目录
- 1.正则表达式
- 1.1 元字符
- 1.2 示例
- 2.Lambda表达式
- 2.1 示例
- 2.2 Lambda表达式简写
- 3. 排序算法
- 3.1 冒泡排序
- 3.2 选择排序
- 3.3 二分选择(非排序算法)
1.正则表达式
正则表达式是用一些规定的字符制定规则,用这个规则来校验数据的合法性。
比如在用户输入注册昵称时,必须对其进行合法性校验。比如长度,大家可能会想, 直接用字符串长度方法加if不就行了,但是如果判断长度的同时还需要判断字符串 是否有敏感词。你可能会说,多重判断不是就可以实现功能,少量可以实现,数量
较多的话那可想而知代码量。
1.1 元字符
字符串中提供了匹配正则表达式方法:
// 匹配成功返回true,否则返回false
public boolean matches(String regex)
// 使用正则替换所有
public String replaceAll(String regex,String newStr)
// 使用正则分割字符串
public String[]split(String regex):- 匹配单个字符:
字符 | 说明 |
[a,b,c] | 符合abc中任意一个即可 |
[^a,b,c] | 除abc中任意一个即可 |
[a-zA-Z] | 包含a-z或A-Z中任意一个即可 |
[a-p[q-z]] | a到p或者q-z |
[a-z&&[d,e,f]] | 包含a-z并且符合d,e,f |
[a-z&&[^d,e,f]] | 包含a-z并且除d,e,f |
. | 匹配任意字符 |
\d | 匹配一个数值 |
\D | 匹配字符为非数值 |
\s | 匹配一个空白字符: [ \t\n\x0B\f\r] |
\S | 匹配非空白字符串 |
\w | 匹配数字,字符和下划线 |
\W | 匹配非单词字符 |
- 匹配多个字符:
字符 | 说明 |
x? | x匹配一次或者0次 |
x* | x匹配0次或者多次 |
x+ | x匹配一次或者多次 |
x{n} | x匹配n次 |
x{n,} | x匹配至少n次 |
x{n,m} | x匹配n到m次 |
1.2 示例
public class StringMatchesTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("a".matches("[a,b,c,d,e]"));
System.out.println("abc".matches("[a-z]"));
System.out.println("abc".matches("[a-z]+"));
System.out.println("9".matches("[\\d]"));
System.out.println("991607476".matches("[\\d]{6,20}"));
String temp = "asb121b4b54jb656";
// 将所有数值替换成A
String a = temp.replaceAll("[\\d]+", "A");
System.out.println(a);
// 以字母进行分割
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(temp.split("[a-zA-Z]+")));
}
}2.Lambda表达式
这是一个java8新特性之一,简化匿名类内部类写法。 Lambda表达式实现的匿名内部类必须是函数式接口
// Lambda格式
(被重写方法的形参列表)->{
代码;
}函数式接口:
@FunctionInterface
public interface 接口名 {
// 仅且只能有这一个抽象方法
返回值类型 方法名称(参数列表);
}2.1 示例
// 接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Animal {
void bark();
}
// 测试类
public class LambdaTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 以往使用匿名内部类
animalBark(new Animal() {
@Override
public void bark() {
System.out.println("现在是通过匿名内部类实现的,喵喵喵。。。");
}
});
// 使用Lambda表达式
animalBark(() -> {
System.out.println("现在是通过Lambda实现的,汪汪汪。。。");
});
}
public static void animalBark(Animal animal) {
animal.bark();
}
}2.2 Lambda表达式简写
- 参数类型可以不写
- 只有一个参数时,参数类型和()可以省略
- 如果实现类只有一行代码,则可以省略{},同时也要省略;
- 如果实现的代码只有一行并且这行代码为return语句,{}和;可以省略并且return也要省略
// 示例
@FunctionalInterface
public interface FunctionInterface1 {
int add(int x, int y);
}
@FunctionalInterface
public interface FunctionInterface2 {
void showParam(String str);
}
public class LambdaTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 就是如此简单
showFunctionInterface1((a, b) -> a * 2 + b * 2);
showFunctionInterface2(a -> a.trim());
}
public static void showFunctionInterface1(FunctionInterface1 functionInterface1) {
int add = functionInterface1.add(1, 2);
System.out.println(add);
}
public static void showFunctionInterface2(FunctionInterface2 functionInterface2) {
functionInterface2.showParam("Hello World");
}
}3. 排序算法
从字面意思理解,是对数据进行一定规则的排序。比如全校学生的某课成绩进行正 序排序。需求并不难实现,但是要在计算速度上有要求就变得有意思了。这时算法 就派上用场,最少的资源进行相同的运算。使用不同的算法对下列数组进行排序。
[94,58,95,4,13,18,70,0,59,21]
3.1 冒泡排序
public class Bubble {
public static int[] x = {94, 58, 95, 4, 13, 18, 70, 0, 59, 21};
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("排序前:" + Arrays.toString(Bubble.x));
for (int i = 0; i < x.length - 1; i++) {
for (int y = 0; y < x.length - 1 - i; y++) {
if (x[y] < x[y + 1]) {
int temp = x[y];
x[y] = x[y + 1];
x[y + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println("排序后:" + Arrays.toString(Bubble.x));
}
}下图是网上找的gif图,上面写的与这个有点出入,我是向数组尾部冒泡的:
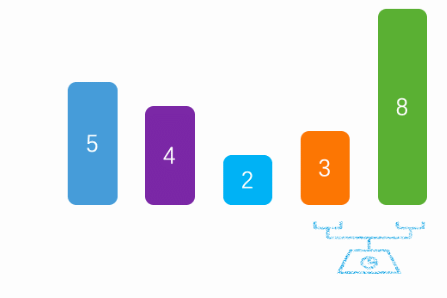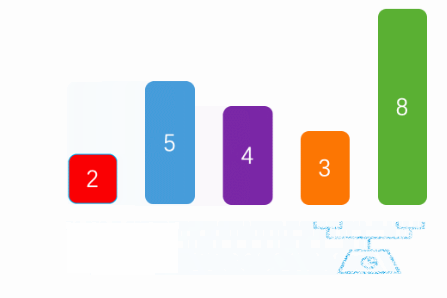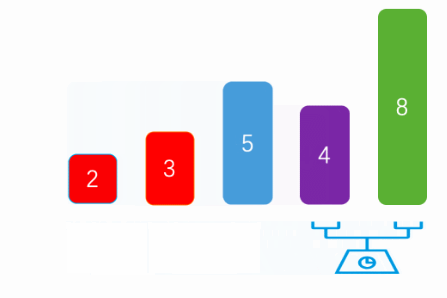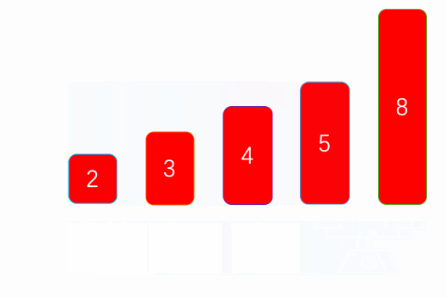
3.2 选择排序
public class Select {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("排序前:" + Arrays.toString(Bubble.x));
// 进行正序排序
for (int i = 0; i < Bubble.x.length - 1; i++) {
for (int y = i + 1; y < Bubble.x.length; y++) {
if (Bubble.x[i] < Bubble.x[y]) {
int temp = Bubble.x[i];
Bubble.x[i] = Bubble.x[y];
Bubble.x[y] = temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println("排序后:" + Arrays.toString(Bubble.x));
}
}思路如下图:
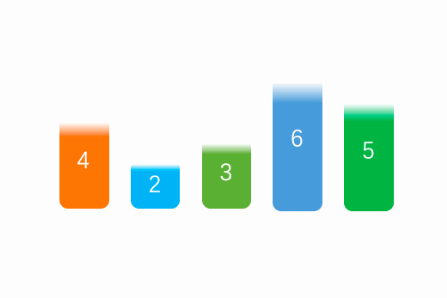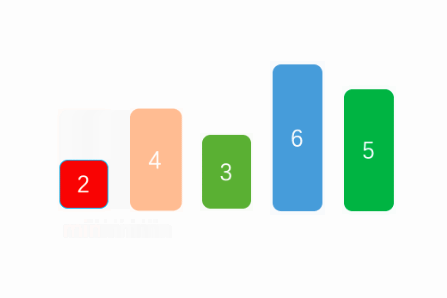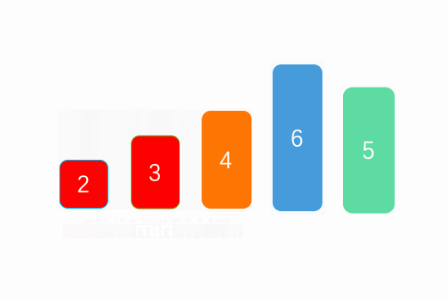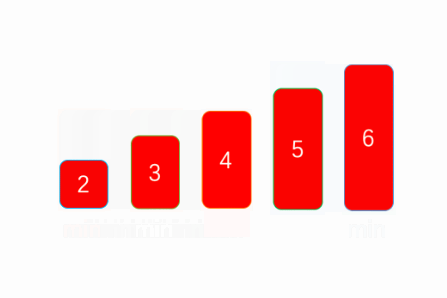
3.3 二分选择(非排序算法)
二分法是为了实现快速找到查找的算法。使用此方法必须先对数组进行排序。
示例:
对以上方法进行排序,然后以最快的速度查找到13。每次取一般进行判断,如果小于
则向下再取一半,否则向上取一半。
public class Dichotomy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 先为数组进行排序
Bubble.sort();
int length = Bubble.x.length;
int index = length / 2;
int select = 95;
while (index >= 0) {
if (Bubble.x[index] == select) {
break;
}
if (Bubble.x[index] > select) {
index = index + (length - index) / 2;
}
if (Bubble.x[index] < select) {
index = index / 2;
}
}
System.out.println(index);
}
}本章结束,用于个人学习和小白入门,大佬勿喷!希望大家多多点赞收藏支撑支撑!





















