Tensorflow读取数据的一般方式有下面3种:
- preloaded直接创建变量:在tensorflow定义图的过程中,创建常量或变量来存储数据
- feed:在运行程序时,通过feed_dict传入数据
- reader从文件中读取数据:在tensorflow图开始时,通过一个输入管线从文件中读取数据
Preloaded方法的简单例子
1 import tensorflow as tf
2
3 """定义常量"""
4 const_var = tf.constant([1, 2, 3])
5 """定义变量"""
6 var = tf.Variable([1, 2, 3])
7
8 with tf.Session() as sess:
9 sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
10 print(sess.run(var))
11 print(sess.run(const_var))
Feed方法
可以在tensorflow运算图的过程中,将数据传递到事先定义好的placeholder中。方法是在调用session.run函数时,通过feed_dict参数传入。简单例子:
1 import tensorflow as tf
2 """定义placeholder"""
3 x1 = tf.placeholder(tf.int16)
4 x2 = tf.placeholder(tf.int16)
5 result = x1 + x2
6 """定义feed_dict"""
7 feed_dict = {
8 x1: [10],
9 x2: [20]
10 }
11 """运行图"""
12 with tf.Session() as sess:
13 print(sess.run(result, feed_dict=feed_dict))
上面的两个方法在面对大量数据时,都存在性能问题。这时候就需要使用到第3种方法,文件读取,让tensorflow自己从文件中读取数据
从文件中读取数据

图引用自 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/27238630
步骤:
- 获取文件名列表list
- 创建文件名队列,调用tf.train.string_input_producer,参数包含:文件名列表,num_epochs【定义重复次数】,shuffle【定义是否打乱文件的顺序】
- 定义对应文件的阅读器>* tf.ReaderBase >* tf.TFRecordReader >* tf.TextLineReader >* tf.WholeFileReader >* tf.IdentityReader >* tf.FixedLengthRecordReader
- 解析器 >* tf.decode_csv >* tf.decode_raw >* tf.image.decode_image >* …
- 预处理,对原始数据进行处理,以适应network输入所需
- 生成batch,调用tf.train.batch() 或者 tf.train.shuffle_batch()
- prefetch【可选】使用预加载队列slim.prefetch_queue.prefetch_queue()
- 启动填充队列的线程,调用tf.train.start_queue_runners
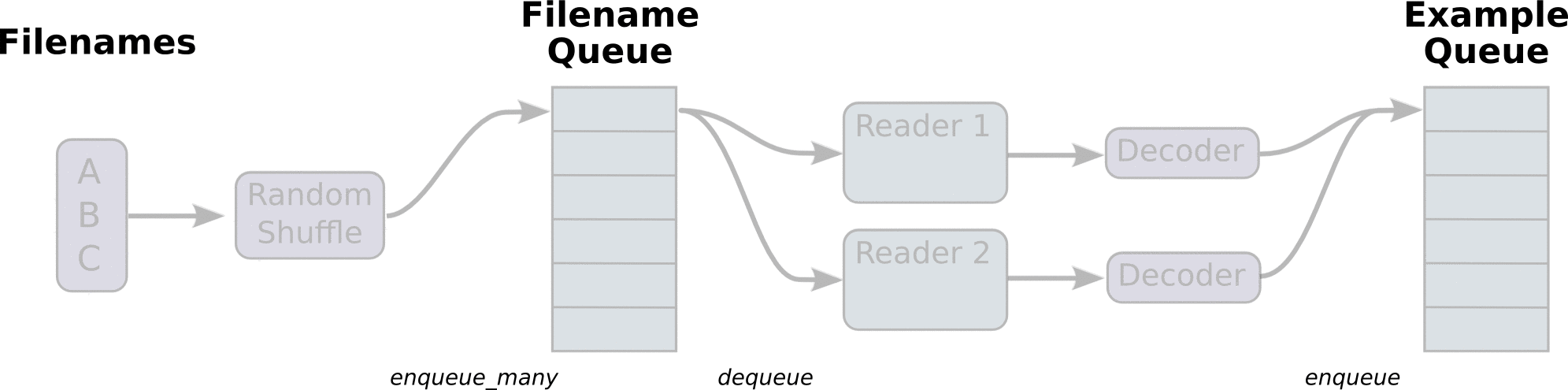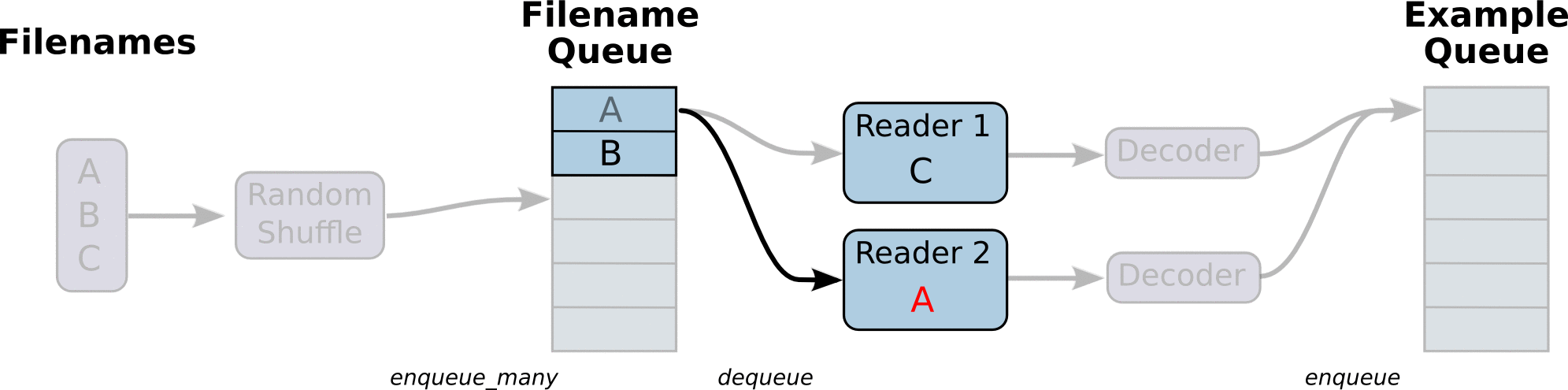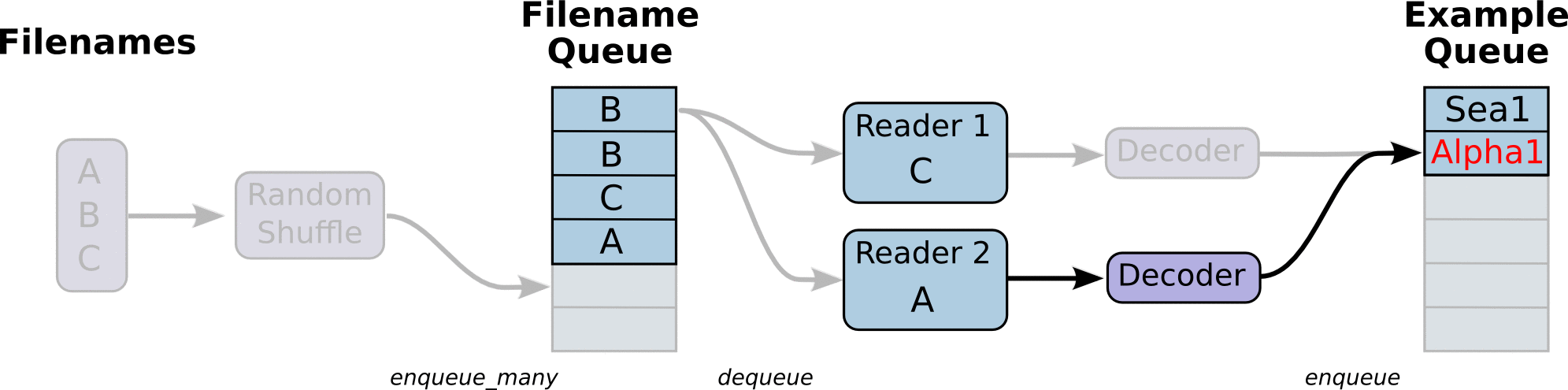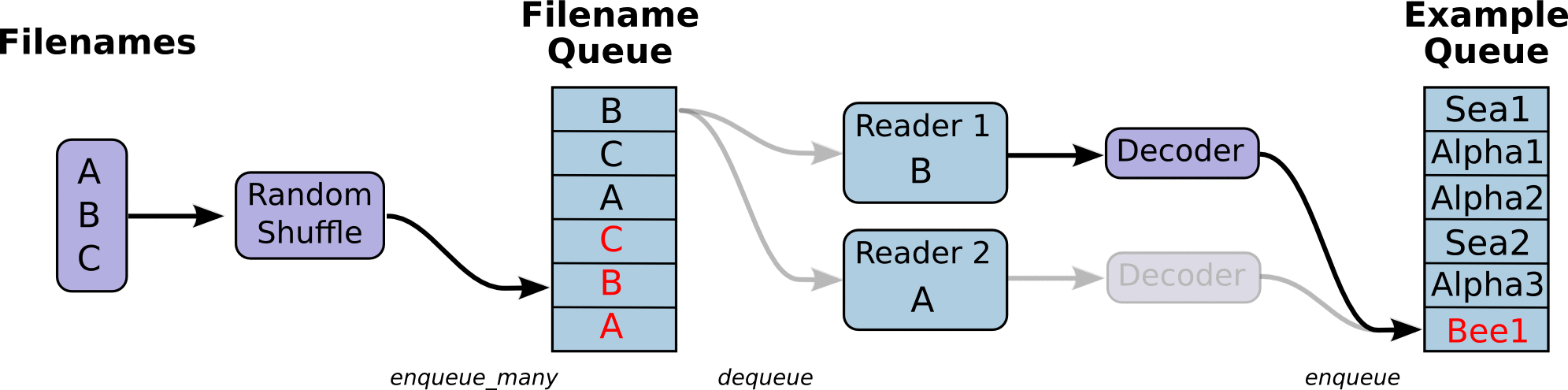
图引用自http://www.yyliu.cn/post/89458415.html
读取文件格式举例
tensorflow支持读取的文件格式包括:CSV文件,二进制文件,TFRecords文件,图像文件,文本文件等等。具体使用时,需要根据文件的不同格式,选择对应的文件格式阅读器,再将文件名队列传为参数,传入阅读器的read方法中。方法会返回key与对应的record value。将value交给解析器进行解析,转换成网络能进行处理的tensor。
CSV文件读取:
阅读器:tf.TextLineReader
解析器:tf.decode_csv
1 filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(["file0.csv", "file1.csv"])
2 """阅读器"""
3 reader = tf.TextLineReader()
4 key, value = reader.read(filename_queue)
5 """解析器"""
6 record_defaults = [[1], [1], [1], [1]]
7 col1, col2, col3, col4 = tf.decode_csv(value, record_defaults=record_defaults)
8 features = tf.concat([col1, col2, col3, col4], axis=0)
9
10 with tf.Session() as sess:
11 coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
12 threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(coord=coord)
13 for i in range(100):
14 example = sess.run(features)
15 coord.request_stop()
16 coord.join(threads)
二进制文件读取:
阅读器:tf.FixedLengthRecordReader
解析器:tf.decode_raw
图像文件读取:
阅读器:tf.WholeFileReader
解析器:tf.image.decode_image, tf.image.decode_gif, tf.image.decode_jpeg, tf.image.decode_png
TFRecords文件读取
TFRecords文件是tensorflow的标准格式。要使用TFRecords文件读取,事先需要将数据转换成TFRecords文件,具体可察看:convert_to_records.py 在这个脚本中,先将数据填充到tf.train.Example协议内存块(protocol buffer),将协议内存块序列化为字符串,再通过tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter写入到TFRecords文件中去。
阅读器:tf.TFRecordReader
解析器:tf.parse_single_example
又或者使用slim提供的简便方法:slim.dataset.Data以及slim.dataset_data_provider.DatasetDataProvider方法
1 def get_split(record_file_name, num_sampels, size):
2 reader = tf.TFRecordReader
3
4 keys_to_features = {
5 "image/encoded": tf.FixedLenFeature((), tf.string, ''),
6 "image/format": tf.FixedLenFeature((), tf.string, 'jpeg'),
7 "image/height": tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64, tf.zeros([], tf.int64)),
8 "image/width": tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64, tf.zeros([], tf.int64)),
9 }
10
11 items_to_handlers = {
12 "image": slim.tfexample_decoder.Image(shape=[size, size, 3]),
13 "height": slim.tfexample_decoder.Tensor("image/height"),
14 "width": slim.tfexample_decoder.Tensor("image/width"),
15 }
16
17 decoder = slim.tfexample_decoder.TFExampleDecoder(
18 keys_to_features, items_to_handlers
19 )
20 return slim.dataset.Dataset(
21 data_sources=record_file_name,
22 reader=reader,
23 decoder=decoder,
24 items_to_descriptions={},
25 num_samples=num_sampels
26 )
27
28
29 def get_image(num_samples, resize, record_file="image.tfrecord", shuffle=False):
30 provider = slim.dataset_data_provider.DatasetDataProvider(
31 get_split(record_file, num_samples, resize),
32 shuffle=shuffle
33 )
34 [data_image] = provider.get(["image"])
35 return data_image
参考资料:
tensorflow 1.0 学习:十图详解tensorflow数据读取机制






















