override
public boolean dispatchKeyEvent(KeyEvent event) {
if (event.getKeyCode() == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK) { //监听的是返回按钮
if (getKeyDispatcherState() == null) {
return super.dispatchKeyEvent(event);
}
if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN && event.getRepeatCount() == 0) {
final KeyEvent.DispatcherState state = getKeyDispatcherState();
if (state != null) {
state.startTracking(event, this);
}
return true;
} else if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_UP) {
final KeyEvent.DispatcherState state = getKeyDispatcherState();
if (state != null && state.isTracking(event) && !event.isCanceled()) {
dismiss();
return true;
}
}
return super.dispatchKeyEvent(event);
} else {
return super.dispatchKeyEvent(event);
}
}@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
if (mTouchInterceptor != null && mTouchInterceptor.onTouch(this, ev)) {
return true;
}
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
final int x = (int) event.getX();
final int y = (int) event.getY();
if ((event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN)
&& ((x < 0) || (x >= getWidth()) || (y < 0) || (y >= getHeight()))) {
dismiss();
return true;
} else if (event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_OUTSIDE) {
dismiss();
return true;
} else {
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
}
dispatchTouchEvent()就是判断是否是该层消费掉事件,还是事件传递下去, onTouchEvent(),消费掉后,就调用该方法。该方法是点击了View所在框的外面,就让弹框消失。
其中 MotionEvent . ACTION_OUTSIDE。
MotionEvent.ACTION_OUTSIDE与setOutsideTouchable(boolean touchable)
可能把这两个放在一块,大家可能就恍然大悟了,表着急,一个个来看。
先看看setOutsideTouchable(boolean touchable)的代码:
public void setOutsideTouchable(boolean touchable) {
mOutsideTouchable = touchable;
}然后再看看mOutsideTouchable哪里会用到下面代码,我做了严重精减,等下会再完整再讲这一块。
private int computeFlags(int curFlags) {
curFlags &= ~(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH);
…………
if (mOutsideTouchable) {
curFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH;
}
…………
return curFlags;
}
这段代码主要是用各种变量来设置window所使用的flag; 首先,将curFlags所在运算的各种Flag,全部置为False;代码如下:
curFlags &= ~(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH);
然后,再根据用户设置的变量来开启:
if (mOutsideTouchable) {
curFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH;
}
既然讲到FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH,那我们来看看FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH所代表的意义:
这段话的意思是说,如果窗体设置了FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH这个flag,那么 用户点击窗体以外的位置时,将会在窗体的MotionEvent中收到MotionEvetn.ACTION_OUTSIDE事件。
所以在PopupViewContainer中添加了对MotionEvent.ACTION_OUTSIDE的捕捉!当用户点击PopupViewContainer以外的区域时,将dismiss掉PopupWindow。
接下来解决一个问题,这个问题是以前的代码造成的,我们看到,不管是否设置了背景,都会封装一层PopupDecorView,该层对事件进行拦截,那么,和网上其他根据旧代码来设置背景后让其可以点击屏幕外就让其消失的疑惑解决了,想让其点击屏幕外面直接设置setOutsideTouchable(true)就可以了。有时候,我们不需要让其消失,是让其中的控件来出发让其消失,就是点击View外面没有用,我们仅仅设置setOutsideTouchable(false)是否不可以的,需要setFocusable(false),默认是关闭的,可以不需要设置。因为我们看到,当我们设置了setFocusable(true),会处理 if (( event . getAction () == MotionEvent . ACTION_DOWN ),那么设置setOutsideTouchable没有任何作用了,都会让其消失,所有,不让其消失,我们setFocusable(false),那么这又说如果不让其点击屏幕外面后消失,就不能使用EditView.因为使用EditView是需要获取焦点了,这样才能弹出输入框。
MainActivity.java
package com.xianlaxuankuang.selectWindown;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.drawable.BitmapDrawable;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.ImageButton;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.PopupWindow;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener,OnItemClickListener{
ListView listView;
EditText editText;
List<String> list;
PopupWindow popupWindow;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
findViewById(R.id.button).setOnClickListener(this);
editText=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.eidtTextId);
list = new ArrayList<String>();
}
//重写点击事件
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
showPopupWindow();
}
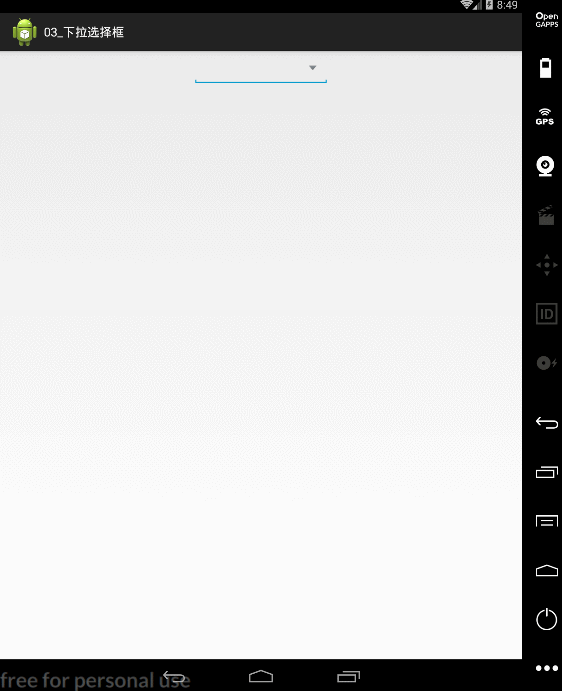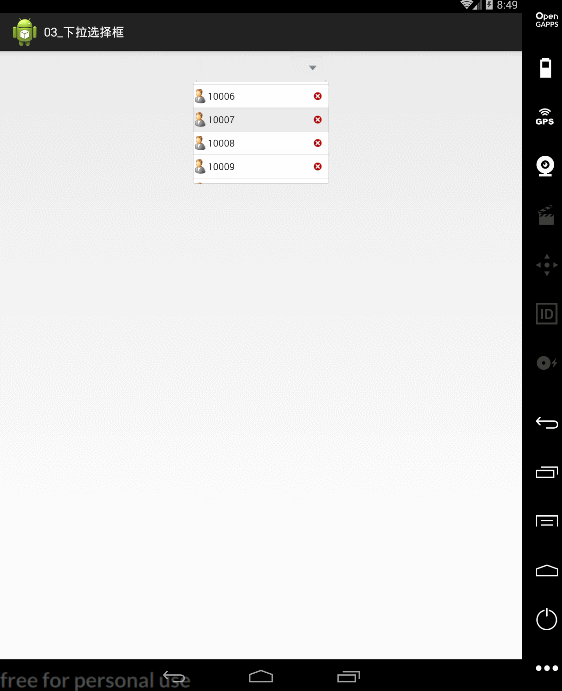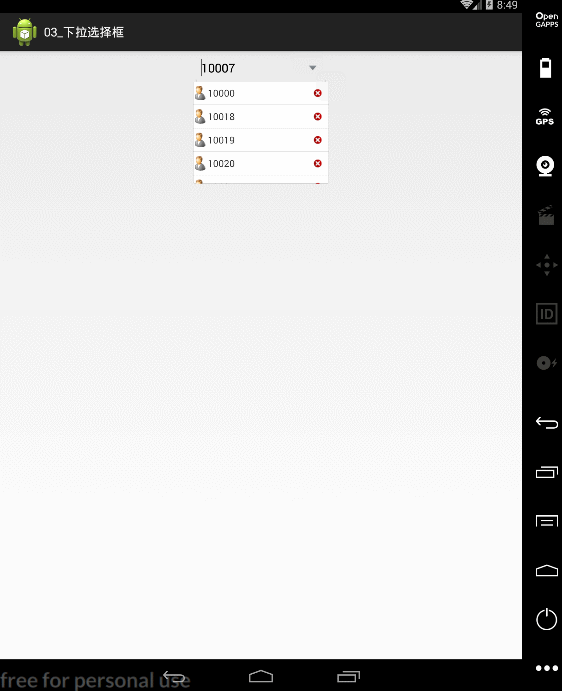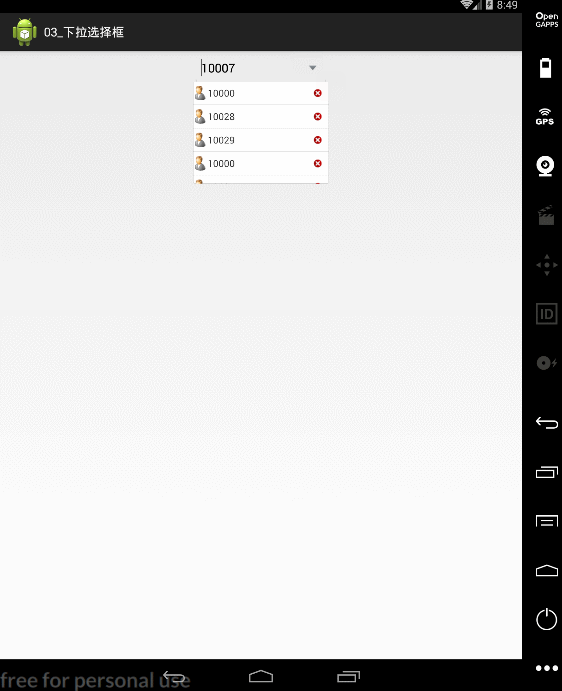
private void showPopupWindow() {
initListView();
//显示下拉选择框
popupWindow=new PopupWindow(listView, editText.getWidth(), 300);
//设置点击外部区域,自动隐藏
popupWindow.setOutsideTouchable(true); //外部可触摸
popupWindow.setBackgroundDrawable(new BitmapDrawable());//设置一个空的背景,响应点击事件
popupWindow.setFocusable(true);//设置可获取焦点
//指定在哪个控件下面
popupWindow.showAsDropDown(editText, 0, -10);
}
private void initListView() {
listView = new ListView(this);
for(int i=0;i<30;i++){
list.add(10000+i+"");
}
listView.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.listview_background);//设置背景图片
listView.setAdapter(new MyAdapter());
listView.setOnItemClickListener(this);
}
class MyAdapter extends BaseAdapter{
@Override
public int getCount() {
return list.size();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return list.get(position);
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return position;
}
@Override
public View getView(final int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
View view;
if(convertView==null){
view=View.inflate(parent.getContext(), R.layout.item_nuber, null);
}else{
view=convertView;
}
TextView textView=(TextView)view.findViewById(R.id.textViewId);
textView.setText(list.get(position));
ImageButton button=(ImageButton)view.findViewById(R.id.image_delete);
button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
list.remove(position);
notifyDataSetChanged();//更新见面
if(list.size()==0){
popupWindow.dismiss();//如果删除的是最后一条那么把该popupWindow隐藏
}
}
});
return view;
}
}
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) {
editText.setText(list.get(position));
popupWindow.dismiss();
}
}
activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="${relativePackage}.${activityClass}" >
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/eidtTextId"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
/>
<ImageButton
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:background="@null"
android:padding="10dp"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:src="@drawable/down_arrow"/>
</RelativeLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
item_nuber.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:descendantFocusability="blocksDescendants"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<!-- android:descendantFocusability="blocksDescendants" -->
<!-- 表示区块点击 -->
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/user"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:id="@+id/textViewId"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<ImageButton
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/image_delete"
android:padding="10dp"
android:background="@null"
android:src="@drawable/delete"/>
<\LinearLayout>





















