一、Shiro框架简单介绍
Apache Shiro是Java的一个安全框架,旨在简化身份验证和授权。Shiro在JavaSE和JavaEE项目中都可以使用。它主要用来处理身份认证,授权,企业会话管理和加密等。Shiro的具体功能点如下:
(1)身份认证/登录,验证用户是不是拥有相应的身份;
(2)授权,即权限验证,验证某个已认证的用户是否拥有某个权限;即判断用户是否能做事情,常见的如:验证某个用户是否拥有某个角色。或者细粒度的验证某个用户对某个资源是否具有某个权限;
(3)会话管理,即用户登录后就是一次会话,在没有退出之前,它的所有信息都在会话中;会话可以是普通JavaSE环境的,也可以是如Web环境的;
(4)加密,保护数据的安全性,如密码加密存储到数据库,而不是明文存储;
(5)Web支持,可以非常容易的集成到Web环境;
Caching:缓存,比如用户登录后,其用户信息、拥有的角色/权限不必每次去查,这样可以提高效率;
(6)shiro支持多线程应用的并发验证,即如在一个线程中开启另一个线程,能把权限自动传播过去;
(7)提供测试支持;
(8)允许一个用户假装为另一个用户(如果他们允许)的身份进行访问;
(9)记住我,这个是非常常见的功能,即一次登录后,下次再来的话不用登录了。
文字描述可能并不能让猿友们完全理解具体功能的意思。下面我们以登录验证为例,向猿友们介绍Shiro的使用。至于其他功能点,猿友们用到的时候再去深究其用法也不迟。
二、Shiro实例详细说明
本实例环境:eclipse + maven
本实例采用的主要技术:spring + springmvc + shiro
2.1、依赖的包
假设已经配置好了spring和springmvc的情况下,还需要引入shiro以及shiro集成到spring的包,maven依赖如下:

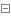
org.apache.shiro
shiro-core
1.2.1
org.apache.shiro
shiro-web
1.2.1
org.apache.shiro
shiro-ehcache
1.2.1
org.apache.shiro
shiro-spring
1.2.1
View Code2.2、定义shiro拦截器
对url进行拦截,如果没有验证成功的需要验证,然后额外给用户赋予角色和权限。
自定义的拦截器需要继承AuthorizingRealm并实现登录验证和赋予角色权限的两个方法,具体代码如下:


packagecom.luo.shiro.realm;importjava.util.HashSet;importjava.util.Set;importorg.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;importorg.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;importorg.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;importorg.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo;importorg.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;importorg.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;importorg.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo;importorg.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;importorg.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;importcom.luo.util.DecriptUtil;public class MyShiroRealm extendsAuthorizingRealm {//这里因为没有调用后台,直接默认只有一个用户("luoguohui","123456")private static final String USER_NAME = "luoguohui";private static final String PASSWORD = "123456";/** 授权*/@OverrideprotectedAuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
Set roleNames = new HashSet();
Set permissions = new HashSet();
roleNames.add("administrator");//添加角色
permissions.add("newPage.jhtml"); //添加权限
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = newSimpleAuthorizationInfo(roleNames);
info.setStringPermissions(permissions);returninfo;
}/** 登录验证*/@OverrideprotectedAuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(
AuthenticationToken authcToken)throwsAuthenticationException {
UsernamePasswordToken token=(UsernamePasswordToken) authcToken;if(token.getUsername().equals(USER_NAME)){return newSimpleAuthenticationInfo(USER_NAME, DecriptUtil.MD5(PASSWORD), getName());
}else{throw newAuthenticationException();
}
}
}
View Code
2.3、shiro配置文件
spring-shiro.xml文件内容如下:
default-lazy-init="true">
Shiro Configuration
/index.jhtml =authc/login.jhtml =anon/checkLogin.json =anon/loginsuccess.jhtml =anon/logout.json =anon/**= authc
depends-on="lifecycleBeanPostProcessor">这里有必要说清楚”shiroFilter” 这个bean里面的各个属性property的含义:
(1)securityManager:这个属性是必须的,没什么好说的,就这样配置就好。
(2)loginUrl:没有登录的用户请求需要登录的页面时自动跳转到登录页面,可配置也可不配置。
(3)successUrl:登录成功默认跳转页面,不配置则跳转至”/”,一般可以不配置,直接通过代码进行处理。
(4)unauthorizedUrl:没有权限默认跳转的页面。
(5)filterChainDefinitions,对于过滤器就有必要详细说明一下:
1)Shiro验证URL时,URL匹配成功便不再继续匹配查找(所以要注意配置文件中的URL顺序,尤其在使用通配符时),故filterChainDefinitions的配置顺序为自上而下,以最上面的为准
2)当运行一个Web应用程序时,Shiro将会创建一些有用的默认Filter实例,并自动地在[main]项中将它们置为可用自动地可用的默认的Filter实例是被DefaultFilter枚举类定义的,枚举的名称字段就是可供配置的名称
3)通常可将这些过滤器分为两组:
anon,authc,authcBasic,user是第一组认证过滤器
perms,port,rest,roles,ssl是第二组授权过滤器
注意user和authc不同:当应用开启了rememberMe时,用户下次访问时可以是一个user,但绝不会是authc,因为authc是需要重新认证的
user表示用户不一定已通过认证,只要曾被Shiro记住过登录状态的用户就可以正常发起请求,比如rememberMe
说白了,以前的一个用户登录时开启了rememberMe,然后他关闭浏览器,下次再访问时他就是一个user,而不会authc
4)举几个例子
/admin=authc,roles[admin] 表示用户必需已通过认证,并拥有admin角色才可以正常发起’/admin’请求
/edit=authc,perms[admin:edit] 表示用户必需已通过认证,并拥有admin:edit权限才可以正常发起’/edit’请求
/home=user 表示用户不一定需要已经通过认证,只需要曾经被Shiro记住过登录状态就可以正常发起’/home’请求
5)各默认过滤器常用如下(注意URL Pattern里用到的是两颗星,这样才能实现任意层次的全匹配)
/admins/**=anon 无参,表示可匿名使用,可以理解为匿名用户或游客
/admins/user/**=authc 无参,表示需认证才能使用
/admins/user/**=authcBasic 无参,表示httpBasic认证
/admins/user/**=user 无参,表示必须存在用户,当登入操作时不做检查
/admins/user/**=ssl 无参,表示安全的URL请求,协议为https
/admins/user/*=perms[user:add:]参数可写多个,多参时必须加上引号,且参数之间用逗号分割,如/admins/user/*=perms[“user:add:,user:modify:*”]
当有多个参数时必须每个参数都通过才算通过,相当于isPermitedAll()方法
/admins/user/**=port[8081]
当请求的URL端口不是8081时,跳转到schemal://serverName:8081?queryString
其中schmal是协议http或https等,serverName是你访问的Host,8081是Port端口,queryString是你访问的URL里的?后面的参数
/admins/user/**=rest[user]
根据请求的方法,相当于/admins/user/**=perms[user:method],其中method为post,get,delete等
/admins/user/**=roles[admin]
参数可写多个,多个时必须加上引号,且参数之间用逗号分割,如/admins/user/**=roles[“admin,guest”]
当有多个参数时必须每个参数都通过才算通过,相当于hasAllRoles()方法
2.4、web.xml配置引入对应的配置文件和过滤器
contextConfigLocation
classpath:application.xml,classpath:shiro/spring-shiro.xml
shiroFilter
org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy
targetFilterLifecycle
true
shiroFilter
*.jhtml
*.json2.5、controller代码


packagecom.luo.controller;importjava.util.HashMap;importjava.util.Map;importjavax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;importorg.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;importorg.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;importorg.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Controller;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;importorg.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;importcom.alibaba.druid.support.json.JSONUtils;importcom.luo.errorcode.LuoErrorCode;importcom.luo.exception.BusinessException;importcom.luo.util.DecriptUtil;@Controllerpublic classUserController {
@RequestMapping("/index.jhtml")public ModelAndView getIndex(HttpServletRequest request) throwsException {
ModelAndView mav= new ModelAndView("index");returnmav;
}
@RequestMapping("/exceptionForPageJumps.jhtml")public ModelAndView exceptionForPageJumps(HttpServletRequest request) throwsException {throw newBusinessException(LuoErrorCode.NULL_OBJ);
}
@RequestMapping(value="/businessException.json", method=RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBodypublicString businessException(HttpServletRequest request) {throw newBusinessException(LuoErrorCode.NULL_OBJ);
}
@RequestMapping(value="/otherException.json", method=RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBodypublic String otherException(HttpServletRequest request) throwsException {throw newException();
}//跳转到登录页面
@RequestMapping("/login.jhtml")public ModelAndView login() throwsException {
ModelAndView mav= new ModelAndView("login");returnmav;
}//跳转到登录成功页面
@RequestMapping("/loginsuccess.jhtml")public ModelAndView loginsuccess() throwsException {
ModelAndView mav= new ModelAndView("loginsuccess");returnmav;
}
@RequestMapping("/newPage.jhtml")public ModelAndView newPage() throwsException {
ModelAndView mav= new ModelAndView("newPage");returnmav;
}
@RequestMapping("/newPageNotAdd.jhtml")public ModelAndView newPageNotAdd() throwsException {
ModelAndView mav= new ModelAndView("newPageNotAdd");returnmav;
}/*** 验证用户名和密码
*@paramString username,String password
*@return
*/@RequestMapping(value="/checkLogin.json",method=RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBodypublicString checkLogin(String username,String password) {
Map result = new HashMap();try{
UsernamePasswordToken token= newUsernamePasswordToken(username, DecriptUtil.MD5(password));
Subject currentUser=SecurityUtils.getSubject();if (!currentUser.isAuthenticated()){//使用shiro来验证
token.setRememberMe(true);
currentUser.login(token);//验证角色和权限
}
}catch(Exception ex){throw newBusinessException(LuoErrorCode.LOGIN_VERIFY_FAILURE);
}
result.put("success", true);returnJSONUtils.toJSONString(result);
}/*** 退出登录*/@RequestMapping(value="/logout.json",method=RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBodypublicString logout() {
Map result = new HashMap();
result.put("success", true);
Subject currentUser=SecurityUtils.getSubject();
currentUser.logout();returnJSONUtils.toJSONString(result);
}
}
View Code上面代码,我们只需要更多地关注登录验证和退出登录的代码。
其中DecriptUtil.MD5(password),对密码进行md5加密解密是我自己写的工具类DecriptUtil,对应MyShiroRealm里面的登录验证里面也有对应对应的方法。
另外,BusinessException是我自己封装的异常类。
最后会提供整个工程源码供猿友下载,里面包含了所有的代码。
2.6、login.jsp代码
password:
登录
var param={
username : $("#username").val(),
password : $("#password").val()
};
$.ajax({
type:"post",
url:"<%=request.getContextPath()%>" + "/checkLogin.json",
data: param,
dataType:"json",
success: function(data) {if(data.success == false){
alert(data.errorMsg);
}else{//登录成功
window.location.href = "<%=request.getContextPath()%>" + "/loginsuccess.jhtml";
}
},
error: function(data) {
alert("调用失败....");
}
});
});2.7、效果演示
(2)如果登录失败和登录成功:
























