oracle中的支持正则表达式的函数主要有下面四个:
1,REGEXP_LIKE :与LIKE的功能相似
2,REGEXP_INSTR :与INSTR的功能相似
3,REGEXP_SUBSTR :与SUBSTR的功能相似
4,REGEXP_REPLACE :与REPLACE的功能相似
regexp_like 只能用于条件表达式,和 like 类似,但是使用的正则表达式进行匹配,语法很简单:
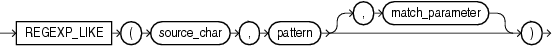
regexp_substr 函数,和 substr 类似,用于拾取合符正则表达式描述的字符子串,语法如下:
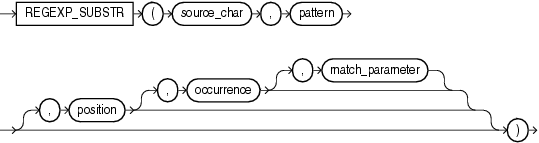
上面这个模式参数就复杂了些 常用组合以下
regexp_substr (string, pattern, position)
regexp_substr (string, pattern, position, occurence)
regexp_substr (string, pattern, position, occurence, match_parameters)
regexp_instr 函数,和 instr 类似,用于标定符合正则表达式的字符子串的开始位置,语法如下:
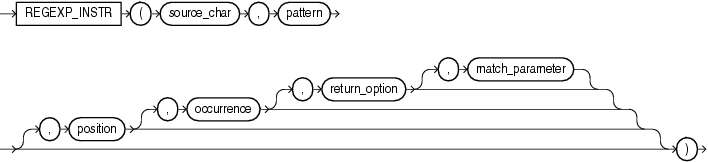
regexp_instr (string, pattern)
regexp_instr (string, pattern, position)
regexp_instr (string, pattern, position, occurence)
regexp_instr (string, pattern, position, occurence, return-option)
regexp_instr (string, pattern, position, occurence, return-option, parameters)
regexp_replace 函数,和 replace 类似,用于替换符合正则表达式的字符串,语法如下:
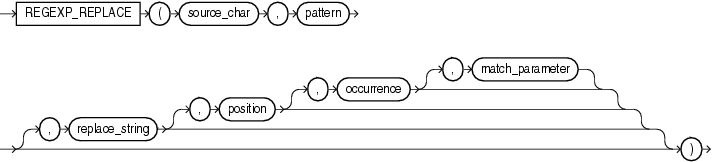
这里解析一下几个参数的含义:
1。source_char,输入的字符串,可以是列名或者字符串常量、变量。
2。pattern,正则表达式。
3。match_parameter,匹配选项取值范围: i:大小写不敏感; c:大小写敏感;n:点号 . 不匹配换行符号;m:多行模式;x:扩展模式,忽略正则表达式中的空白字符。
4。position,标识从第几个字符开始正则表达式匹配。
5。occurrence,标识第几个匹配组。
6。replace_string,替换的字符串。
在新的函数中使用正则表达式来代替通配符‘%’和‘_’。
正则表达式由标准的元字符(metacharacters)所构成:
'^' 匹配输入字符串的开始位置,在方括号表达式中使用,此时它表示不接受该字符集合。
'$' 匹配输入字符串的结尾位置。如果设置了 RegExp 对象的 Multiline 属性,则 $ 也匹配 'n' 或 'r'。
'.' 匹配除换行符 n之外的任何单字符。
'?' 匹配前面的子表达式零次或一次。
'+' 匹配前面的子表达式一次或多次。
'*' 匹配前面的子表达式零次或多次。
'|' 指明两项之间的一个选择。例子'^([a-z]+|[0-9]+)$'表示所有小写字母或数字组合成的字符串。
'( )' 标记一个子表达式的开始和结束位置。
'[]' 标记一个中括号表达式。
'{m,n}' 一个精确地出现次数范围,m=<出现次数<=n,'{m}'表示出现m次,'{m,}'表示至少出现m次。
num 匹配 num,其中 num 是一个正整数。对所获取的匹配的引用。
字符簇:
[[:alpha:]] 任何字母。
[[:digit:]] 任何数字。
[[:alnum:]] 任何字母和数字。
[[:space:]] 任何白字符。
[[:upper:]] 任何大写字母。
[[:lower:]] 任何小写字母。
[[:punct:]] 任何标点符号。
[[:xdigit:]] 任何16进制的数字,相当于[0-9a-fA-F]。
各种操作符的运算优先级
转义符
(), (?:), (?=), [] 圆括号和方括号
*, +, ?, {n}, {n,}, {n,m} 限定符
^, $, anymetacharacter 位置和顺序
| “或”操作
说了一堆文绉绉的,现在开始实例演练了,在此之前先建好一个表。
create table tmp as with data as ( select 'like' as id ,'a9999' as str from dual union all select 'like' ,'a9c' from dual union all select 'like' ,'A7007' from dual union all select 'like' ,'123a34cc' from dual union all select 'substr' ,'123,234,345' from dual union all select 'substr' ,'12,34.56:78' from dual union all select 'substr' ,'123456789' from dual union all select 'instr' ,'192.168.0.1' from dual union all select 'replace' ,'(020)12345678' from dual union all select 'replace' ,'001517729C28' from dual ) select * from data ;
select * from tmp ; ID STR ------- ------------- like a9999 like a9c like A7007 like 123a34cc substr 123,234,345 substr 12,34.56:78 substr 123456789 instr 192.168.0.1 replace (020)12345678 replace 001517729C28
regexp_like 例子:
select str from tmp where id='like' and regexp_like(str,'A\d+','i'); -- 'i' 忽略大小写 STR ------------- a9999 a9c A7007 123a34cc
select str from tmp where id='like' and regexp_like(str, 'a\d+'); STR ------------- a9999 a9c 123a34cc
select str from tmp where id='like' and regexp_like(str,'^a\d+'); STR ------------- a9999 a9c
select str from tmp where id='like' and regexp_like(str,'^a\d+c$'); STR ------------- a9999
regexp_substr 例子:
col str format a15;
select
str,
regexp_substr(str,'[^,]+') str,
regexp_substr(str,'[^,]+',1,1) str,
regexp_substr(str,'[^,]+',1,2) str, -- occurrence 第几个匹配组
regexp_substr(str,'[^,]+',2,1) str -- position 从第几个字符开始匹配
from tmp
where id='substr';
STR STR STR STR STR
--------------- --------------- --------------- --------------- ---------------
123,234,345 123 123 234 23
12,34.56:78 12 12 34.56:78 2
123456789 123456789 123456789 23456789
select
str,
regexp_substr(str,'\d') str,
regexp_substr(str,'\d+' ,1,1) str,
regexp_substr(str,'\d{2}',1,2) str,
regexp_substr(str,'\d{3}',2,1) str
from tmp
where id='substr';
STR STR STR STR STR
--------------- --------------- --------------- --------------- ---------------
123,234,345 1 123 23 234
12,34.56:78 1 12 34
123456789 1 123456789 34 234
select regexp_substr('123456789','\d',1,level) str --取出每位数字,有时这也是行转列的方式
from dual
connect by level<=9
STR
---------------
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9regex_instr 例子:
col ind format 9999;
select
str,
regexp_instr(str,'\.' ) ind ,
regexp_instr(str,'\.',1,2) ind ,
regexp_instr(str,'\.',5,2) ind
from tmp where id='instr';
STR IND IND IND
--------------- ----- ----- -----
192.168.0.1 4 8 10
select
regexp_instr('192.168.0.1','\.',1,level) ind , -- 点号. 所在的位置
regexp_instr('192.168.0.1','\d',1,level) ind -- 每个数字的位置
from dual
connect by level <= 9
IND IND
----- -----
4 1
8 2
10 3
0 5
0 6
0 7
0 9
0 11
0 0regex_replace 例子:
select
str,
regexp_replace(str,'020','GZ') str,
regexp_replace(str,'(\d{3})(\d{3})','<\2\1>') str -- 将第一、第二捕获组交换位置,用尖括号标识出来
from tmp
where id='replace';
STR STR STR
--------------- --------------- ---------------
(020)12345678 (GZ)12345678 (020)<456123>78
001517729C28 001517729C28 <517001>729C28综合应用的例子:
col row_line format a30;
with sudoku as (
select '020000080568179234090000010030040050040205090070080040050000060289634175010000020' as line
from dual
),
tmp as (
select regexp_substr(line,'\d{9}',1,level) row_line,
level col
from sudoku
connect by level<=9
)
select regexp_replace( row_line ,'(\d)(\d)(\d)(\d)(\d)(\d)(\d)(\d)(\d)','\1 \2 \3 \4 \5 \6 \7 \8 \9') row_line
from tmp
ROW_LINE
------------------------------
0 2 0 0 0 0 0 8 0
5 6 8 1 7 9 2 3 4
0 9 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 3 0 0 4 0 0 5 0
0 4 0 2 0 5 0 9 0
0 7 0 0 8 0 0 4 0
0 5 0 0 0 0 0 6 0
2 8 9 6 3 4 1 7 5
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 2 0






















